The commitment to so-called smart cities is currently one of the major commitments to technological innovation in the public sector, especially in the local sphere. This type of initiative aims to address challenges to sustainability in the urban context and, through the advanced use of information and communication technologies, to optimise resources and make public services more efficient.
The report ‘Open Data and Smart Cities: an alternative legal perspective’ that we published on Datos.gob.es approaches the scope and legal analysis of data openness in this type of project. It is particularly important to provide legal security for the investments and efforts being made by both local governments and service providers and, in general, for the involvement of civil society in this field. As analysed in this report, the plurality of actors and services involved determines the diversity of legal standards in a context where information and communication technologies require interoperability.
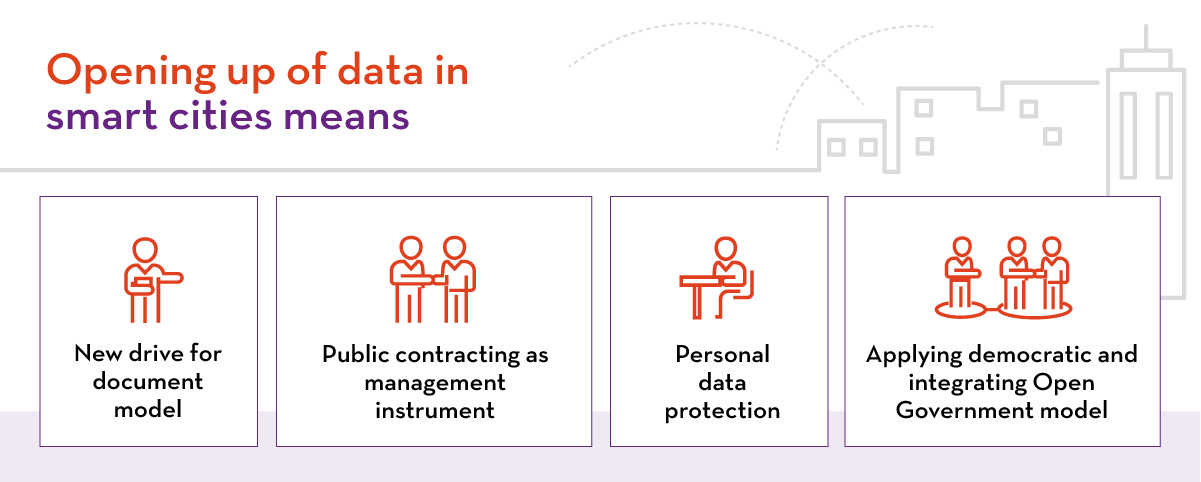
Structured into five chapters, the report deals with Law as a tool to serve smart cities, the diversity of actors as a subjective element, the plurality of services involved in a technological context as an objective element, and the scope of the regulatory framework applicable to intelligent cities from the perspective of open data. This last section details the regulations on electronic Government, the legal provisions on transparency and access to public sector information, the legal provisions on the re-use of public sector information, and the legislation covering the protection of personal data.
In the fifth and final chapter, which focuses on the prominence of legal means, the report raises the need for paradigm shifts to drive open data in smart city projects. In particular, it advocates the promotion of a management model based on the foundation of Open Government at the municipal government level, using its legal powers and means. It also proposes a series of prerequisites required to allow the opening of data in smart cities in order to facilitate the re-use of the data generated.
In conclusion, the report ‘Open Data and Smart Cities: an alternative legal perspective’ refers to the need to be aware of the fragmentation of the existing regulatory framework and the challenge for local governments when making reasonable modifications to their own regulations and supporting effective leadership in order to offer value-added services based on their re-use according to the principles of open data.
The attached Report can be downloaded in PDF, Word, and ODT format.
Cities are increasingly gaining population. While large cities only occupy around 2% of the planet's land mass, nowadays half of humanity lives in cities, 70% of the population in Europe, and it is expected that by the year 2030, almost 60% of the world population will live in urban areas consuming approximately 80% of the planet's resources.
Demographic growth will be a major challenge in the sustainable and efficient management of cities.Transport, education, health care, waste management ... are just some of the areas that will be affected and may become an obstacle on the way to the Smart Cities. In this global context, data is an essential resource and its openness and reuse are key aspects to understand what is happening in cities and make the right decisions to ensure the optimal management of Smart Cities.
Aware of the potential of Open Data, Iniciativa Aporta has published a new version of its report "Open Data, as a tool for Smart Cities". A document that addresses both the strategic aspects of Open Data for a local administration and the necessary components for the success of an initiative of this nature, all exemplified by real cases of different cities in the world. In this way, the reader can locate in the globe the most significant international initiatives that re-use information of the public sector to improve the quality of life of citizens.
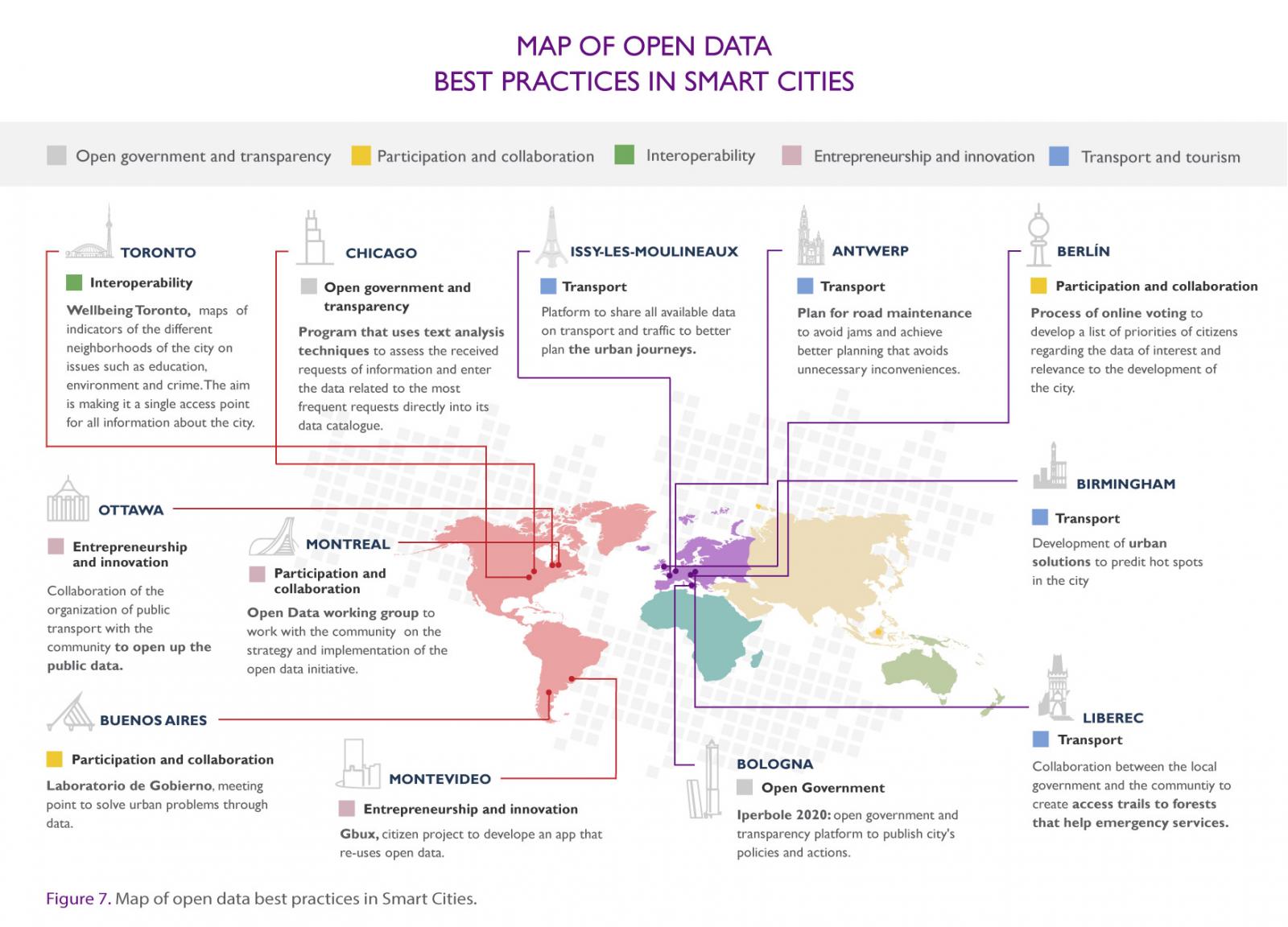
In order to improve and update this material, the content has been enriched with graphic elements that help its comprehension and dissemination. In addition, a map has been included where the world's most relevant Open Data and Smart Cities projects are located according to five priority themes: transport, tourism, open government, interoperability and entrepreneurship.
All the materials created to date are available in the Documentation section of the new portal datos.gob.es, where not only the documents are published but the user has also the opportunity to find resources from other organisms, all related to the re-use of public sector information.