The future new version of the Technical Standard for Interoperability of Public Sector Information Resources (NTI-RISP) incorporates DCAT-AP-ES as a reference model for the description of data sets and services. This is a key step towards greater interoperability, quality and alignment with European data standards.
This guide aims to help you migrate to this new model. It is aimed at technical managers and managers of public data catalogs who, without advanced experience in semantics or metadata models, need to update their RDF catalog to ensure its compliance with DCAT-AP-ES. In addition, the guidelines in the document are also applicable for migration from other RDF-based metadata models, such as local profiles, DCAT, DCAT-AP or sectoral adaptations, as the fundamental principles and verifications are common.
Why migrate to DCAT-AP-ES?
Since 2013, the Technical Standard for the Interoperability of Public Sector Information Resources has been the regulatory framework in Spain for the management and openness of public data. In line with the European and Spanish objectives of promoting the data economy, the standard has been updated in order to promote the large-scale exchange of information in distributed and federated environments.
This update, which at the time of publication of the guide is in the administrative process, incorporates a new metadata model aligned with the most recent European standards: DCAT-AP-ES. These standards facilitate the homogeneous description of the reusable data sets and information resources made available to the public. DCAT-AP-ES adopts the guidelines of the European metadata exchange scheme DCAT-AP (Data Catalog Vocabulary – Aplication Profile), thus promoting interoperability between national and European catalogues.
The advantages of adopting DCAT-AP-ES can be summarised as follows:
- Semantic and technical interoperability: ensures that different catalogs can understand each other automatically.
- Regulatory alignment: it responds to the new requirements provided for in the NTI-RISP and aligns the catalogue with Directive (EU) 2019/1024 on open data and the re-use of public sector information and Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/138 establishing a list of specific High Value Datasets or HVD), facilitating the publication of HVDs and associated data services.
- Improved ability to find resources: Makes it easier to find, locate, and reuse datasets using standardized, comprehensive metadata.
- Reduction of incidents in the federation: minimizes errors and conflicts by integrating catalogs from different Administrations, guaranteeing consistency and quality in interoperability processes.
What has changed in DCAT-AP-ES?
DCAT-AP-ES expands and orders the previous model to make it more interoperable, more legally accurate and more useful for the maintenance and technical reuse of data catalogues.
The main changes are:
- In the catalog: It is now possible to link catalogs to each other, record who created them, add a supplementary statement of rights to the license, or describe each entry using records.
- In datasets: New properties are added to comply with regulations on high-value sets, support communication, document provenance and relationships between resources, manage versions, and describe spatial/temporal resolution or website. Likewise, the responsibility of the license is redefined, moving its declaration to the most appropriate level.
- For distributions: Expanded options to indicate planned availability, legislation, usage policy, integrity, packaged formats, direct download URL, own license, and lifecycle status.
A practical and gradual approach
Many catalogs already meet the requirements set out in the 2013 version of NTI-RISP. In these cases, the migration to DCAT-AP-ES requires a reduced adjustment, although the guide also contemplates more complex scenarios, following a progressive and adaptable approach.
The document distinguishes between the minimum compliance required and some extensions that improve quality and interoperability.
It is recommended to follow an iterative strategy: starting from the minimum core to ensure operational continuity and, subsequently, planning the phased incorporation of additional elements, such as data services, contact, applicable legislation, categorization of HVDs and contextual metadata. This approach reduces risks, distributes the effort of adaptation, and favors an orderly transition.
Once the first adjustments have been made, the catalogue can be federated with both the National Catalogue, hosted in datos.gob.es, and the Official European Data Catalogue, progressively increasing the quality and interoperability of the metadata.
The guide is a technical support material that facilitates a basic transition, in accordance with the minimum interoperability requirements. In addition, it complements other reference resources, such as the DCAT-AP-ES Application Profile Model and Implementation Technical Guide, the implementation examples (Migration from NIT-RISP to DCAT-AP-ES and Migration from NTI-RISP to DCAT-AP-ES HHD), and the complementary conventions to the DCAT-AP-ES model that define additional rules to address practical needs.
Context and need for an update
Data is a key resource in the digital transformation of public administrations. Ensuring its access, interoperability and reuse is fundamental to improve transparency, foster innovation and enable the development of efficient public services centered on citizens.
In this context, the Technical Standard for Interoperability for the Reuse of information Resources (NTI-RISP) is the regulatory framework in Spain for the management and opening of public data since 2013. The standard sets common conditions on selection, identification, description, format, terms of use and provision of documents and information resources produced or held by the public sector, relating to numerous areas of interest such as social, economic, legal, tourism, business, education information, etc., fully complying with the provisions of Law 37/2007, of November 16.
In recent months, the text has been undergoing modernization in line with the European and Spanish objective of boosting the data economy, promoting its large-scale exchange within distributed and federated environments, guaranteeing adequate cybersecurity conditions and respecting European principles and values.
The new standard, currently in the processing stage, refers to a new metadata model aligned with the latest versions of European standards, which facilitate the description of datasets and reusable information resources made publicly available.
This new metadata model, called DCAT-AP-ES, adopts the guidelines of the European metadata exchange schema DCAT-AP (Data Catalog Vocabulary – Application Profile) with some additional restrictions and adjustments. DCAT-AP-ES is aligned with the European standards DCAT-AP 2.1.1 and the extension DCAT-AP-HVD 2.2.0, which incorporates the requirements for High-Value Datasets (HVD) defined by the European Commission.
What is DCAT-AP and how is it applied in Spain?
DCAT-AP is an application profile based on the DCAT vocabulary from the W3C, designed to improve the interoperability of public sector open data catalogues in Europe. Its goal is to provide a common metadata model that facilitates the exchange, aggregation and federation of catalogues from different countries and organizations (interoperability).
DCAT-AP-ES, as the Spanish application profile of DCAT-AP, is designed to adapt to the particulars of the national context, ensuring efficient management of open data at the national, regional and local levels.
DCAT-AP-ES is established as the standard to be considered in the new version of the NTI-RISP, which in turn is framed within the National Interoperability Framework (ENI), regulated by Royal Decree 4/2010, which sets the conditions for the reuse of public sector information in Spain.
Main news in DCAT-AP-ES
The new version of DCAT-AP-ES introduces significant improvements that facilitate interoperability and data management in the digital ecosystem. Among others:
Alignment with DCAT-AP
- Greater compatibility with European open data catalogues by aligning NTI-RISP with the EU standard DCAT-AP.
- Inclusion of advanced properties to improve the description of datasets and data services, to ensure the possibilities indicated below.
Incorporation of metadata for the description of High-Value Datasets (HVD)
- Facilitates compliance with European regulation on high-value data.
- Enables detailed description of data in key sectors such as geospatial, meteorology, earth observation and environment, statistics, mobility and business.
Improvements in the description of data services
- Inclusion of specific metadata to describe APIs and data access services.
- Possibility to express a dataset in different contexts (e.g. geospatial, with a map server, or statistical, with a data API).
Support for provenance and data quality
- Incorporation of new properties to manage lifecycle, versioning and origin.
- Implementation of validation and quality control mechanisms using SHACL, ensuring consistency and structure of metadata in catalogues.
Use of controlled vocabularies and best practices
- Adaptation of standardized vocabularies for licenses, data formats, languages and themes.
- Greater clarity in data classification to facilitate discovery.
Data governance and improved agent management
- Specification of agent roles (creator, publisher) and contact points.
- Enhanced metadata to represent resource provenance.
Validation of conformity and metadata quality
- Guides to help validate metadata that comply with DCAT-AP-ES.
- Validation of DCAT-AP-ES graphs against SHACL templates.
Key benefits of the update
The adoption of DCAT-AP-ES represents a qualitative leap in the management and reuse of open data in Spain. Among its benefits are:
✅ Facilitates the federation of catalogues and the discovery of data.
✅ Improves interoperability with the European open data ecosystem.
✅ Complies with European open data regulations.
✅ Increases metadata quality through validation mechanisms.
✅ Ensures that data are FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable).
Implementation and next steps
When will it come into force?
The new application profile DCAT-AP-ES will be progressively implemented in Spain's open data catalogues. Its application will be mandatory once the modification text of the standard comes into force which, as mentioned earlier, is currently undergoing administrative processing but is already compatible with the datos.gob.es data federator.
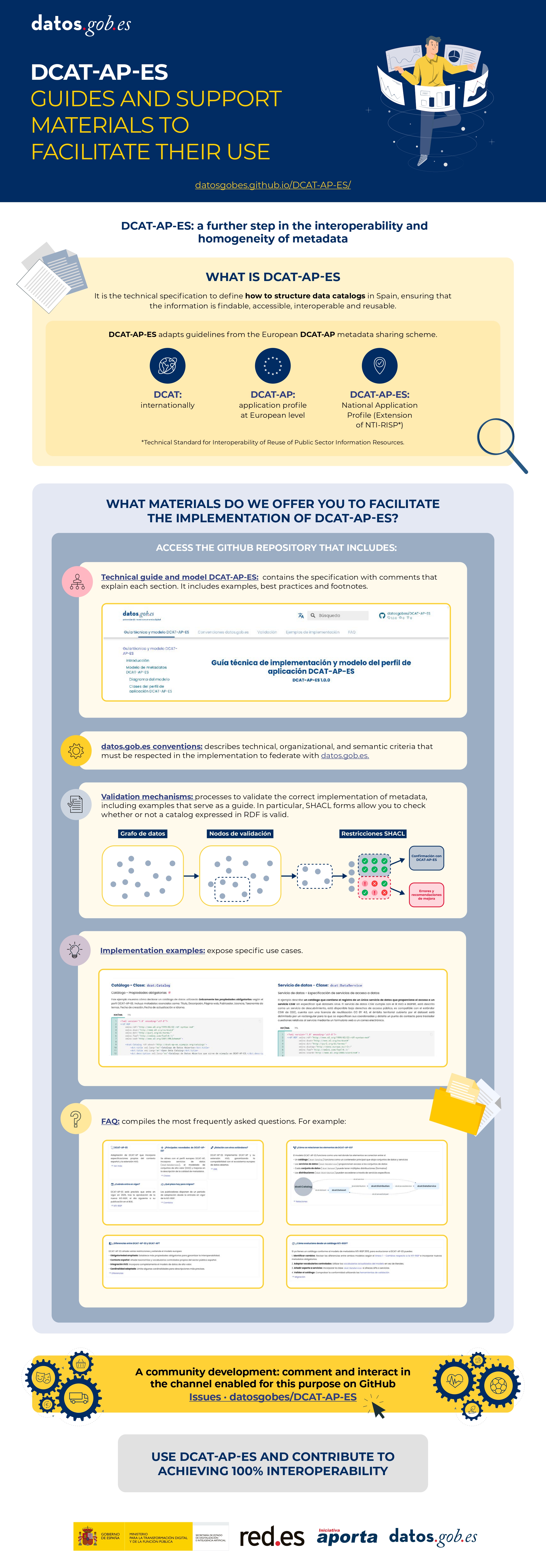
Are there supporting materials and resources for implementing DCAT-AP-ES?
The management team of the datos.gob.es platform has developed the DCAT-AP-ES Technical guide and model, available in the datos.gob.es repository.
This repository will be enriched as new needs of users applying the standard are identified. Likewise, help guides and educational resources will be developed to facilitate its adoption by publishing organizations. All the news and resources produced in the context of the application profile will be announced and referenced punctually on datos.gob.es.
Where to find more information?
The updated documentation, guides and resources will be accessible on datos.gob.es and in the associated code repository. At present the following are available:
- DCAT-AP-ES Technical guide and model
- DCAT-AP-ES Conventions
- DCAT-AP-ES Implementation examples
- DCAT-AP-ES Frequently Asked Questions
- DCAT-AP-ES Metadata validation
- DCAT-AP explanatory video: Spanish / English
- datos.gob.es
Learn more in this video:
And this infographic (click to access the interactive and accessible version):
One of the main challenges that arise when addressing an Open Data initiative is to define the information architecture and facilitate interoperability between data catalogs published by different portals on the Web. In order to solve this challenge, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) published the Data Catalog Vocabulary (DCAT), an RDF vocabulary to describe data catalogs based on 3 key concepts: catalog, dataset and distribution.

Based on this vocabulary, and within the JoinUP project, a collaborative platform created by the European Commission, an international group of experts developed the DCAT Application profile for data portals in Europe (DCAT-AP): a specification that describes restrictions (such as properties range) on the DCAT model. The objective is to facilitate homogenization and cross-searching, using metadata, between different European data portals generated by public sector and placed at citizens disposal for reuse.
The report DCAT-AP and its extensions: context and evolution, developed within the Aporta Initiative framework, arose to contextualize and delve into DCAT-AP, and DCAT vocabulary. The report includes a description of both publications, as well as a definition of the agencies and institutions involved in its definition.
DCAT-AP extensions and modifications
Based on DCAT-AP, sector extensions have been developed, some of the most relevant in specific areas of application are described in this report: DCAT-AP HVD, DCAT-AP extension for the description of high-value data, GeoDCAT-AP, focused on the exchange of descriptions of geospatial datasets and services, StatDCAT-AP, an extension of DCAT-AP for the exchange of descriptions of statistical datasets and services, MLDCAT-AP extending DCAT-AP in the field of machine learning, and BRegDCAT-AP for the description of fundamental aspects of public administrative records.
Since its appearance and throughout these years, practically all the Member States of the European Union have extended the DCAT-AP application profile to meet their needs. Special emphasis is placed on Spain, where there is the peculiarity that the "extension" - the Norma Técnica de Interoperabilidad de Reutilización de recursos de información (NTI-RISP) - preceded the DCAT-AP specification itself, which at the time of writing has evolved into the DCAT-AP-ES reference extension.. (NTI-RISP) establishes the common framework for opening and using documents and information resources produced or held by public administrations. This technical standard aims to ensure the persistence of information and the use of formats, and to promote appropriate terms and conditions of use. The NTI-RISP standard predates the first versions of DCAT and DCAT-AP, which has resulted in some differences.
Finally, some DCAT-AP extensions implemented by the different Member States are listed for reference.
The National Interoperability Scheme establishes a set of technical standards for the interoperability of public sector information, which must be complied by public administrations in Spain. As part of this scheme, there is the Technical Standard for the Interoperability of the Re-use of Public Sector Information Resources, which includes a series of conditions on the selection, identification, description, format, use conditions and availability of public data.
In order to facilitate the implementation of this technical standard, an implementation guide is available to users, which explains in detail the guidelines for public administrations to develop their own policies for the open data re-use and resources within their areas of responsibility.
A new version of this document has been recently published, which includes new materials that complement and optimize the advice provided by this guide. Thus, two additional chapters are included to illustrate from several good practices different sections and aspects of the National Interoperability Standard:
Good practices of Share-PSI
Share-PSI is a thematic network offering advice on implementation of the European Directive on the Public Sector Information. This group comprises a great number of public bodies, academic institutions, independent entities and experts who, through different workshops, review and offer good practices in this area.
In this new version of the implementation guide, the Annex III includes twelve examples of such practices collected by the Share-PSI in relation to the national document and the European Directive 2013/37 / EU on the re-use of information, such as elements to establish an open data ecosystem, standards for geospatial data or characteristics of a dataset, among others.
Good practices of web data by W3C
In addition, a table is also shown in the fourth Annex where the best data practices documented by the W3C, applicable and related to the sections of the guide, are collected:
- The persistent use of URIs as identifiers of datasets, their associated versions and series, as well as data;
- The reuse of standardized vocabularies for metadata;
- Real-time and up-to-date access;
- The constant enrichment of information;
- The possibility of bulk download and the use of standard and machine readable formats.
This latest update of the implementation guide provides an opportunity to learn and analyze successful practices in other countries, serving as a reference for the national sector to improve both the open data policies and initiatives in Spain.