Although local governments are the closest actors to citizens, they often face limitations in terms of resources and capacities to implement open data effectively. The diputations, as intermediate institutions between central government and municipalities, play a key role in coordinating, supporting and facilitating open data at the local level.
In this article, we will explore the work of the Diputaciones in this area, showing some examples.
Why is it important for local authorities to commit to open data?
Local open data is of great importance to citizens because of its high granularity. These data provide information on specific settings, which gives a detailed picture of the situation of citizens in that area and shows disparities between municipalities.
This offers multiple advantages. On the one hand, public administrationscan develop better policies and manage resources more efficiently. On the other hand, businesses, researchers and entrepreneurshave the opportunity to develop new, more customised solutions based on the needs of each location. It also improves transparency and accountability, fostering trust in local institutions, and facilitates citizen participationby giving residents access to key data about their municipalities, which can contribute to more active and informed decision-making.
Challenges for local authorities in opening up their data
Despite the advantages, local authorities face a number of challenges in trying to make their data available to citizens, many of which are related to resource constraints and technical capacity:
- Lack of technical and human resources: Many municipalities, especially small and medium-sized ones, do not have the trained staff and resources to manage and publish open data. Lack of IT and data management expertise can hinder the implementation of open data initiatives.
- Inadequate infrastructure: Open data requires adequate technological infrastructure, such as platforms and storage systems to host data in an accessible and secure way.
- Awareness and resistance to change: In some municipalities, both policy makers and public employees may not fully understand the benefits of open data, leading to resistance to change.
- Data quality and standardisation issues: Municipal data are often scattered across different systems and formats, which can make standardisation and validation difficult. Ensuring that data is correct, up to date and in reusable formats is a major technical challenge.
- Cost of implementing, maintaining and updating data: Opening up data involves not only having the right infrastructure and staff, but also investing in platforms, software and other tools needed to make the information accessible to the public, which can be a barrier for municipalities with tight budgets. Moreover, once data is available to the public, it is necessary to keep it up to date and ensure that it remains relevant, which is a constant effort.
How can county councils help local authorities to overcome these challenges?
The Diputaciones are supra-municipal entities whose functions include legal, economic and technical assistance and cooperation to the municipalities in their province, especially those of smaller size or fewer resources. Among other things, they offer support in technological and managerial matters, for example in administrative tasks, the provision of public services or economic development.
In the context of open data, local councils can act as "facilitators" of open data at local level, through different actions:
-
Technical advice and training
The Diputaciones offer training to municipalities so that municipal employees can learn how to manage and open data. This is something that the Diputación de Salamanca, for example, has done with this course, whose objectives included raising participants' awareness of the importance of open data as a means to enhance citizen participation, helping them to understand technical issues in order to boost the degree of openness of institutions.
The Diputación de Castellón, for its part, provides support to small municipalities in opening their data, offering support materials related to open data. Another example is the Provincial Council of Albacete, which provides technical assistance, monitoring and support to its 87 municipalities through the Provincial Sustainability Observatory of Albacete (OPSA), an entity in collaboration with the University of Castilla-La Mancha. To this end, it offers sustainability reports (with 25 indicators), monitors its localization plans and emission studies, offers training and guides related to the sustainability of its municipalities related to open data, etc.
-
Technological infrastructure
Some councils provide digital platforms and tools for municipalities to upload and share data in a simple way. This includes hosting open data portals or analysis and visualisation tools.
This is the case of the Diputación de Bizkaia, whose scope affects the foral public sector (Foral Entities) and the Local Entities of Bizkaia. Through the BiscayTIK foundation, municipalities can join the Open Data Bizkaia portal so that their data can appear on this portal. In addition, a customised view is generated that can be embedded in the municipality's own website, in case they want to have their own open data portal.
Another example is the Diputación de Córdoba. Its provincial strategy consists of unifying efforts and making a common platform for all municipalities, through automated processes of extraction and processing of structured information for publication, without the need for manual dedication on the part of staff. Through the Enlaza project, the platform receives and monitors information obtained both from citizens and from the sensors and systems of the multiple municipal services, and then carries out a cross analysis of the data. With this service, all the town councils in the province of Cordoba can have a homogeneous catalogue of open data with automated loading, which in turn is federated with datos.gob.es, saving this procedure for smaller administrations.
The Diputación de Albacete, for its part, has a platform with an open data exhibition of the panel of local indicators of the province (48 sub-indicators with a historical series of +15 years). The standardization of open data facilitates municipal and provincial analysis, allowing the comparison of municipalities with graphical and georeferenced output. Includes download space with user registration.
Thanks to these actions double efforts and duplication of uploading of information on various platforms are avoided. In addition, the standardisation of open data facilitates regional analysis and comparison between municipalities, generating new opportunities for innovation and improvement in the quality of life of citizens.
-
Grants or funding
Sometimes, the local councils allocate financial resources so that small municipalities can implement open data projects. An example of this is the Diputación de Valencia, whose functions include fostering and developing the right of access to information, as well as promoting the re-use of public data. To this end, in 2024, it launched a series of aids.
In this line the Diputación de Albacete has an annual aid or call for municipalities to implement their Agendas 2030 or projects related to sustainability and included in their plans. For example, in February 2025 the call was published with a budget of € 325,000.
-
Awareness-raising and reuse promotion actions
Another area where county councils can help is the promotion of favourable frameworks for data re-use. The Diputación de Castellón, for example, maintains a close relationship with civil society organisations and universities to meet their data demands. With the collaboration of the Diputación de Barcelona and the Government of Aragón, organised in 2024 the III National Open Data Meeting, where the importance of open data as a resource for understanding and achieving interesting and sustainable tourism was disseminated.
For its part, the Diputación de Bizkaia is launching competitions such as the Open Data & Artificial Intelligence Challenge, aimed at identifying initiatives that combine the reuse of data available on the Open Data Bizkaia portal with the use of this disruptive technology in various sectors.
In conclusion, the collaboration between councils and municipalities makes it possible to generate greater cohesion in the opening of data throughout the territory, ensuring that all municipalities, regardless of their size or resources, have access to the necessary tools and knowledge. However, local councils also have their technical and resource limitations, so this is an area where further progress needs to be made, with a focus on raising awareness of the benefits of open data and collaboration between institutions.
31 May 2024 is the date chosen to celebrate the 3rd National Open Data Meeting organised once again this year by the Provincial Council of Castellón, with the collaboration of the Provincial Council of Barcelona and the Government of Aragon. Under the slogan "Data to boost the tourism sector", experts in the field will meet in a unique setting, Peñíscola Castle, to discuss the importance of the availability and reuse of open data in this sector.
Among other issues, during the event, the importance of open data as a resource for understanding and achieving relevant and sustainable tourismwill be disseminated. This will be done by sharing resources that can benefit different users. The value of open data for implementing innovative technological solutions, e.g. based on artificial intelligence, will also be discussed.
Who is it aimed at?
This is an open event, where any citizen interested in the subject is welcome. In particular, it may be of particular interest to:
- Technicians and professionals in the field of tourism.
- Mayors' offices, councillors' offices, departments and departments of the state, territorial and local administration.
- Journalists and communication professionals.
- Tour operators.
- Responsible for data governance and open data portals of administrations.
What is the programme?
The event will start at 9:00 with the inauguration by María Tormo Casañ, representative of the Diputación de Castellón. It will be followed by the inaugural address by José Norberto Mazón López, professor of computer languages and systems at the University of Alicante.
This will be followed by a series of round tables and presentations:
- 10.00 Table 1. Tourism and the economy: a data space for growth and development.
- 11:30 Coffee break.
- 12:00 Table 2. How data can improve experiences and make tourism sustainable.
- 13.30 Presentation: conclusions of the technical challenges on open data.
- 14:15 Lunch.
- 15.45 Public management roundtable: data-driven public policies to improve tourism activity.
The event will end at 17.30, after the presentation of the conclusions.
How can I register?
The event can only be followed in person, as there will be no live broadcast. As mentioned at the beginning, the event will take place on 31 May in the Gothic hall of Peñíscola Castle. To register you must complete the form available at this link.
The importance of open data in tourism
Open data on tourism allows us to understand the state of the sector so that both tourism businesses and public bodies can make informed decisions to help boost this important economic driver. At the same time, they can serve as a basis for implementing technological solutions that improve the travellers' experience and allow them to easily organise and enjoy their trip. This is the case of some of the applications with information on accommodation, restaurants, tourist sites, activities of interest, etc.
Public bodies are aware of this situation and therefore there are more and more spaces where data on this issue can be shared. In this sense, we find national initiatives, such as Dataestur or promoted by autonomous regional bodies, such as the asturias tourism data catalogue. For its part, the Castellón Provincial Council is currently developing a specific area on tourism in its Open Data Portal specific space on tourism in its Open Data Portal, which aims to bring together all the knowledge which aims to bring together all the knowledge generated around the 3rd National Open Data Meeting.
If you are interested in the subject, in the tourism sectorial of datos.gob.es you will find featured datasets, news and analysis articles, as well as examples of applications and companies reusers that base their activity on open data from the tourism sector.
Events such as the III National Open Data Meeting are another interesting opportunity to keep up to date with developments in the sector. Remember that you can sign up through this link.
The first National Open Data Meeting will take place in Barcelona on 21 November. It is an initiative promoted and co-organised by Barcelona Provincial Council, Government of Aragon and Provincial Council of Castellón, with the aim of identifying and developing specific proposals to promote the reuse of open data.
This first meeting will focus on the role of open data in developing territorial cohesion policies that contribute to overcoming the demographic challenge.
Agenda
The day will begin at 9:00 am and will last until 18:00 pm.
After the opening, which will be given by Marc Verdaguer, Deputy for Innovation, Local Governments and Territorial Cohesion of the Barcelona Provincial Council, there will be a keynote speech, where Carles Ramió, Vice-Rector for Institutional Planning and Evaluation at Pompeu Fabra University, will present the context of the subject.
Then, the event will be divided into four sessions where the following topics will be discussed:
- 10:30 a.m. State of art: lights and some shadows of opening and reusing data.
- 12:30 p.m. What does society need and expect from public administrations' open data portals?
- 15:00. Local commitment to fight against depopulation through open data
- 4:30 p.m. What can Public Administrations do using their data to jointly fight depopulation?
Experts linked to various open data initiatives, public organisations and business associations will participate in the conference. Specifically, the Aporta Initiative will participate in the first session, where the challenges and opportunities of the use of open data will be discussed.
The importance of addressing the demographic challenge
The conference will address how the ageing of the population, the geographical isolation that hinders access to health, administrative and educational centres and the loss of economic activity affect the smaller municipalities, both rural and urban. A situation with great repercussions on the sustainability and supply of the whole country, as well as on the preservation of culture and diversity.
The number of public institutions and local governments that continue to commit to implementing initiatives aimed at bringing open information closer to the public is growing all the time. If a few months ago we shared the work of Gipuzkoa Irekia or Open Data BizKaia, now it is the turn of the Provincial Council of Castellón, which has just presented a new open data portal.
How has the open data portal changed?
Son muchas las actividades en materia de datos abiertos que llevan a cabo desde la Diputación de Castellón en general, y su servicio de Servicio de Administración e Innovación Pública, en particular, pero en todas ellas el foco está puesto, básicamente, en la difusión, en el conocimiento y la reutilización de la información procedente de los datos abiertos.
There are many open data activities carried out by the Castellón Provincial Council in general, and its Public Administration and Innovation Service in particular, but in all of them the focus is basically on the dissemination, knowledge and reuse of information from open data.
Thus, on the one hand, an open data strategy has been drawn up with the aim of marking the way forward and, on the other, a council of re-users is working with the aim of advising the staff in charge of the governance of the portal, to identify and develop specific content that can be published openly.
Continuing with the idea of improving the open data strategy and bringing it closer to companies and users, the Castellón Provincial Council has completed the process of redesigning its portal, two years after its implementation. The portal maintains its technical and data governance functionalities, but includes important new features in terms of its image and themes.
Design of the new cover
Of all the visual changes recently implemented, perhaps the most significant has been the redesign of the new homepage. It has opted to offer a more visual orientation, which seeks, on the one hand, to highlight a series of data stories, created by combining the most consulted datasets on the portal, and on the other, to highlight the data relating to the fight against depopulation.
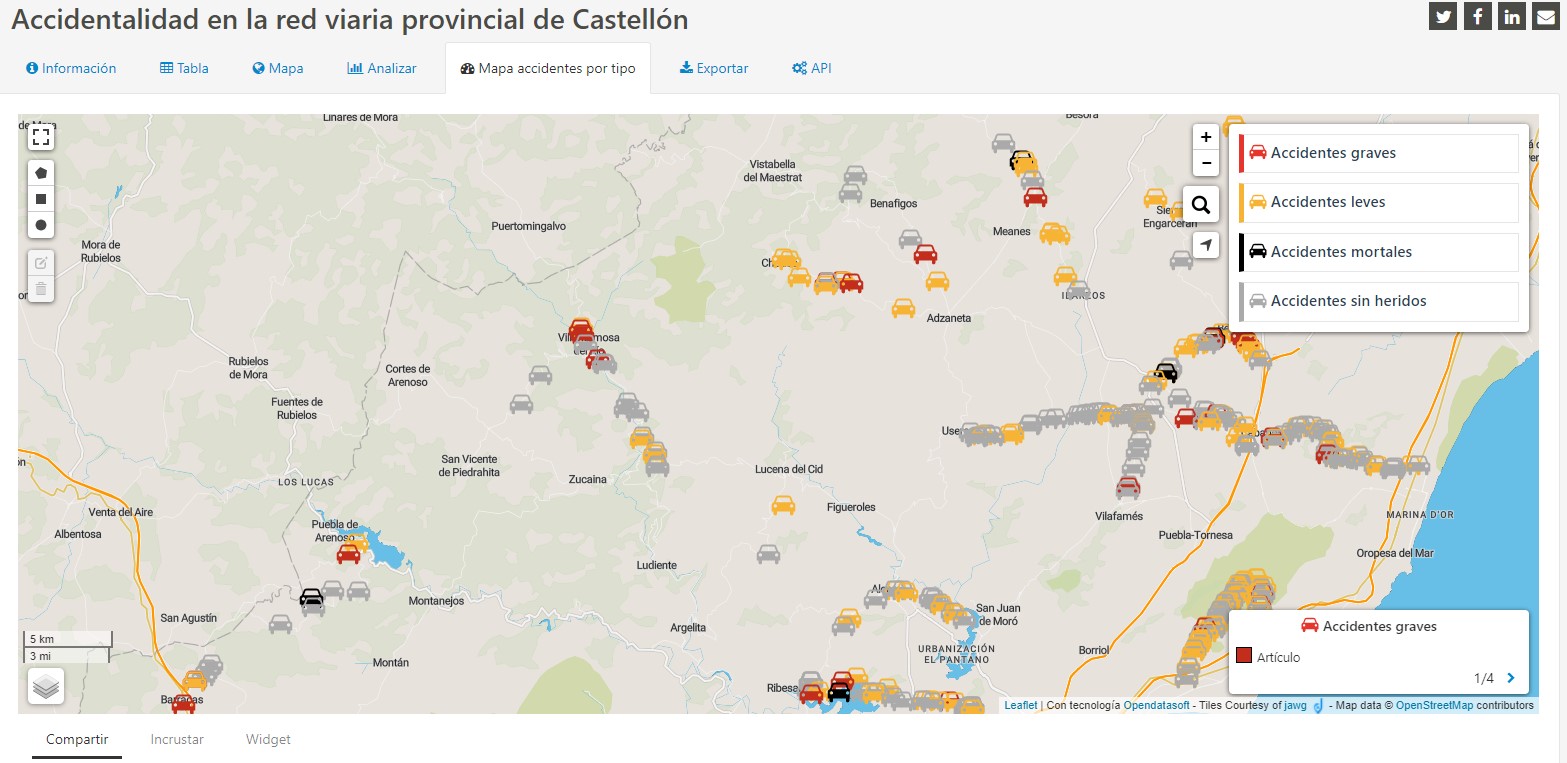
The dashboards or visualisations incorporated into the new front page are a great help for better monitoring and analysing information on key datasets.
Dataset and user statistics
The Castellón Provincial Council's data catalogue currently consists of 96 datasets that are classified in 17 thematic areas of the NTI-RISP. In addition, it should be noted that 49 of these datasets contain geographic information.
The most popular datasets are:
- Urban planning
- Demography
- Mayors of the province
In numerical terms, the urban planning dataset totals 1200 downloads and 33 thousand API calls. In terms of users, the estimated number of unique users who interacted with the domain last April reached 1,000.
Data against depopulation
Another important new feature of the new open data portal is the section dedicated to the depopulation of the territory, which includes all the datasets related to the services provided to the rural world to combat depopulation.
At present, this section is made up of six datasets with information related or linked to the towns in the interior of the province.

The 6 datasets included in this section on depopulation are distributed as follows:
- ATMs against depopulation, which aim to provide financial services in rural areas where it is difficult to find one.
- Electric vehicle recharging points, which aim to promote the use of electric vehicles to the detriment of more polluting conventional vehicles.
- Housing in municipalities in the province, to highlight the unequal distribution of the population between municipalities, based on geographical location within the province.
- Care centres, so that any citizen who needs them knows where to go if they require assistance.
- WiFi points in the province of Castellón, so that citizens who need it can access the Internet easily and free of charge, wherever they are.
- A list of defibrillators so that citizens can be informed of their location so that they can be called upon in the event of an emergency.
The final purpose of these 6 datasets is to make users aware of the closest services available to them, with the added intention of strengthening their presence in those areas of the province where they are currently scarce. This solution highlights the value of open data: it provides useful information to prevent regressive impacts of the population in the short and medium term, while helping to make an x-ray of the basic needs in terms of services and urgent facilities.
To generate these datasets, the Castellón Provincial Council has partnered with external institutions such as the Agència Valenciana Antidespoblament (AVANT), and with other internal departments that facilitate access to information on basic services and facilities in the towns of the interior of the province of Castellón.
In addition, for some of the datasets with geographical information, the Castellón Provincial Council has produced an interactive map. Specifically, in these six dashboards, different types of graphs and indicators are presented, which are automatically updated with the data, accompanied by a short story that facilitates their interpretation.
Data visualisations
Another of the highlights of the new data portal of the Castellón Provincial Council is the commitment to the visual content of the datasets. For each dataset, the user can generate their own graphs and maps that can be shared or embedded either through an iFrame or as a widget.
Assistance to municipalities
The government of the data portal maintains a close relationship with the Provincial Service of Assistance to Municipalities (SEPAM) in order to, in an act of openness and transparency, contribute to providing updated information on the municipalities of Castellón in terms of their political composition, territorial organisation and presence in social networks.
With this new measure, the portal aims to disseminate and facilitate knowledge of the municipalities of Castellón from the perspective of open data, and to serve as a useful and efficient mechanism for reuse.
On the other hand, it is also intended that the open data portal serves as an element of documentation, to contribute to the reliable and accurate use of the information available on the composition of the local councils and their characteristic elements: population, contact details, etc. The ultimate goal is to bring local governments closer to citizens and businesses.
Data journalism
In recent years, a new journalism specialism that uses open data to tell the news and produce stories has been gaining increasing prominence. Known as data journalism, it uses large datasets to conduct investigations and relies on digital techniques, analysis strategies and data visualisation tools to facilitate understanding of the data. Thanks to data journalism, open data portals of public administrations, agencies and institutions are becoming increasingly important as sources.
Precisely for this reason, the open data portal of the Castellón Provincial Council has designed a specific section dedicated to data journalism, accessible from the home page itself and located within the SPECIALITIES AND EXCHANGES block.

Such is the commitment of the Castellón Provincial Council to make the open data portal known to information professionals that, during the celebrations of the last Open Data Day 2022, journalists were made aware of the possibilities offered by open data. Furthermore, in order to introduce them to the use of datasets and the subsequent analysis and management required by the data, the Provincial Council itself organised a specific event with journalists and professionals from the communication sector in general.
How to expand the open data ecosystem at the provincial level?
With the aim of continuing to disseminate the potential of open data, the Castellón Provincial Council has set a series of objectives aimed at expanding the community and interest in it. These are some of the actions planned for the coming months:
- Seek integration in various international organisations to promote information sharing and good practices in the field of data.
- Continue with the design of new open data visualisations.
- Create a provincial Data Office.
- Hold activities for the promotion and dissemination of open data in partnership with other entities or through participation in commemorative events.
- Constantly review and improve the open data strategy.
In short, the work carried out by the Castellón Provincial Council through the redesign and new strategy of the open data portal highlights the value of local data for citizens and public institutions themselves. Precisely for this reason it is not surprising that more and more councils are being encouraged to open their data and generate valuable services based on it.