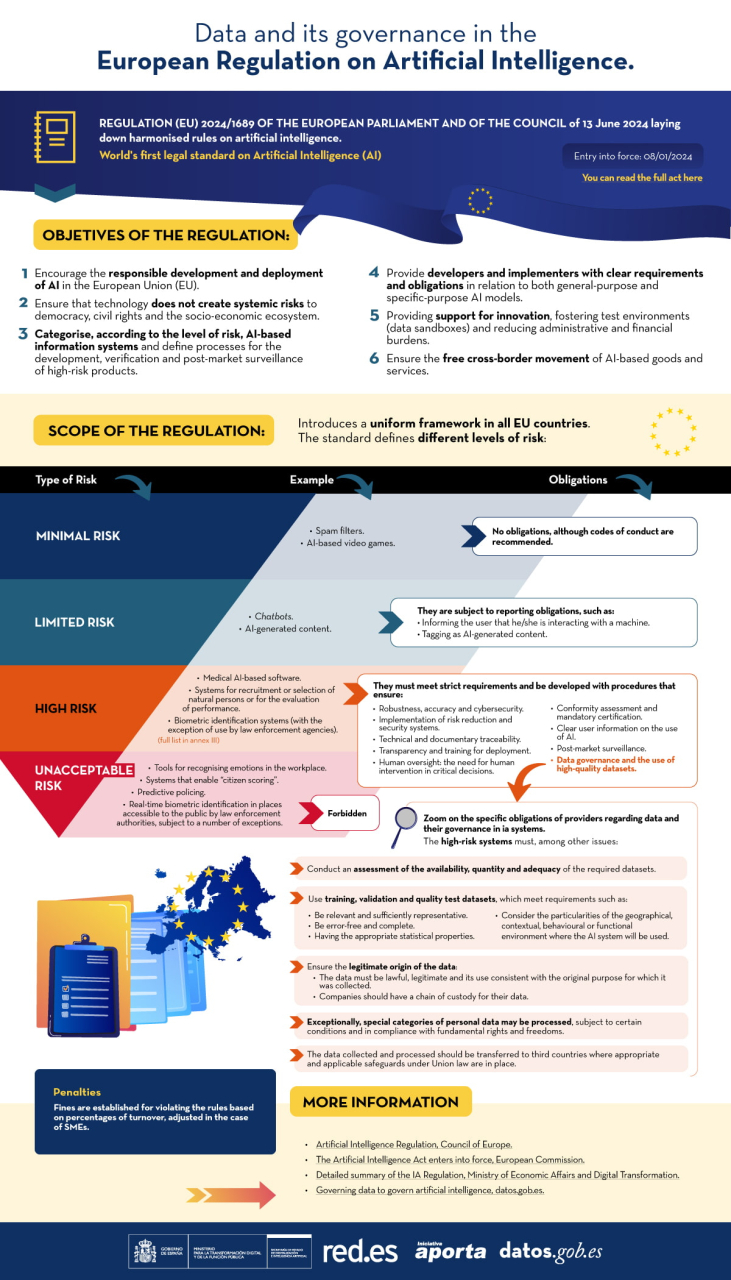
The publication on Friday 12 July 2024 of the Artificial Intelligence Regulation (AIA) opens a new stage in the European and global regulatory framework. The standard is characterised by an attempt to combine two souls. On the one hand, it is about ensuring that technology does not create systemic risks for democracy, the guarantee of our rights and the socio-economic ecosystem as a whole. On the other hand, a targeted approach to product development is sought in order to meet the high standards of reliability, safety and regulatory compliance defined by the European Union.
Scope of application of the standard
The standard allows differentiation between low-and medium-risk systems, high-risk systems and general-purpose AI models. In order to qualify systems, the AIA defines criteria related to the sector regulated by the European Union (Annex I) and defines the content and scope of those systems which by their nature and purpose could generate risks (Annex III). The models are highly dependent on the volume of data, their capacities and operational load.
AIA only affects the latter two cases: high-risk systems and general-purpose AI models. High-risk systems require conformity assessment through notified bodies. These are entities to which evidence is submitted that the development complies with the AIA. In this respect, the models are subject to control formulas by the Commission that ensure the prevention of systemic risks. However, this is a flexible regulatory framework that favours research by relaxing its application in experimental environments, as well as through the deployment of sandboxes for development.
The standard sets out a series of "requirements for high-risk AI systems" (section two of chapter three) which should constitute a reference framework for the development of any system and inspire codes of good practice, technical standards and certification schemes. In this respect, Article 10 on "data and data governance" plays a central role. It provides very precise indications on the design conditions for AI systems, particularly when they involve the processing of personal data or when they are projected on natural persons.
This governance should be considered by those providing the basic infrastructure and/or datasets, managing data spaces or so-called Digital Innovation Hubs, offering support services. In our ecosystem, characterised by a high prevalence of SMEs and/or research teams, data governance is projected on the quality, security and reliability of their actions and results. It is therefore necessary to ensure the values that AIA imposes on training, validation and test datasets in high-risk systems, and, where appropriate, when techniques involving the training of AI models are employed.
These values can be aligned with the principles of Article 5 of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and enrich and complement them. To these are added the risk approach and data protection by design and by default. Relating one to the other is ancertainly interesting exercise.
Ensure the legitimate origin of the data. Loyalty and lawfulness
Alongside the common reference to the value chain associated with data, reference should be made to a 'chain of custody' to ensure the legality of data collection processes. The origin of the data, particularly in the case of personal data, must be lawful, legitimate and its use consistent with the original purpose of its collection. A proper cataloguing of the datasets at source is therefore indispensable to ensure a correct description of their legitimacy and conditions of use.
This is an issue that concerns open data environments, data access bodies and services detailed in the Data Governance Regulation (DGA ) or the European Health Data Space (EHDS) and is sure to inspire future regulations. It is usual to combine external data sources with the information managed by the SME.
Data minimisation, accuracy and purpose limitation
AIA mandates, on the one hand, an assessment of the availability, quantity and adequacy of the required datasets. On the other hand, it requires that the training, validation and test datasets are relevant, sufficiently representative and possess adequate statistical properties. This task is highly relevant to the rights of individuals or groups affected by the system. In addition, they shall, to the greatest extent possible, be error-free and complete in view of their intended purpose. AIA predicates these properties for each dataset individually or for a combination of datasets.
In order to achieve these objectives, it is necessary to ensure that appropriate techniques are deployed:
- Perform appropriate processing operations for data preparation, such as annotation, tagging, cleansing, updating, enrichment and aggregation.
- Make assumptions, in particular with regard to the information that the data are supposed to measure and represent. Or, to put it more colloquially, to define use cases.
- Take into account, to the extent necessary for the intended purpose, the particular characteristics or elements of the specific geographical, contextual, behavioural or functional environment in which the high-risk AI system is intended to be used.
Managing risk: avoiding bias
In the area of data governance, a key role is attributed to the avoidance of bias where it may lead to risks to the health and safety of individuals, adversely affect fundamental rights or give rise to discrimination prohibited by Union law, in particular where data outputs influence incoming information for future operations. To this end, appropriate measures should be taken to detect, prevent and mitigate possible biases identified.
The AIA exceptionally enables the processing of special categories of personal data provided that they offer adequate safeguards in relation to the fundamental rights and freedoms of natural persons. But it imposes additional conditions:
- the processing of other data, such as synthetic or anonymised data, does not allow effective detection and correction of biases;
- that special categories of personal data are subject to technical limitations concerning the re-use of personal data and to state-of-the-art security and privacy protection measures, including the pseudonymisation;
- that special categories of personal data are subject to measures to ensure that the personal data processed are secured, protected and subject to appropriate safeguards, including strict controls and documentation of access, to prevent misuse and to ensure that only authorised persons have access to such personal data with appropriate confidentiality obligations;
- that special categories of personal data are not transmitted or transferred to third parties and are not otherwise accessible to them;
- that special categories of personal data are deleted once the bias has been corrected or the personal data have reached the end of their retention period, whichever is the earlier;
- that the records of processing activities under Regulations (EU) 2016/679 and (EU) 2018/1725 and Directive (EU) 2016/680 include the reasons why the processing of special categories of personal data was strictly necessary for detecting and correcting bias, and why that purpose could not be achieved by processing other data.
The regulatory provisions are extremely interesting. RGPD, DGA or EHDS are in favour of processing anonymised data. AIA makes an exception in cases where inadequate or low-quality datasets are generated from a bias point of view.
Individual developers, data spaces and intermediary services providing datasets and/or platforms for development must be particularly diligent in defining their security. This provision is consistent with the requirement to have secure processing spaces in EHDS, implies a commitment to certifiable security standards, whether public or private, and advises a re-reading of the seventeenth additional provision on data processing in our Organic Law on Data Protection in the area of pseudonymisation, insofar as it adds ethical and legal guarantees to the strictly technical ones. Furthermore, the need to ensure adequate traceability of uses is underlined. In addition, it will be necessary to include in the register of processing activities a specific mention of this type of use and its justification.
Apply lessons learned from data protection, by design and by default
Article 10 of AIA requires the documentation of relevant design decisions and the identification of relevant data gaps or deficiencies that prevent compliance with AIA and how to address them. In short, it is not enough to ensure data governance, it is also necessary to provide documentary evidence and to maintain a proactive and vigilant attitude throughout the lifecycle of information systems.
These two obligations form the keystone of the system. And its reading should even be much broader in the legal dimension. Lessons learned from the GDPR teach that there is a dual condition for proactive accountability and the guarantee of fundamental rights. The first is intrinsic and material: the deployment of privacy engineering in the service of data protection by design and by default ensures compliance with the GDPR. The second is contextual: the processing of personal data does not take place in a vacuum, but in a broad and complex context regulated by other sectors of the law.
Data governance operates structurally from the foundation to the vault of AI-based information systems. Ensuring that it exists, is adequate and functional is essential. This is the understanding of the Spanish Government's Artificial Intelligence Strategy 2024 which seeks to provide the country with the levers to boost our development.
AIA makes a qualitative leap and underlines the functional approach from which data protection principles should be read by stressing the population dimension. This makes it necessary to rethink the conditions under which the GDPR has been complied with in the European Union. There is an urgent need to move away from template-based models that the consultancy company copies and pastes. It is clear that checklists and standardisation are indispensable. However, its effectiveness is highly dependent on fine tuning. And this calls particularly on the professionals who support the fulfilment of this objective to dedicate their best efforts to give deep meaning to the fulfilment of the Artificial Intelligence Regulation.
You can see a summary of the regulations in the following infographic:
Content prepared by Ricard Martínez, Director of the Chair of Privacy and Digital Transformation. Professor, Department of Constitutional Law, Universitat de València. The contents and points of view reflected in this publication are the sole responsibility of its author.