The unstoppable advance of ICTs in cities and rural territories, and the social, economic and cultural context that sustains it, requires skills and competences that position us advantageously in new scenarios and environments of territorial innovation. In this context, the Provincial Council of Badajoz has been able to adapt and anticipate the circumstances, and in 2018 it launched the initiative "Badajoz Es Más - Smart Provincia".
What is "Badajoz Es Más"?
The project "Badajoz Is More" is an initiative carried out by the Provincial Council of Badajoz with the aim of achieving more efficient services, improving the quality of life of its citizens and promoting entrepreneurship and innovation through technology and data governance in a region made up of 135 municipalities. The aim is to digitally transform the territory, favouring the creation of business opportunities, social improvement andsettlement of the population.
Traditionally, "Smart Cities" projects have focused their efforts on cities, renovation of historic centres, etc. However, "Badajoz Es Más" is focused on the transformation of rural areas, smart towns and their citizens, putting the focus on rural challenges such as depopulation of rural municipalities, the digital divide, talent retention or the dispersion of services. The aim is to avoid isolated "silos" and transform these challenges into opportunities by improving information management, through the exploitation of data in a productive and efficient way.

Citizens at the Centre
The "Badajoz es Más" project aims to carry out the digital transformation of the territory by making available to municipalities, companies and citizens the new technologies of IoT, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, etc. The main lines of the project are set out below.
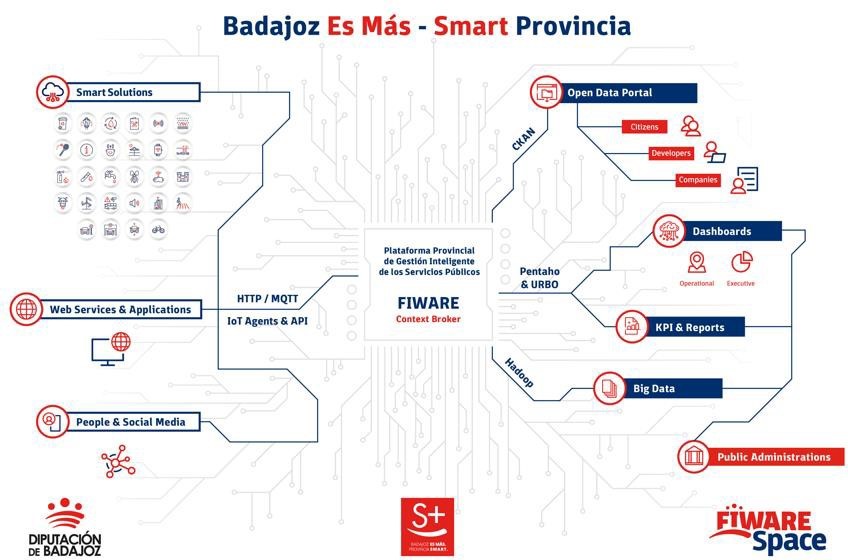
Provincial Platform for the Intelligent Management of Public Services
It is the core component of the initiative, as it allows for the integration of information from any IoT device, information system or data source in one place for storage, visualisation and in a single place for storage, visualisation and analysis. Specifically, data is collected from a variety of sources: the various sensors of smart solutions deployed in the region, web services and applications, citizen feedback and social networks.
All information is collected on a based on the open source standard FIWARE an initiative promoted by the European Commission that provides the capacity to homogenise data (FIWARE Data Model) and favour its interoperability. Built according to the guidelines set by AENOR (UNE 178104), it has a central module Orion Context Broker (OCB) which allows the entire information life cycleto be managed. In this way, it offers the ability to centrally monitor and manage a scalable set of public services through internal dashboards.
The platform is "multi-entity", i.e. it provides information, knowledge and services to both the Provincial Council itself and its associated Municipalities (also known as "Smart Villages"). The visualisation of the different information exploitation models processed at the different levels of the Platform is carried out on different dashboards, which can provide service to a specific municipality or locality only showing its data and services, or also provide a global view of all the services and data at the level of the Provincial Council of Badajoz.
Some of the information collected on the platform is also made available to third parties through various channels:
- Portal of open dopen data portal. Collected data that can be opened to third parties for reuse is shared through its open data portal. In it we can find information as diverse as real time data on the beaches with blue flags blue flag beaches in the region (air quality, water quality, noise pollution, capacity, etc. are monitored) or traffic flow, which makes it possible to predict traffic jams.
- Portal for citizens Digital Province Badajoz. This portal offers information on the solutions currently implemented in the province and their data in real time in a user-friendly way, with a simple user experience that allows non-technical people to access the projects developed.
The following graph shows the cycle of information, from its collection, through the platform and distribution to the different channels. All this under strong data governance.
Efficient public services
In addition to the implementation and start-up of the Provincial Platform for the Intelligent Management of Public Services, this project has already integrated various existing services or "verticals" for:
-
To start implementing these new services in the province and to be the example and the "spearhead" of this technological transformation.
- Show the benefits of the implementation of these technologies in order to disseminate and demonstrate them, with the aim of causing sufficient impact so that other local councils and organisations will gradually join the initiative.
There are currently more than 40 companies sending data to the Provincial Platform, more than 60 integrated data sources, more than 800 connected devices, more than 500 transactions per minute... It should be noted that work is underway to ensure that the new calls for tender include a clause so that data from the various works financed with public money can also be sent to the platform.
The idea is to be able to standardise management, so that the solution that has been implemented in one municipality can also be used in another. This not only improves efficiency, but also makes it possible to compare results between municipalities. You can visualise some of the services already implemented in the Province, as well as their Dashboards built from the Provincial Platform at this video.

Innovation Ecosystem
In order for the initiative to reach its target audience, the Provincial Council of Badajoz has developed an innovation ecosystem that serves as a meeting point for the Badajoz Provincial Council:
-
Citizens, who demand these services.
-
Entrepreneurs and educational entities, which have an interest in these technologies.
-
Companies, which have the capacity to implement these solutions.
- Public entities, which can implement this type of project.
The aim is to facilitate and provide the necessary tools, knowledge and advice so that the projects that emerge from this meeting can be carried out.
At the core of this ecosystem is a physical innovation centre called the FIWARE Space. FIWARE Space carries out tasks such as the organisation of events for the dissemination of Smart technologies and concepts among companies and citizens, demonstrative and training workshops, Hackathons with universities and study centres, etc. It also has a Showroom for the exhibition of solutions, organises financially endowed Challenges and is present at national and international congresses.
In addition, they carry out mentoring work for companies and other entities. In total, around 40 companies have been mentored by FIWARE Space, launching their own solutions on several occasions on the FIWARE Market, or proposing the generated data models as standards for the entire global ecosystem. These companies are offered a free service to acquire the necessary knowledge to work in a standardised way, generating uniform data for the rest of the region, and to connect their solutions to the platform, helping and advising them on the challenges that may arise.
One of the keys to FIWARE Space is its open nature, having signed many collaboration agreements and agreements with both local and international entities. For example, work on the standardisation of advanced data models for tourism is ongoing with the Future Cities Institute (Argentina). For those who would like more information, you can follow your centre's activity through its weekly blog.

Next steps: convergence with Data Spaces and Gaia-X
As a result of the collaborative and open nature of the project, the Data Space concept fits perfectly with the philosophy of "Badajoz is More". The Badajoz Provincial Council currently has a multitude of verticals with interesting information for sharing (and future exploitation) of data in a reliable, sovereign and secure way. As a Public Entity, comparing and obtaining other sources of data will greatly enrich the project, providing an external view that is essential for its growth. Gaia-X is the proposal for the creation of a data infrastructure for Europe, and it is the standard towards which the "Badajoz es Más" project is currently converging, as a result of its collaboration with the gaia-X Spain hub.
60 participants, 10 mentors and €2,000 in prizes. These are the figures managed by DiValHack, the Hackathon promoted by Red.es and the Diputación de Valencia to bring the project "Connecta Valencia: Smart and Sustainable Tourism Territory" to the citizens. This project, financed by the public entity Red.es with FEDER funds, seeks to improve the tourism competitiveness of Valencian municipalities, increasing their knowledge to offer a better and more sustainable experience to tourists.
What is DiValHack?
DiValHack participants must develop a technological solution that responds to a challenge using the resources and infrastructures that Connecta Valencia offers.
Participants can propose a challenge of their choice related to Connecta Valencia or try to respond to some of the organisation's proposals:
- Mobility challenges: for example, determining the actual congestion of different points of interest, helping to locate parking spaces or helping tourists to travel with a lower carbon footprint.
- Environmental challenges: such as monitoring the air situation or comparing environmental quality between municipalities.
- Tourism challenges: e.g. showcasing thematic routes or promoting nomadism and rural tourism.
Solutions that address several challenges, as well as combining different data sources, from Connecta Valencia and other external repositories, will be considered positively. For example, solutions that monitor noise in contrast to the influx of people or that recommend routes based on the weather or air quality.
When does it take place?
The hackathon will be held on 10 and 17 November 2022, starting at 12:30. Both sessions will be face-to-face.
In the first session, resources will be presented and teams and roadmaps will be defined.
During the week the teams will work on their projects, supported by online mentoring.
On the 17th, the teams will present their solutions, which will be evaluated by a jury, and prizes will be awarded to the three solutions with the best scores. The evaluation criteria are defined in the terms and conditions of the call.
Who can participate?
The hackathon is aimed at students and professionals. The only requirement is to be of legal age.
Participation will take place in teams of three to six people. The team should be multidisciplinary, including technological, financial, business, communication and/or social science profiles, as the evaluation criteria are not only technical.
What do the prizes consist of?
The three proposals with the best scores will receive cash prizes of 2,000 euros, distributed as follows:
- First prize: 1,000 euros
- Second prize: 750 euros
- Third prize: 250 euros
How can I participate?
Participation is free of charge. The deadline for registration is 30 October. To register you must fill in this form.
You can register alone or in a group. If you register alone, the organisation will find a group for you at the event.
Find out more about Connecta Valencia
The Connecta Valencia project has provided the 266 Valencian municipalities with the necessary infrastructure to analyse the flow of tourists in their territory, as well as their impact on the environment, by installing devices that measure mobility and environmental quality. This information allows informed decisions to be taken and public policies to be improved.
To this end, an open source platform has been set up to facilitate access to data through two mechanisms: an API and an open data portal that offers datasets in CSV and JSON formats. Among other information, users can access to data from meteorological and environmental sensors, mobility flows, etc.
You can learn more about the project in the following videos:
The health situation we have been experiencing for a couple of years now had changed the way of celebrating major events to date, moving from a face-to-face to an online format.
This year, however, we are slowly beginning to see a return to the normality that existed before the pandemic. Several of the major technology events to be held in 2022 have already announced that they will be held in hybrid format, or even exclusively in person, if health conditions permit.
Here is a brief review of the events related to the world of technology and data, both public and private, that will be held over the coming months and that you should mark in red on your calendar.
Mobile World Congress (MWC)
February 28 to March 03, 2022 – Barcelona
We begin by talking about the most global technological event in our country, which is about to begin, and which aims to reconnect and reinvent the connectivity industry. It is one of the most influential events worldwide, as this congress represents the largest exhibition of telephony, Internet and mobile applications within the industry.
The MWC is attended by mobile operators, device manufacturers and service providers to create a place to facilitate networking and showcase the most innovative and current technologies.
Among the conferences that will take place at this event, we find some related to the field of data, such as ‘Strategies for energising the data economy’ or ‘The data opportunity: making mobility smart’. Also noteworthy is the conference ‘Digital policies to speed the post-Covid recovery’, which will feature a presentation by Nadia Calviño, First Vice President of Spain and Minister of Economy and Digitalization.
Four Years From Now (4YFN)
February 28 to March 03, 2022 – Barcelona
As has become customary in recent years, the MWC will also host the internal event for start-ups 4YFN (4 Years From Now), which seeks to support contact between new companies and investors, thus facilitating access to an international network of contacts and different business opportunities. Red.es will collaborate in this event by making a selection of Spanish companies and startups to participate in the different representation spaces that are organized. Among the participating companies there are some focused on the world of data and its reuse.
In addition, 4YFN will have outstanding speakers such as Francisco Polo, High Commissioner for Spain Entrepreneurial Nation, or Carme Artigas, Secretary of State for Digitalization and Artificial Intelligence, who will participate on March 1 in a session that will analyze the existing challenges in developing a European ecosystem that is favorable to the creation, growth and investment of new companies and start-ups.
OpenExpo Europe 2022
June 30, 2022 – Madrid
OpenExpo Europe is a space for the dissemination of technological innovation, digital transformation and open source in Europe. Among its main objectives is to disseminate among professionals in the technology sector the latest trends, tools and services in innovation and technology, as well as helping them to increase their network of contacts.
The OpenExpo Virtual Experience initiative emerged in 2020, following the success of the dissemination of content in online format about fields such as: cybersecurity, blockchain, AI, Virtual Reality, IoT or big data, among other topics.
As of today, the agenda of this event is not yet available. However, through this link you can pre-register for the event that will take place on June 30 at La Nave (Madrid).
Advanced Factories
March 29th to 31st, 2022 – Barcelona
The city of Barcelona will once again host this annual summit, which brings together the most cutting-edge companies in Industry 4.0. This event, European leader in advanced and digital industry, will bring together more than 17,000 professionals, in addition to offering 100 hours of conferences on fields such as robotics, industry 4.0, automation or 3D printing, among others.
Some of the central themes of this world-class meeting will be: productivity improvement, connectivity, data analysis, industrial symbiosis or reduction of the digital gap between large manufacturing factories and SMEs.
South Summit
June 08 to 10, 2022 – Madrid
Next June will see the arrival of South Summit, a contest-like showcase designed to offer more visibility to disruptive projects seeking new clients, financing or strategic partnerships. As in previous editions, it will feature investors and leading innovation companies from Spain, Southern Europe and Latin America. You can register for the start-up competition through this link.
Unlike last year, in 2022 South Summit will once again be held in a fase-to-face format in Madrid, in addition to maintaining the virtual presentations of the projects through a 100% digital omnichannel model.
IoT Solutions World Congress
May 10-12, 2022 - Barcelona, Spain
After the cancellation of the last edition last October, due to the high incidence of the pandemic in our country, this event returns with more strength in 2022. Barcelona will bring together industry experts to analyze how IoT is transforming production, transportation, logistics and public services, as well as sectors such as healthcare and energy.
The central theme of this edition will be "The new normal", and will analyze the main innovation challenges faced by companies through five thematic axes such as security, connectivity, business optimization, intelligence and customer experience.
Among the topics to be presented are some related to the world of data such as: "Data are the fuel that drives the energy transition: exploring the smart energy network at Eneco" or "Konecranes: driving business and providing commercial advantages with industrial IoT, perimeter and data analytics".
Smart City Expo World Congress
November 15-17, 2022 - Barcelona, Spain
Smart City Expo World Congress (SCEWC) has established itself over the last few years as a benchmark event that blends technological innovation with the Smart Cities sector. This smart cities congress will bring together once again experts, companies and entrepreneurs with the aim of collectivizing urban innovation and promoting new projects around the world.
The last editions were developed in digital format, which has led to the creation of Tomorrow.City, a digital content platform aimed at public administrations and new talents, which seeks to disseminate knowledge, promote training and promote research on an uninterrupted basis. This partnership combines the event with a digital platform open all year round and dedicated to the growth of sustainable mobility.
EU Datathon
October 20, 2022 – Online
The EU Datathon is the competition that seeks to boost the creation of products based on open data, such as mobile or web applications, that offer an answer to different challenges related to EU priorities. The deadline for submissions is March 31, 2022, with the final on October 20.
This challenge is linked to the European Union Open Data Days, organized by the Publications Office of the European Union, which last year held its first edition and will presumably hold the second one during the last months of 2022, although this information is yet to be confirmed.
Other events of interest
There are a multitude of technological events related to the field of data that can also be very interesting. We can not collect them all in detail in a single article, so here are some of the most popular both nationally and internationally:
In Spain
- Barcelona Cybersecurity Congress: May 10 to 12, 2022 in Barcelona
- CTO Summit 2022: June 24 and 25, 2022 in Valencia
- Digital Enterprise Show: June 14-16, 2022 in Malaga
- EShow: July 2022 in Barcelona and October 2022 in Madrid
Internationally
- OpenScience Conference 2022: March 08 to 10, 2022 – Online
- 9th International Data Science Summit: May 2022 - Dublin
- Learning Technologies: May 04 and 05, 2022 – London
- Gartner Data & Analytics Summit 2022: August 22-24, 2022 - Orlando, FL
- Esri User Conference: July 11-15, 2022 - San Diego, California
- AI & Big Data Expo Global 2022: December 01 and 02 - London
This has been just a selection of the main technological events that 2022 has in store for us. If you know of any other that you would like to highlight, do not hesitate to write us a comment or send us your proposal through our email contacto@datos.gob.es.
Autonomous vehicles, smart waste management services, trainers that monitor how much we exercise... We live in an increasingly digital and connected environment, with greater similarities to the future we dreamed of as children. It is the so-called Internet of Things (IoT), a network of physical objects that use sensors and APIs to connect with each other and exchange data over the Internet. Its rise is unstoppable and by 2025 it is expected that there will be more than 30 billion IoT connections in the world, which is an average of almost 4 IoT devices per person.
This boom means that the amount of data to be processed and managed is increasing. Traditionally, these connected objects collect information and send it to large data centres for processing. But sending the data to the data centre for processing takes time that we sometimes don't have, and the problem comes in certain use cases where fast responses are needed and every millisecond is crucial, such as in autonomous driving. This is where the edge computing paradigm comes in, as a way to improve agility and efficiency.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a new approach to running certain services as close as possible to the source of the data. In other words, computational processes are performed on the connected devices themselves or on local peripheral servers (edge nodes). This brings a number of advantages:
- Lower latency time and higher speed. Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to be transferred within the network. By avoiding the step of sending all the information for processing to the cloud, the response time is reduced, providing immediacy.
- Lower bandwidth requirement, as it is not necessary to send all raw data to servers. Edge computing reduces global traffic loads, avoiding system saturation.
- Reduced security risks. It is true that edge computing expands the potential attack surface, but it reduces the impact on the organisation as a whole. When you centralise all data, analytics and processing, a single denial-of-service attack can disrupt all operations. By distributing the loads across the various nodes, the risk is also distributed. One process may fail, but the rest could continue to operate.
- Facilitates scalability. Given the exponential growth of data and analytics capabilities, it is difficult to foresee the IT infrastructure needs to cope with the future (e.g. servers with the capacity to analyse all incoming information). By incorporating edge computing services, organisations can quickly and cost-effectively extend the reach of their network by adding a new edge node.
- Reduced costs. Edge computing devices require more software capabilities for optimal performance than those that simply capture data and send it for remote analysis. However, they also allow data to be sorted from a management perspective. In other words, devices can be deployed with customised capabilities for various analytics, without the need to over-invest.
Advances in edge computing go hand in hand with 5G, which enables more devices to connect to each other and exchange data at higher speeds.
Edge computing will also continue to be complemented by cloud environments: edge computing capabilities will be more appropriate where speed and low latency in data transfer are needed, while the cloud will continue to be essential for handling large volumes of data that require greater computing power.
The impact of edge computing on smart cities
Given the above advantages, it seems obvious that edge computing represents a breakthrough for data management in various sectors, from healthcare and telemedicine to Industry 4.0. For example, Navantia, the Spanish public shipbuilding company, is implementing this technology, with the support of Red.es. Combining 5G, edge computing and the use of augmented reality glasses, it is innovating in construction processes and remote technical assistance.
But if there is one area where edge computing is particularly important, it is in smart cities. In essence, smart cities rely on IoT devices to provide connectivity and situational data analysis. Devices such as security cameras and various sensors - which transmit data related to transportation, lighting or smart buildings - operate within a city-wide network to provide a better experience for citizens. Edge computing and 5G facilitate real-time decisions, which can be made automatically by the devices themselves rather than sending data to another central computer for processing, making it easier to manage the city. This can also have an impact on the publication of open data, which could be made more agile and accessible through dynamic services.
In the city of Barcelona, edge computing use cases are being tested in different applications, such as urban transport, public safety and health services, also with the support of Red.es. Among other issues, thanks to these technologies, they are measuring in real time the best routes for getting around or achieving faster action by the urban police in the event of atmospheric phenomena.
The future of edge computing
Edge computing is expected to gradually take hold. According to EU data - based on an IDC estimate - in 2018, 80% of data processing was carried out in centralised computing facilities and 20% in the smart connected objects themselves. In 2025, the situation will be the other way around, as the following graph shows.

The European Commission, among its activities, also seeks to boost the deployment of technologies linked to edge computing, due to the numerous opportunities it offers. In this respect, its cloud activities fall into two categories:
- Invest funds in cutting-edge projects related to cloud and edge computing.
- Develop policies and standards that protect users, make cloud services more secure, ensure fair competition and create the optimal framework conditions for a thriving European industry.
In the case of Spain, we face the challenge of building 1,000 edge nodes in nine years.
In short, we are facing a new technological paradigm that is necessary due to the enormous amount of data generated not only by smart cities, but also by practically all sectors that are increasingly seeking to be more connected. This generates a need for speed and immediate analysis capabilities that edge computing can help to boost.
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
The Alcazar of Jerez de la Frontera will host, on 23 and 24 September, the II Regional Meeting of Smart Municipalities. Its objective is to advance in the smart development of Andalusian municipalities, in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. The event is organised by the Provincial Council of Cadiz and the Andalusian Federation of Municipalities and Provinces, with the collaboration of the Regional Government of Andalusia, the City Council of Jerez, the University of Cadiz and the Smart City Cluster.
More than 20 presentations and round tables will take place over two days. Industry 4.0, artificial intelligence, SmartAgriFood or digital administration are some of the topics that will be discussed. The full programme (in Spanish) can be seen here.
The event will also host a hackathon with the aim of boosting the use and intelligence of data.
Hack4ERMI2021
Under the motto "Objective Smart and Resilient Territory", participants in the hackathon will have to use their creative and innovative thinking to find concrete and feasible solutions to 4 challenges:
- Ecological transition, climate change and environmental sustainability 2.
- Resilience and security
- Data economy, competitiveness and progress
- Health and welfare
All solutions should have in common the use and exploitation of open datasets, which can be combined with other sources of public information or data from IoT devices.
open data sets, which can be combined with other sources of public information or information from IoT devices.
To participate, a team of two to five people is required. Teams should be diverse in terms of gender, expertise and experience.
The competition will take place in several phases:
- Preliminary phase, from 23 August to 10 September. Teams must submit a maximum of three ideas that respond to the challenges indicated above. To do so, they will have to submit a dossier explaining the idea and a video through the form provided for registration. A jury will evaluate the proposals and choose the five best ones, which will go on to the next phase. Those participants whose ideas have not been chosen may, if they wish, join one of the finalist teams.
- Workshop. 16th September. Selected teams will have the opportunity to participate in an online workshop to learn how to use FiWoo, a FIWARE-based Smart City platform.
- Hack4ERMI202: Ideas, Tech & Rock ́n Roll, 23-24 September. The teams will have a room available throughout the II Regional Meeting of Smart Municipalities, where they will be able to finalise the definition of the solutions presented. On the 24th they will present their proposals to the public at the congress.
The jury, made up of representatives of the organising and collaborating entities of the Meeting, will choose the 3 winners. The first winner will receive 2,000 euros, the second 1,000 euros and the third 500 euros.
If you have any questions, please contact the organisers by email at hack4ermi2021@dipucadiz.es.
Do you want to attend the II Regional Meeting of Smart Municipalities?
Participation in the hackathon is open to all citizens who wish to participate, but attendance at the II Regional Meeting of Smart Municipalities is limited, due to the pandemic situation.
Attendance in person is limited and by registration at the following link. However, the meeting can be followed online in its entirety via YouTube. The link will be available on the event's website in the coming weeks.
Mobility is a key economic driver. Increasing the efficiency and quality of a country's mobility system contributes both to the strength of its economy and to improving the quality of life of its citizens. This is particularly important in the mobility systems of cities and their metropolitan areas, where most of the population and, thus, most of the economic activity is concentrated.
Aware of this - and because we citizens demand it - local authorities have for decades allocated a significant part of their annual resources to expanding, improving and making their transport and mobility networks more efficient.
In the last decade, open data has been one of the most important vectors of innovation that have been introduced in the mobility strategies developed by cities, giving rise to initiatives that would have been difficult to imagine in previous periods. Despite all the complexities involved, opening both static and real-time mobility datasets for reuse is actually cheap and simple compared to the cost of building a new transport infrastructure or the cost of acquiring and maintaining the operational support systems (OSS) associated with mobility services. In addition, the existence of an increasing deployment of sensor networks, accessible through control systems deployed in the context of "smart city" strategies, makes the task a little easier.
We should not forget, moreover, that public transport is key to tackling climate change as it is one of the fastest growing sources of greenhouse gas emissions, and public transport offers the best mobility solution to move people quickly and efficiently in cities around the world. As shown in the figure, simply shifting passengers using their private vehicles to public transport has a major impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The Bus Industry Confederation estimates that shifting passengers from cars to public transport can lead to a 65% reduction in emissions during peak hours. This reduction could be as high as 95% in emissions during off-peak hours for those commuters who switch from private cars to public transport.
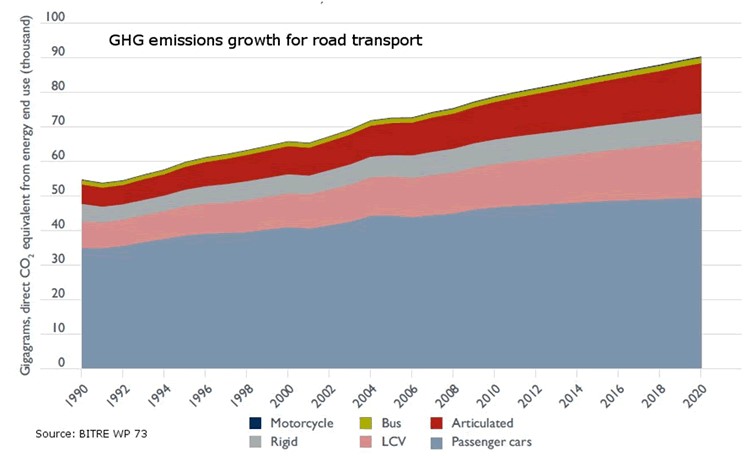
For all these reasons, there are already numerous examples where freeing up transport and mobility data to put it in the hands of travellers is proving to be a policy with important benefits for many cities: it allows better use of resources and contributes to more efficient mobility in urban space.
Let's look at some examples that may not be as well-known as the ones that usually reach the media, but which demonstrate how the release of data allows for innovations that benefit both users and, in some cases, the authorities themselves.
Redesigning New York City bus routes
All cities are constantly thinking of ways to improve their bus routes in order to provide the best possible service to citizens. In New York City, however, the open data policy, as an unplanned consequence, provided an important aid to the authorities, based on the analysis of data from the bus network users themselves.
The rider-driven Bus Turnaround Coalition campaign, supported by TransitCenter, a foundation working to improve public transport in US cities, and the Riders Alliance, is using open data to raise awareness about the state of New York City's bus network, proposing solutions for improvement to the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA).
To formulate their recommendations, the organisations analysed bus arrival times using the MTA's own location maps, incorporated real-time data through the GTFS specification, reviewed ridership data, and mapped (and optimised) bus routes.
Among the most innovative proposals is the shift in approach to route design criteria. Instead of trying to cater to all types of travellers, the Bus Turnaround Coalition, after analysing how people actually move around the city and what type of transport they would need to achieve their goals efficiently, proposed the following recommendations:
- Add lines to take passengers from the outskirts of the city directly to the underground lines, facilitating a quick trip.
- Improve lines to offer short, fast routes within a neighbourhood for people who want to run a quick errand or visit a close friend.
- Split routes that are too long to minimise the risk of delays.
- Readjust the distance between stops, which are often too close together, complementing gaps in metro coverage.
Open data has turned frequent rider protests and complaints about poor network performance into a set of reasoned, data-driven inputs, which have been captured in a series of MTA commitments to improve New York's bus network, such as redesigning the network by 2021, increasing journey speeds by 25%, and proactively managing bus maintenance.
Bicycle usage data in San Francisco
Like many other cities, San Francisco, through its Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA), records travel data from users of its public bike-sharing system and makes it available as open data. In this case, the transport authority itself publishes regular reports, both on the overall use of the system and on the conclusions it draws for the improvement of the city's own mobility.
By documenting and analysing the volumes and trends of bicycle use in San Francisco, they are able to support the goals of the SFMTA's Strategic Plan, which aims to prioritise other forms of travel in the city than the private car.
For example, ongoing analysis of bicycle passenger volumes at key intersections in the city and citizen input has reduced traffic congestion and accidents by re-prioritising vehicle traffic priorities according to actual roadway usage at any given time of day.
Efficient parking in Sacramento
Many cities try to address traffic congestion problems from different perspectives including efficient parking management. Therefore, one of the datasets frequently published by cities with open data initiatives is public parking occupancy.
In the city of Sacramento, California, the open data initiative publishes datasets from the citywide sensor network that monitors parking availability at parking meters and not only in the city's public car parks. In this way they have managed to reduce emissions as vehicles spend less time looking for parking, while significantly improving traffic flow and the satisfaction of citizens using the Sacpark app.
In 2020, due to the pandemic, passenger transport around the world was drastically reduced due to the mobility restriction policies that governments around the world had to deploy to curb the spread of the virus, as seen in the image below.
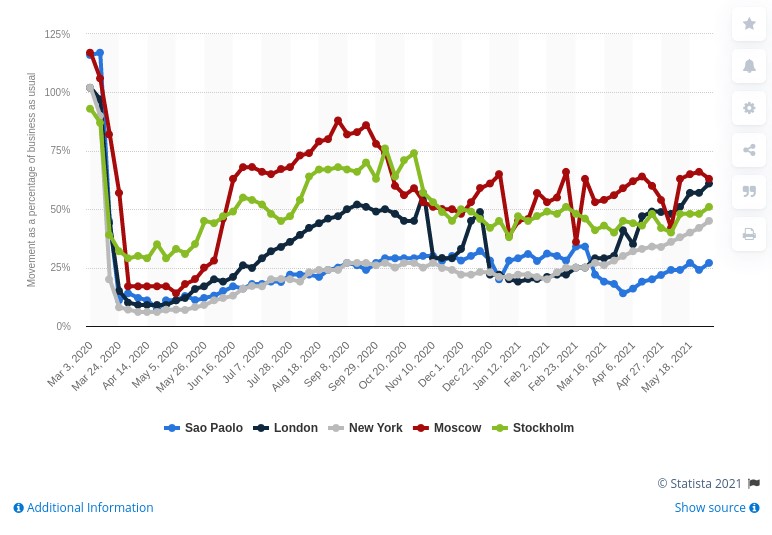
In June 2021 cities are still far from recovering the levels of mobility they had in March 2020, but we continue to make progress in making data the basis on which to build useful information, and essential in the new innovations coming through artificial intelligence.
So, as the pandemic recedes, and many initiatives resume, we continue to see how open data is at the heart of smart, connected and environmentally friendly mobility strategies.
Content prepared by Jose Luis Marín, Senior Consultant in Data, Strategy, Innovation & Digitalization.
The contents and views reflected in this publication are the sole responsibility of the author.
The current healthcare situation has changed the way in which major events are held, with most of them moving from being held in person to online. However, little by little, the face-to-face format is being taken up again, returning to the offline format and even combining both experiences.
In this article we are going to discover some events related to the world of technology and data, both private and public, that will be held in the coming weeks and that you should not miss. Join us to discover them!
OpenExpo Virtual Experience 2021
8 to 10 June 2021 – Online
OpenExpo Europe has positioned itself in recent years as one of the main windows for dissemination in technological innovation, digital transformation and open source in Europe. Its main objective is to disseminate the latest trends, tools and services in innovation and technology among professionals in the technology sector, as well as helping them to increase their network of contacts.
The OpenExpo Virtual Experience initiative was launched last year, following the success achieved with the dissemination of online content on cybersecurity, blockchain, AI, virtual reality, IoT and big data, among other topics.
At this event, attendees will be able to enjoy more than 50 activities led by professional experts in technology and innovation: presentations, case studies, interviews, debates, workshops, Q&A sessions, 1to1 meetings, etc. Some of the topics to be addressed are Govtech and the public administration's commitment to innovation, free educational software and Gaia-X, one of the European Commission's major projects in the field of data.
Advanced Factories
8 to 10 June 2021 – Barcelona
Barcelona will host the annual Advanced Factories summit, which brings together the most cutting-edge companies in Industry 4.0. Some of the focal points of this world-class meeting will be: industrial automation, sensors, energy efficiency, artificial intelligence, blockchain, machine learning and big data.
For the fourth consecutive year, this summit will host the Industry 4.0 Congress under the slogan "We are the future of automation", which will begin with a presentation on the role of data in the transformation of this sector.
Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2021
28 June to 01 July 2021 – Barcelona
This great technological event was suspended in 2020, but in 2021 it will re-emerge as a new event with great guarantees of health safety. As a novelty, this year's MWC will feature several virtual activities that will complement the on-site edition of the event. "Connected Impact" is the chosen theme, which places the COVID-19 pandemic as the main element influencing this year's technological trends.
As usual, leading professionals from the sector and prominent speakers will be taking part. Among them is Carme Artigas, Secretary of State for Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence, who will participate with a presentation on data in the age of intelligence.
As in previous years, the in-house event for startups 4YFN (4 Years From Now) will be held as part of the MWC. Its aim is to support contact between startups and investors, providing access to an international network of contacts and different business opportunities. Among the participating companies we can find many focused on the world of data and its reuse. Red.es selects Spanish companies and startups to participate in the different representation spaces that are organised.
South Summit
5 to 7 October 2021 – Online
The autumn will see the arrival of South Summit, a showcase in the form of a competition to give more visibility to disruptive projects seeking new customers, funding or strategic partnerships. It will feature investors and leading innovation companies from Spain, southern Europe and Latin America, regardless of the industry, country of origin or stage of development of the project.
This year the organisation has decided not to hold the event in person, so the project presentations will take place virtually.
IoT Solutions World Congress
5 to 7 October 2021 – Barcelona
This is undoubtedly one of the most high-profile IoT events in the world. Due to the growing demand from the sector, more than 8,000 visitors are expected to attend an event that will bring together industry experts to analyse how the Internet of Things is transforming production, transport, logistics, public services and sectors such as healthcare and energy.
Some of the papers to be presented include "Leveraging EdgeX Foundry as an Open, Trusted Data Framework for Smart Meter Monitoring", "Using Mobile, IoT and Data Analytics to Take a Localized Approach to the Global Waste Problem" and "Making Cities, Infrastructures & Construction Sites Smarter with Time Series Data".
Semantic Web for E-Government
24 October - online
This online event will focus on a review of the semantic web and its importance in achieving interoperability and integration between the different organisational levels of public administrations. Two current e-government and open data initiatives will be presented:
- The European Data Portal, a platform for integrating and assessing Europe's Linked Open Government Data. It will address the multiple applications of semantic web standards in the European Data Portal, such as DCAT, SKOS, SHACL and DQV. Special attention will also be given to the measurement and publication of quality information.
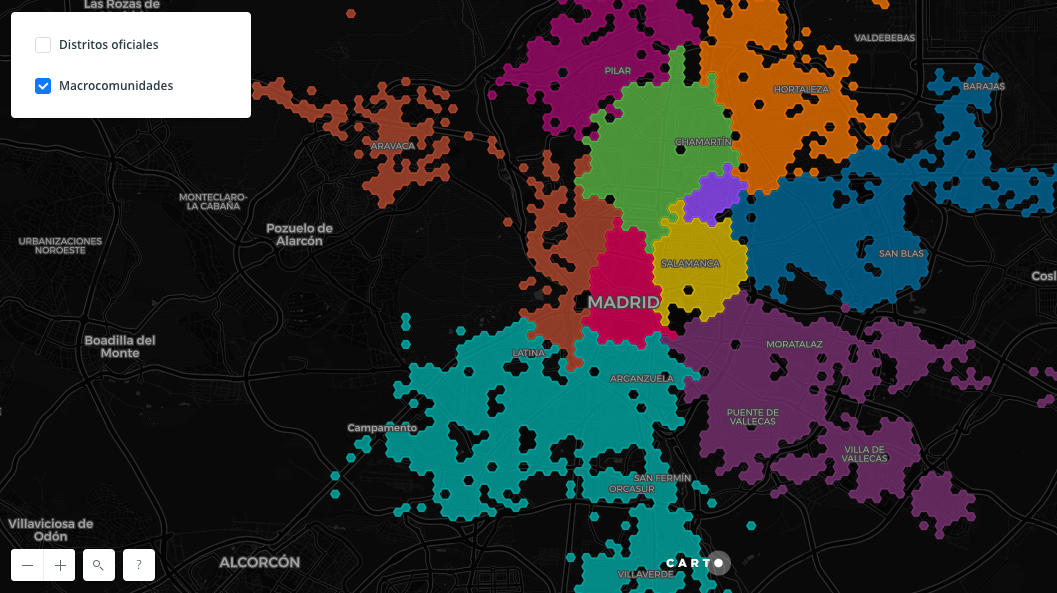
- Ciudades Abiertas: good practices for data harmonisation with local public administrations. It will be explained how a set of vocabularies is being developed to support a homogeneous provision of open data in the framework of Ciudades Abiertas, a collaborative project with four Spanish cities (Zaragoza, A Coruña, Madrid and Santiago de Compostela).
Smart City Expo World Congress
16 to 18 November 2021 – Barcelona
For several years now, Smart City Expo World Congress (SCEWC) has become a benchmark event that combines technological innovation with the field of Smart Cities. It brings together experts, companies and entrepreneurs with the aim of creating synergies and promoting new projects.
In 2021, the congress celebrates its tenth anniversary and its organisers will once again opt to hold the event in person, combined with a digital platform that will offer a multitude of opportunities to its attendees.
This event is usually the framework chosen by Open Data Barcelona to showcase the finalists of its World Data Viz Challenge, although the 2021 edition has not yet been announced.
EU Open Data Days
23 to 25 November 2021 - Online
This year we will also attend the first edition of the EU Open Data Days, organised by the Publications Office of the European Union in collaboration with the Aporta Initiative. The event will be virtual and will be divided into two activities:
- EU Dataviz 2021 (23-24 November). A programme of conferences focusing on open data and visualisations. They are currently defining the agenda which we will share with you soon.
- EU Datathon 2021 (25 November). In the months leading up to this event, a competition will be held to encourage the creation of products based on open data, such as mobile or web applications, that offer a response to different challenges related to EU priorities. The deadline for submissions is 11 June. The final will be held on 25 November as part of the Open Days.
This is just a selection of some of the major technology events coming up - do you know of any more you would like to highlight? Then don't hesitate to write us a comment or send us your proposal by email to contacto@datos.gob.es.
Making a city "smart" is not easy. According to the report Smart cities: understanding the challenges and opportunities, the budget constraints and the lack of infrastructure are the two main barriers for populations wanting to implement Smart cities initiatives. In this context, interoperability and collaborative platforms that allow the sharing of resources are key to success.
It was with this idea that the Ciudades Abiertas (Open Cities) project emerged 3 years ago, an open, collaborative and interoperable government platform, which was a beneficiary of the II Call for Smart Cities.
Collaboration between municipalities based on 4 lines of action
The Ciudades Abiertas project is led by Red.es and four city councils: A Coruña, Madrid, Santiago de Compostela and Zaragoza. Together, these city councils are developing various initiatives that can be reused by other bodies.
Recently, Ciudades Abiertas has updated its website, incorporating a new design, a highlights section with the latest news of the project and additional functionalities such as execution indicators.
The actions have been developed around 4 pillars:
- Open data: Open data is the most critical requirement of Smart Cities, as the above-mentioned study rightly pointed out. In this sense, the Open Cities project provides the technical and conceptual means necessary for the "management of unique shared data, open by default, georeferenced and semantically annotated by the city". Work is currently underway on the publication of a generic data REST API - or the development of a SPARQL access point to perform complex queries on several datasets at once, among other actions.
- Vocabulariums: The platform offers a catalogue of common and open vocabularies and data structures on Github for use by participating municipalities or any other entity. You can already access the vocabularies on the Municipal Agenda, Population Register or Public Bicycle, the last one to be incorporated in April of this year. They are currently working on other vocabularies such as Traffic or Budget and Budgetary Execution. Within this framework, a couple of videos have also been created to inform about what the vocabularies are and how they are generated and to raise awareness about the advantages of their use, in a simple and didactic way.
- Participation: The project seeks to promote citizen participation in several of the legislative, implementation and control activities carried out by the municipalities, in areas such as participatory budgets or day-to-day management. To this end, a methodology has been developed and two catalogues are provided, one of participatory processes and the other of instruments for participation. A list has also been included with specific examples of participatory processes that can be taken as a reference when setting up an initiative of this type.
- Transparency: Accountability is also a fundamental area of Smart Cities, so mechanisms are needed to ensure that all activities carried out by the council are provided with full transparency. One way to provide this information is through simple visualizations, easy to understand by citizens without technical knowledge. The project explores different ways to facilitate these visualisations. Two interesting reports have been prepared: Report with the Analysis of External Visualisation Systems and the Report with the Analysis of Visualisation Extensions for CKAN.
Next steps
The Open Cities project is still in full development. Among the activities to be developed in the coming months is the definition of new vocabularies until completing those recommended by the UNE 178301:2015 standard, or the creation of a general scorecard that allows comparisons of all the transparency indicators between cities, thanks to the homogenization of the data and its availability in reusable formats. They are also working, through collaborative workshops with citizens, on the design of visualizations that allow to offer information on transparency in an interactive way and with a simple language.
All these actions will facilitate the creation of new Smart Cities projects not only in these cities but in various territories throughout the country.
People, governments, economy, infrastructure, environment ... all these elements come together in our cities and they have to make the most of the constant flow of data on their streets to be more efficient. Analysis of the efficiency of services, monitoring of investment, improvement of public transport, participation and collaboration with citizens, reduction of waste or prevention of natural disasters are just some of the multiple examples of innovation in cities driven by data that how local governments are getting better services and improving the quality of life of their citizens thanks to the openness and better exploitation of their data.
From finding a parking space to discover new leisure places or simply move around the city. The applications that facilitate us day by day are already part of the usual urban landscape. At the same time, the data is also transforming the cities little by little and offers us an alternative vision of them through the definition of new virtual neighborhoods based on the footprint we are leaving with our actions and our data.
Hyperconnected cities, driven by data, managed by artificial intelligence and inhabited by a greater number of robots than humans will no longer be exclusive to science fiction movies and series, but real projects in the middle of the desert with already defined plans that have been launched in search of diversification and with the aim of transforming and renewing economies that are too dependent on the old oil ironically thanks to the supposed new oil of the data. Returning for a moment to the present, we also find examples of how this transformation through data is real and is happening in such tangible cases as the prevention of crimes and the reduction of violence in the favelas of Rio de Janeiro.
But not all expectations are so optimistic, since the transformative vision that some technology companies have for our neighborhoods also generates serious doubts, not only about how our most personal data will be managed and who will actually be the othe that have access and control over them, but also on the supposed transforming power of the data itself.
Right now the only thing that seems to be totally clear is that the role of data in the transformation of cities and citizens of the immediate future will be essential and we must find our own way halfway between the most optimistic and the most pessimistic visions to define what we understand as the new paradigm of Smart Cities, but always with a focus on the human element and not only on purely technological aspects and with participation and co-creation as key elements.
The city councils of Barcelona and the Japanese city of Kobe have launched a new edition of the World Data Viz Challenge 2019 Barcelona-Kobe, a data analysis and visualization contest. This contest was born last year, to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the twinning agreement of both cities. The large number of participants and the quality of the works presented, which can be consulted here, have led the organizers to promote this new call.
What does it consist of?
The contest is held in parallel in the cities of Barcelona and Kobe. In both cities, participants will have to analyze data and generate visualizations in order to improve specific aspects of the city. In the case of Barcelona, participants will have to use at least one data set from the Open Data BCN portal. Visualizations can be presented in the form of infographics, charts, interactive maps, etc.
Although visualizations of any theme related to the city are accepted, this year works related to the climatic emergency will receive special attention. In this way, the World Data Viz Challenge 2019 Barcelona-Kobe aligns with the Climate Plan, which integrates all the lines of action that the Barcelona City Council carries out in relation to this matter.
Who can participate?
Anyone who has the skills and abilities to work with open data, analyse and visualize them.
Participants can submit their projects individually or in teams, which should be made up of a maximum of three people.
How can you participate?
The deadline for submitting the projects ends October 31, 2019. Candidates must be submitted through this participation form.
How are the winners selected?
A jury formed by professionals specialized in data analysis and information technologies will review the works presented and will elect 6 finalists, whose name will be known on November 11, 2019. In parallel, another 6 finalists will also be selected in the city of Kobe.
All of them, among other benefits, will be awarded with a 3-DAY CONGRESS PAS ticket in addition to being able to present their work on November 19 in the framework of the Smart City Expo World Congress that will be held in Barcelona between 19 and 21.
For more information, you can check the participation conditions here.