In 2010, following the devastating earthquake in Haiti, hundreds of humanitarian organizations arrived in the country ready to help. They encountered an unexpected obstacle: there were no updated maps. Without reliable geographic information, coordinating resources, locating isolated communities, or planning safe routes was nearly impossible.
That gap marked a turning point: it was the moment when the global OpenStreetMap (OSM) community demonstrated its enormous humanitarian potential. More than 600 volunteers from all over the world organized themselves and began mapping Haiti in record time. This gave impetus to the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team project.
What is Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team?
Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team, known by the acronym HOT, is an international non-profit organization dedicated to improving people's lives through accurate and accessible geographic data. Their work is inspired by the principles of OSM, the collaborative project that seeks to create an open, free and editable digital map for anyone.
The difference with OSM is that HOT is specifically aimed at contexts where the lack of data directly affects people's lives: it is about providing data and tools that allow more informed decisions to be made in critical situations. That is, it applies the principles of open software and data to collaborative mapping with social and humanitarian impact.
In this sense, the HOT team not only produces maps, but also facilitates technical capacities and promotes new ways of working tools, the for different actors who need precise spatial data. Their work ranges from immediate response when a disaster strikes to structural programs that strengthen local resilience to challenges such as climate change or urban sprawl.
Four priority geographical areas
While HOT is not limited to a single country or region, it has established priority areas where its mapping efforts have the greatest impact due to significant data gaps or urgent humanitarian needs. It currently works in more than 90 countries and organizes its activities through four Open Mapping Hubs (regional centers) that coordinate initiatives according to local needs:
- Asia-Pacific: challenges range from frequent natural disasters (such as typhoons and earthquakes) to access to remote rural areas with poor map coverage.
- Eastern and Southern Africa: this region faces multiple intertwined crises (droughts, migratory movements, deficiencies in basic infrastructure) so having up-to-date maps is key for health planning, resource management and emergency response.
- West Africa and North Africa: in this area, HOT promotes activities that combine local capacity building with technological projects, promoting the active participation of communities in the creation of useful maps for their environment.
- Latin America and the Caribbean: frequently affected by hurricanes, earthquakes, and volcanic hazards, this region has seen a growing adoption of collaborative mapping in both emergency response and urban development and climate resilience initiatives.
The choice of these priority areas is not arbitrary: it responds to contexts in which the lack of open data can limit rapid and effective responses, as well as the ability of governments and communities to plan their future with reliable information.
Open source tools developed by HOT
An essential part of HOT's impact lies in the open-source tools and platforms that facilitate collaborative mapping and the use of spatial data in real-world scenarios. To this end, an E2E Value Chain Mapping was developed, which is the core methodology that enables communities to move from image capture and mapping to impact. This value chain supports all of its programs, ensuring that mapping is a transformative process based on open data, education, and community empowerment.
These tools not only support HOT's work, but are available for anyone or community to use, adapt, or expand. Specifically, tools have been developed to create, access, manage, analyse and share open map data. You can explore them in the Learning Center, a training space that offers capacity building, skills strengthening and an accreditation process for interested individuals and organisations. These tools are described below:
It allows drone flights to be planned for up-to-date, high-resolution aerial imagery, which is critical when commercial imagery is too expensive. In this way, anyone with access to a drone – including low-cost and commonly used models – can contribute to a global repository of free and open imagery, democratizing access to geospatial data critical to disaster response, community resilience, and local planning.
The platform coordinates multiple operators and generates automated flight plans to cover areas of interest, making it easy to capture 2D and 3D images accurately and efficiently. In addition, it includes training plans and promotes safety and compliance with local regulations, supporting project management, data visualization and collaborative exchange between pilots and organizations.

Figure 1. Drone Tasking Manager (DroneTM) screenshot. Source: Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT).
It is an open-source platform that offers access to a community library of openly-licensed aerial imagery, obtained from satellites, drones, or other aircraft. It has a simple interface where you can zoom in on a map to search for available images. OAM allows you to both download and contribute new imagery, thus expanding a global repository of visual data that anyone can use and plot in OpenStreetMap.
All imagery hosted on OpenAerialMap is licensed under CC-BY 4.0, which means that they are publicly accessible and can be reused with attribution, facilitating their integration into geospatial analysis applications, emergency response projects, or local planning initiatives. OAM relies on the Open Imagery Network (OIN) to structure and serve these images.
It facilitates collaborative mapping in OpenStreetMap. Its main purpose is to coordinate thousands of volunteers from all over the world to aggregate geographic data in an organized and efficient way. To do this, it breaks down a large mapping project into small "tasks" that can be completed quickly by people working remotely.
The way it works is simple: projects are subdivided into grids, each assignable to a volunteer in order to map out elements such as streets, buildings, or points of interest in OSM. Each task is validated by experienced mappers to ensure data quality. The platform clearly shows which areas still need mapping or review, avoiding duplication and improving the efficiency of collaborative work.

Figure 2. Tasking Manager screenshot. Source: Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT).
It uses artificial intelligence to assist the mapping process in OpenStreetMap for humanitarian purposes. Through computer vision models, fAIr analyzes satellite or aerial images and suggests the detection of geographical elements such as buildings, roads, watercourses or vegetation from free images such as those of OpenAerialMap. The idea is that volunteers can use these predictions as an aid to map faster and more accurately, without performing automated mass imports, always integrating human judgment into the validation of each element.
One of the most outstanding features of fAIr is that the creation and training of AI models is in the hands of the mapping communities themselves: users can generate their own training sets adjusted to their region or context, which helps reduce biases of standard models and makes predictions more relevant to local needs.
It is a mobile and web application that facilitates the coordination of mapping campaigns directly in the field. Field-TM is used in conjunction with OpenDataKit (ODK), a data collection platform on Android that allows information to be entered in the field using mobile devices themselves. Thanks to it, volunteers can enter geospatial information verified by local observation, such as the purpose of each building (whether it is a store, a hospital, etc.).
The app provides an interface to assign tasks, track progress, and ensure data consistency. Its main purpose is to improve the efficiency, organization and quality of fieldwork by enriching it with local information, as well as to reduce duplications, avoid uncovered areas and allow clear monitoring of the progress of each collaborator in a mapping campaign.
Transform conversations from instant messaging apps (like WhatsApp) into interactive maps. In many communities, especially in disaster-prone or low-tech literacy areas, people are already using chat apps to communicate and share their location. ChatMap leverages those exported messages, extracts location data along with texts, photos, and videos, and automatically renders them on a map, without the need for complex installations or advanced technical knowledge.
This solution works even in conditions of limited or offline connectivity, relying on the phone's GPS signal to record locations and store them until the information can be uploaded.

Figure 3. ChatMap screenshot. Source: OpenStreetMap Humanitarian Team (HOT).
Facilitate access to and download of up-to-date geospatial data from OpenStreetMap in useful formats for analysis and projects. Through this web platform, you can select an area of interest on the map, choose what data you want (such as roads, buildings, or services), and download that data in multiple formats, such as GeoJSON, Shapefile, GeoPackage, KML, or CSV. This allows the information to be used in GIS (Geographic Information Systems) software or integrated directly into custom applications. You can also export all the data for a zone or download data associated with a specific project from the Tasking Manager.
The tool is designed to be accessible to both technical analysts and non-GIS experts: in a matter of minutes, custom OSM extracts can be generated without the need to install specialized software. It also offers an API and data quality metrics.
It is an open-source interactive map creation platform that allows anyone to easily visualize, customize, and share geospatial data. Based on OpenStreetMap maps, uMap allows you to add custom layers, markers, lines and polygons, manage colors and icons, import data in common formats (such as GeoJSON, GPX or KML) and choose licenses for the data, without the need to install specialized software. The maps created can be embedded in websites or shared using links.
The tool offers templates and integration options with other HOT tools, such as ChatMap and OpenAerialMap, to enrich the data on the map.
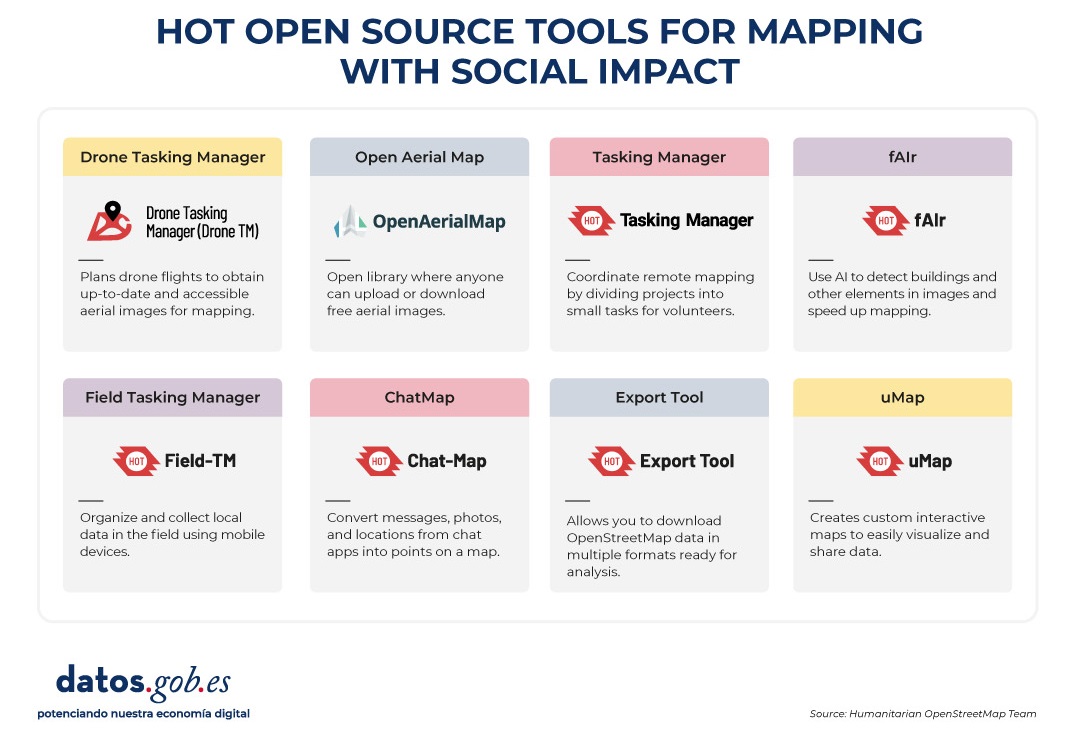
Figure 4. HOT open source tools for mapping with social impact. Source: Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT).
All of these tools are available to local communities around the world. HOT also offers training to promote its use and improve the impact of open data in humanitarian responses.
How can you join HOT's impact?
HOT is built alongside a global community that drives the use of open data to strengthen decision-making and save lives. If you represent an organization, university, collective, public agency, or community initiative and have a project idea or interest in an alliance, the HOT team is open to exploring collaborations. You can write to partnerships@hotosm.org.
When communities have access to accurate data, open tools, and the knowledge to generate geospatial information on an ongoing basis, they become informed agents, ready to make decisions in any situation. They are better equipped to identify climate risks, respond to emergencies, solve local problems, and mobilize support. Open mapping, therefore, does not only represent territories: it empowers people to transform their reality with data that can save lives.
Open source artificial intelligence (AI) is an opportunity to democratise innovation and avoid the concentration of power in the technology industry. However, their development is highly dependent on the availability of high quality datasets and the implementation of robust data governance frameworks. A recent report by Open Future and the Open Source Initiative (OSI) analyses the challenges and opportunities at this intersection, proposing solutions for equitable and accountable data governance. You can read the full report here.
In this post, we will analyse the most relevant ideas of the document, as well as the advice it offers to ensure a correct and effective data governance in artificial intelligence open source and take advantage of all its benefits.
The challenges of data governance in AI
Despite the vast amount of data available on the web, accessing and using it to train AI models poses significant ethical, legal and technical challenges. For example:
- Balancing openness and rights: In line with the Data Governance Regulation (DGA), broad access to data should be guaranteed without compromising intellectual property rights, privacy and fairness.
- Lack of transparency and openness standards: It is important that models labelled as "open" meet clear criteria for transparency in the use of data.
- Structural biases: Many datasets reflect linguistic, geographic and socio-economic biases that can perpetuate inequalities in AI systems.
- Environmental sustainability: the intensive use of resources to train AI models poses sustainability challenges that must be addressed with more efficient practices.
- Engage more stakeholders: Currently, developers and large corporations dominate the conversation on AI, leaving out affected communities and public organisations.
Having identified the challenges, the report proposes a strategy for achieving the main goal: adequate data governance in open source AI models. This approach is based on two fundamental pillars.
Towards a new paradigm of data governance
Currently, access to and management of data for training AI models is marked by increasing inequality. While some large corporations have exclusive access to vast data repositories, many open source initiatives and marginalised communities lack the resources to access quality, representative data. To address this imbalance, a new approach to data management and use in open source AI is needed. The report highlights two fundamental changes in the way data governance is conceived:
On the one hand, adopting a data commons approach which is nothing more than an access model that ensures a balance between data openness and rights protection.. To this end, it would be important to use innovative licences that allow data sharing without undue exploitation. It is also relevant to create governance structures that regulate access to and use of data. And finally, implement compensation mechanisms for communities whose data is used in artificial intelligence.
On the other hand, it is necessary to transcend the vision focused on AI developers and include more actors in data governance, such as:
- Data owners and content-generating communities.
- Public institutions that can promote openness standards.
- Civil society organisations that ensure fairness and responsible access to data.
By adopting these changes, the AI community will be able to establish a more inclusive system, in which the benefits of data access are distributed in a manner that is equitable and respectful of the rights of all stakeholders. According to the report, the implementation of these models will not only increase the amount of data available for open source AI, but will also encourage the creation of fairer and more sustainable tools for society as a whole.
Advice and strategy
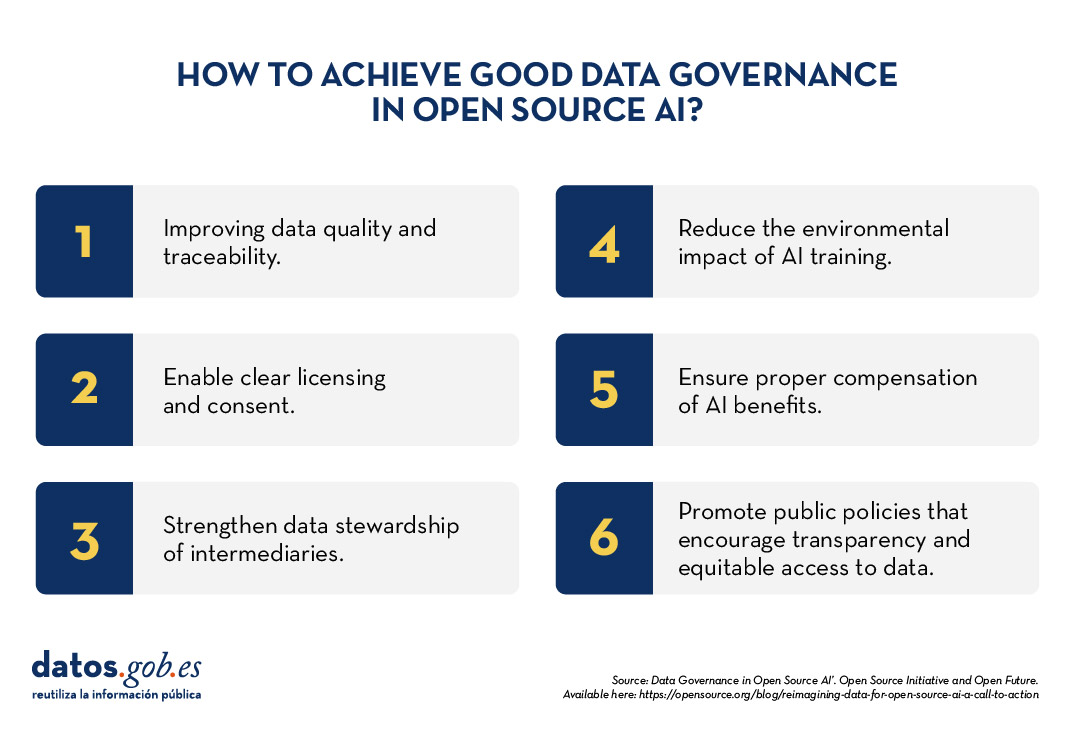
To make robust data governance effective in open source AI, the report proposes six priority areas for action:
- Data preparation and traceability: Improve the quality and documentation of data sets.
- Licensing and consent mechanisms: allow data creators to clearly define their use.
- Data stewardship: strengthen the role of intermediaries who manage data ethically.
- Environmental sustainability: Reduce the impact of AI training with efficient practices.
- Compensation and reciprocity: ensure that the benefits of AI reach those who contribute data.
- Public policy interventions: promote regulations that encourage transparency and equitable access to data.
Open source artificial intelligence can drive innovation and equity, but to achieve this requires a more inclusive and sustainable approach to data governance. Adopting common data models and broadening the ecosystem of actors will build AI systems that are fairer, more representative and accountable to the common good.
The report published by Open Future and Open Source Initiative calls for action from developers, policymakers and civil society to establish shared standards and solutions that balance open data with the protection of rights. With strong data governance, open source AI will be able to deliver on its promise to serve the public interest.
The Big Data Test Infrastructure (BDTI) is a tool funded by the European Digital Agenda, which enables public administrations to perform analysis with open data and open source tools in order to drive innovation.
This free-to-use, cloud-based tool was created in 2019 to accelerate digital and social transformation. With this approach and also following the European Open Data Directive, the European Commission concluded that in order to achieve a digital and economic boost, the power of public administrations' data should be harnessed, i.e. its availability, quality and usability should be increased. This is how BDTI was born, with the purpose of encouraging the reuse of this information by providing a free analysis test environment that allows public administrations to prototype solutions in the cloud before implementing them in the production environment of their own facilities.
What tools does BDTI offer?
Big Data Test Infrastructure offers European public administrations a set of standard open source tools for storing, processing and analysing their data. The platform consists of virtual machines, analysis clusters, storage and network facilities. The tools it offers are:
- Databases: to store data and perform queries on the stored data. The BDTI currently includes a relational database(PostgreSQL), a document-oriented database(MongoDB) and a graph database(Virtuoso).
- Data lake: for storing large amounts of structured and unstructured data (MinIO). Unstructured raw data can be processed with deployed configurations of other building blocks (BDTI components) and stored in a more structured format within the data lake solution.
- Development environments: provide the computing capabilities and tools necessary to perform standard data analysis activities on data from external sources, such as data lakes and databases.
- JupyterLab, an interactive, online development environment for creating Jupyter notebooks, code and data.
- Rstudio, an integrated development environment for R, a programming language for statistical computing and graphics.
- KNIME, an open source data integration, reporting and analytics platform with machine learning and data mining components, can be used for the entire data science lifecycle.
- H2O.ai, an open sourcemachine learning ( ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) platform designed to simplify and accelerate the creation, operation and innovation with ML and AI in any environment.
- Advanced processing: clusters and tools can also be created to process large volumes of data and perform real-time search operations(Apache Spark, Elasticsearch and Kibana)
- Display: BDTI also offers data visualisation applications such as Apache Superset, capable of handling petabyte-scale data, or Metabase.
- Orchestration: for the automation of data-driven processes throughout their lifecycle, from preparing data to making data-driven decisions and taking actions based on those decisions, is offered:
- Apache Airflow, an open source workflow management platform that allows complex data pipelines to be easily scheduled and executed.
Through these cloud-based tools, public workers in EU countries can create their own pilot projects to demonstrate the value that data can bring to innovation. Once the project is completed, users have the possibility to download the source code and data to continue the work themselves, using environments of their choice. In addition, civil society, academia and the private sector can participate in these pilot projects, as long as there is a public entity involved in the use case.
Success stories
These resources have enabled the creation of various projects in different EU countries. Some examples of use cases can be found on the BDTI website. For example, Eurostat carried out a pilot project using open data from internet job advertisements to map the situation of European labour markets. Other success stories included the optimisation of public procurement by the Norwegian Agency for Digitisation, data sharing efforts by the European Blood Alliance and work to facilitate understanding of the impact of COVID-19 on the city of Florence .
In Spain, BDTI enabled a data mining project atthe Conselleria de Sanitat de la Comunidad Valenciana. Thanks to BDTI, knowledge could be extracted from the enormous amount of scientific clinical articles, a task that supported clinicians and managers in their clinical practices and daily work.

Courses, newsletter and other resources
In addition to publishing use cases, theBig Data Test Infrastructure website offers an free online course to learn how to get the most out of BDTI. This course focuses on a highly practical use case: analysing the financing of green projects and initiatives in polluted regions of the EU, using open data from data.europa.eu and other open sources.
In addition, a monthly newsletter on the latest BDTI news, best practices and data analytics opportunities for the public sector has recently been launched .
In short, the re-use of public sector data (RISP) is a priority for the European Commission and BDTI(Big Data Test Infrastructure) is one of the tools contributing to its development. If you work in the public administration and you are interested in using BDTI register here.
On June 1, Madrid will host the fourth edition of Conference on FLOSS (software and free code) and Open Economy. The aim of the Open Expo is bringing together leading companies and institutions, developers, hackers, experts, suppliers and users to learn about technology solutions and trends on open source, open source, open data and innovation.
Since 2012, each of the events has sought to promote the use and development of free and open software to boost the collaborative philosophy and democratize the access to information technologies. For that purpose, there have been several events dedicated to specific topics such as e-commerce, business intelligence, content managers or elearning, among others.
On this occasion, the Open Expo is focused on addressing the latest challenges related to open source and digital transformation. An opportunity to discover how this technology can modernize businesses and help companies on their way to innovation and the digital transformation of their corporate operations.
In this regard, the organisers of the event has launched a call to find speakers who participate in the congress sharing their success stories and experiences in the field of open technologies, showing how open source and free software have helped improve their business activities or presenting their open source projects.
To participate, it is necessary to apply before March 2 through the official page of the event; a jury will analyze the proposals and select the most relevant ideas in the field to be discussed.
In addition, among the activities organized this year, apart from the showroom where the main companies of the industry show their services and products, there will be an investment forum, Open StartUp Connector, where a twelve start-ups will present to potential investors their ICT projects based onpen code/data, or developed through free tools or software.
At the same time, networking activities with experts are also planned to discuss on cybersecurity, big data and IoT solutions and, moreover, the Open Awards Spain 2017 will take place, which awardsthe best solutions developed with open source technology at the national level.