Digital transformation has reached almost every aspect and sector of our lives, and the world of products and services is no exception. In this context, the Digital Product Passport (DPP) concept is emerging as a revolutionary tool to foster sustainability and the circular economy. Accompanied by initiatives such as CIRPASS (Circular Product Information System for Sustainability), the DPP promises to change the way we interact with products throughout their life cycle. In this article, we will explore what DPP is, its origins, applications, risks and how it can affect our daily lives and the protection of our personal data.
What is the Digital Product Passport (DPP)? Origin and importance
The Digital Product Passport is a digital collection of key information about a product, from manufacturing to recycling. This passport allows products to be tracked and managed more efficiently, improving transparency and facilitating sustainable practices. The information contained in a DPP may include details on the materials used, the manufacturing process, the supply chain, instructions for use and how to recycle the product at the end of its life.
The DPP has been developed in response to the growing need to promote the circular economy and reduce the environmental impact of products. The European Union (EU) has been a pioneer in promoting policies and regulations that support sustainability. Initiatives such as the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan have been instrumental in driving the DPP forward. The objectives of this plan are as follows:
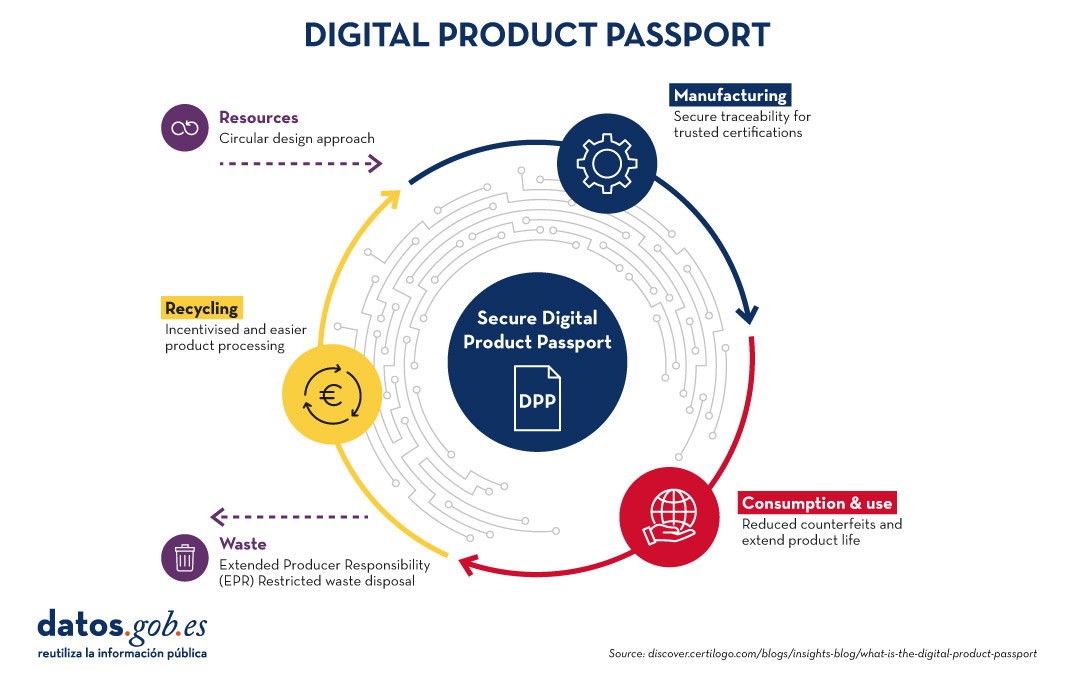
- Greater Transparency: Consumers no longer have to guess about the origin of their products and how to dispose of them correctly. With a machine-readable DPP (e.g. QR code or NFC tag) attached to end products, consumers can make informed purchasing decisions and brands can eliminate greenwashing with confidence.
- Simplified Compliance: By creating an audit of events and transactions in a product's value chain, the DPP provides the brand and its suppliers with the necessary data to address compliance demands efficiently.
- Sustainable Production: By tracking and reporting the social and environmental impacts of a product from source to disposal, brands can make data-driven decisions to optimise sustainability in product development.
- Circular Economy: The DPP facilitates a circular economy by promoting eco-design and the responsible production of durable products that can be reused, remanufactured and disposed of correctly.
The following image summarises the main advantages of the digital passport at each stage of the digital product manufacturing process:
CIRPASS as a facilitator of DPP implementation
CIRPASS is a platform that supports the implementation of the DPP. This European initiative aims to standardise the collection and exchange of data on products, facilitating their traceability and management throughout their life cycle. CIRPASS plays a crucial role in creating an interoperable digital framework that connects manufacturers, consumers and recyclers.
DPP applications in various sectors
On 5 March 2024, CIRPASS, in collaboration with the European Commission, organised an event on the future development of the Digital Product Passport. The event brought together various stakeholders from different industries and organisations, who, with an eminently practical approach presented and discussed various aspects of the upcoming regulation and its requirements, possible solutions, examples of use cases, and the obstacles and opportunities for the affected industries and businesses.
The following are the applications of DPP in various sectors as explained at the event:
- Textile industry: It allows consumers to know the origin of the garments, the materials used and the working conditions in the factories.
- Electronics: Facilitates recycling and reuse of components, reducing electronic waste.
- Automotive: It assists in tracking parts and materials, promoting the repair and recycling of vehicles.
- Power supply: It provides information on food traceability, ensuring safety and sustainability in the supply chain.
The impact of the DPP on citizens' lives
But what impact will the use of this kind of novel paradigm have on our daily lives? And how does this impact on us as end users of multiple products and services such as those mentioned above? We will focus on four base cases: informed consumers in any field, ease of product repair, trust and transparency, and efficient recycling.
The DPP provides consumers with access to detailed information about the products they buy, such as their origin, materials and production practices. This allows consumers to make more informed choices and opt for products that are sustainable and ethical. For example, a consumer can choose a garment made from organic materials and produced under fair labour conditions, thus promoting responsible and conscious consumption.
Similarly, one of the great benefits of the DPP is the inclusion of repair guides within the digital passport. This means that consumers can easily access detailed instructions on how to repair a product instead of discarding it when it breaks down. For example, if an appliance stops working, the DPP can provide a step-by-step repair manual, allowing the user to fix it himself or take it to a technician with the necessary information. This not only extends the lifetime of products, but also reduces e-waste and promotes sustainability.
Also, access to detailed and transparent product information through the DPP can increase consumers' trust in brands. Companies that provide a complete and accurate DPP demonstrate their commitment to transparency and accountability, which can enhance their reputation and build customer loyalty. In addition, consumers who have access to this information are better able to make responsible purchasing decisions, thus encouraging more ethical and sustainable consumption habits.
Finally, the DPP facilitates effective recycling by providing clear information on how to break down and reuse the materials in a product. For example, a citizen who wishes to recycle an electronic device can consult the DPP to find out which parts can be recycled and how to separate them properly. This improves the efficiency of the recycling process and ensures that more materials are recovered and reused instead of ending up in landfill, contributing to a circular economy.
Risks and challenges of the DPP
Similarly, as a novel technology and as part of the digital transformation that is taking place in the product sectors, the DPP also presents certain challenges, risks and challenges such as:
- Data Protection: The collection and storage of large amounts of data can put consumers' privacy at risk if not properly managed.
- Security: Digital data is vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which requires robust security measures.
- Interoperability: Standardisation of data across different industries and countries can be complex, making it difficult to implement the DPP on a large scale.
- Costs: Creating and maintaining digital passports can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Data protection implications
The implementation of the DPP and systems such as CIRPASS implies careful management of personal data. It is essential that companies and digital platforms comply with data protection regulations, such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Organisations must ensure that the data collected is used in a transparent manner and with the explicit consent of consumers. In addition, advanced security measures must be implemented to protect the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
Relationship with European Data Spaces
The European Data Spaces are an EU initiative to create a single market for data, promoting innovation and the digital economy. The DPP and CIRPASS are aligned with this vision, as they encourage the exchange of information between different actors in the economy. Data interoperability is essential for the success of the European Data Spaces, and the DPP can contribute significantly to this goal by providing structured and accessible product data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Digital Product Passport and the CIRPASS initiative represent a significant step towards a more circular and sustainable economy. Through the collection and exchange of detailed product data, these systems can improve transparency, encourage responsible consumption practices and reduce environmental impact. However, their implementation requires overcoming challenges related to data protection, security and interoperability. As we move towards a more digitised future, the DPP and CIRPASS have the potential to transform the way we interact with products and contribute to a more sustainable world.
Content prepared by Dr. Fernando Gualo, Professor at UCLM and Data Governance and Quality Consultant The content and the point of view reflected in this publication are the sole responsibility of its author.


