After New Year, it seems that Christmas comes to an end, but we still have a date marked on our agenda: Three Kings Day. Adults and children hope to get up on January 6 and discover what the Three Wise Men from the East have brought us. And what better gift than a book that can help us expand our knowledge and skills.
For those who have not yet finished their Christmas purchases and are rushing at the last minute, in datos.gob.es we have collected a selection of books on data and disruptive technologies that can be a good option to gift to your loved ones. We have all levels books: basic, to encourage your younger relatives to study a career focused on data management and analysis (professions that will be highly demanded in the coming years) or advanced, for those professionals who want to improve their knowledge and gain a competitive advantage to boost their career in 2020.
Las bases de Big Data, by Rafael Caballero and Enrique Martín.
What is it about? Disclosure book that explains what Big Data is and how it works, including details and curiosities that allow the reader to better understand the big data world, its processing and the business involved. It also explains basic aspects of the Hadoop ecosystem or databases, both relational and non-relational.
Who is it for? It is an introductory and easy-to-read book. The book does not include a technical vision, but it is detailed and critical so that the reader wants to continue going deeper into the subject.
Storytelling with data. Data visualization for Business professionals, by Cole Nussbaumer Knaflic.
What is it about? A book to learn how to tell stories using data. Cole Nussbaumer tells us about the fundamentals of data visualization through real examples that help to understand the theory in a simple way. The book helps the user to reflect on the stories he/she wants to tell and how to tell them, teaching him to choose different types of graphics and tools according to the audience.
Who is it for? It is a simple and quick-to-read book, perfect for those who work with data, do not have a technical profile and want to improve the way they show the results.
Introduction to Data Science: Data Analysis and Prediction Algorithms with R, by Rafael A. Irizarry.
What is it about? Rafael A. Irizarry presents concepts and skills to solve the challenges of real-world data analysis. The book covers concepts from probability, statistical inference, linear regression, machine learning, R programming, data visualization, predictive algorithms building, file organization with UNIX / Linux shell, version control with Git and GitHub and preparation of reproducible documents.
Who is it for? To first-year data science students, so it is perfect to introduce this subject.
Learning Path: Understanding Tool Integration for Big Data Architecture, by O'Reilly Media
What is it about? The book explains how to integrate Hadoop components with the goal of implementing big data solutions for a variety of use cases, including clickstream analytics, time series problems, transferring data between Hadoop and relational databases, and applications in the finance sector.
Who is it for? Book aimed at professionals with technical knowledge related to the universe of data or advanced students.
Prediction Machines: The Simple Economics of Artificial Intelligence by Ajay Agrawal, Joshua Gans y Avi Goldfarb
What is it about? The book starts from a question: how should companies establish strategies, governments design policies and citizens plan their lives in a world marked by technology and Artificial Intelligence? 3 eminent economists try to clarify this issue by demystifying artificial intelligence and examining it through standard economic theory.
Who is it for? To all those who want to understand the reality of artificial intelligence, although it is especially aimed at entrepreneurs, business leaders or public policy makers.
The State of Open Data: Histories and Horizons, by Tim Davies, Stephen B. Walker y Mor Rubinstein.
What is it about? Book that reviews the lessons learned in the 10 years of the open data movement and looks to the future to make the reader reflect on how open data initiatives will respond to new privacy concerns, and the inclusion of artificial intelligence.
Who is it for? For those involved in the open data ecosystem, but also those who are curious about the evolution of the movement. The book is also available in free version here.
As in previous years, the list is just a selection that we have prepared based on recommendations from experts who collaborate with data.gob.es, but we know that there are many more interesting books on these topics. Therefore, we encourage you to share new recommendations in the comments.
The adoption of innovative technologies could bring great competitive advantages for companies, optimizing processes, improving the customer experience and even creating new products and services. Therefore, an increasing number of organizations demand professionals with knowledge in areas such as data analytics, business intelligence or Deep Learning, but where can we find qualified personnel who can lead and execute these initiatives?
According to a report elaboreted by the consulting firm B-Talent, 87% of surveyed companies think that there is a lack of qualified personnel to implement digital transformation in Spain. In the specific case of Big Data, we have already written about the lack of talent, highlighted in Generación de talento Big Data en España report: on 2015 the number of vacancies for Big Data professionals grew by 93%, but there were only seven candidates, on average, per vacancy. In addition, the situation is expected to get worse. In the next two or three years (2020-2021), Big Data analyst will be the most difficult position to fill in Spain.
The fact that there is no personnel prepared to face the new professional challenges is due, among other reasons, to the scarcity of educational offer. As COTEC indicated in the report, education is the main pillar to generate talent. Therefore, in order to avoid steps that could inflame the situation, it is necessary to adapt academic programs, so the new generations would have the required training in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics, known as STEM.
Universities and schools are trying to quickly update their offer to face this situation. In our country, training related to new technologies is beginning to emerge, such as the Degree in Science and Data Engineering of Carlos III University of Madrid or the Master in Artificial Intelligence at the University of Barcelona. But the lack of specialized teachers, as well as documentation related to these subjects, hinders the creation of new courses.
MOOC, the alternative to traditional training
In this context, MOOC courses (Massive Online Open Courses) are positioned as a good academic alternative for those professionals who want to acquire or improve their skills. A MOOC is an online course that allow free and unlimited access to content.
Usually accessible from mobile devices, tablets and computers, MOOCs allow a personalized and flexible training through a mix of different specialized courses. The wide offer includes different duration courses, both for beginners and experts who want to delve a little deeper into their abilities.
Two types of platforms can be differentiated: those belonging to academic centers, with their own digital training offer, such as HarvardX, and general-purpose platforms, with agreements with different university centers, foundations and companies, such as edX, Coursera or Udacity. The objective of these platforms is to democratize access to quality training for free or at competitive prices.
The main characteristics of each of these platforms are described below:
- Coursera
Founded in 2011 by Stanford academics, Coursera offers more than 2,000 general programs, more than 180 specializations and 4 online degrees, all of them focused on business, computer science and data science, through nearly 150 partner universities. Those courses include video lectures previously recorded with subtitles in more than 30 languages, real business cases projects, self-assessments and community discussion forums. A strength point is the academic and technical support by dedicated community of course mentors and the knowledgeable learner support team.
- EDX
EDX was created in 2012, thanks to Harvard University and MIT collaboration, as a non-profit organization based on open standards. EDX offers almost 2,000 courses in IT, languages, engineering, psychology, writing, electronics, biology or marketing, with specialties in Data Science or Deep Learning. They highlights MicroMasters programs, offered by prestigious universities and recognized by relevant companies such as IBM or Volvo.
- Udacity
Founded in 2012 by professionals previously linked to universities such as Stanford and companies like Google, it has eight million students worldwide. Udacity offers value training through free courses and its Nanodegree program: small masters oriented to avant-garde skills that have been designed together with leading companies in global innovation, such as Google, IBM, Facebook or Amazon. Udacity even has a Nanodegree Plus program, which guarantees a job (if a student does not get a job after six months after, the registration fee is refunded). Among its courses, there is a Data Science, Analytics or Virtual Reality Offer.
These are just three examples of the possibilities offered by this type of training platform, but there are more - some examples are included in the aforementioned report. Among other factors such as flexibility, its success is due to the fact that they can provide deeper specialization, difficult to find nowadays in other scenarios.
Even when universities and study centers expand their offer in data analysis and innovation technology, this kind of courses will not disappear: they just will be part of those new plans or an alternative to complete knowledge through micro-courses, accessible from any corner of the planet.
In recent years we have been discovering new field to apply data science, as the solution of old problems that we can now solve thanks to the new techniques and methodologies that are available. Data science is being configured as a key capability for digital transformation and, therefore, companies from all industries and sectors are investing in the creation of data science teams.
Perhaps, this is the main reason for the current explosion of demand for data science jobs. We will use two data to illustrate this growth: in the period 2012-2017 the demand of these professionals has multiplied up to ten in the USA, and some studies, like this one of IBM, predict a growth of 28% until 2020. Spain is not an exception to this global trend: Big Data market grows 30% each year and, already in 2015, the demand of Big Data talent grew by 93%, according to a Cotec Foundation report.
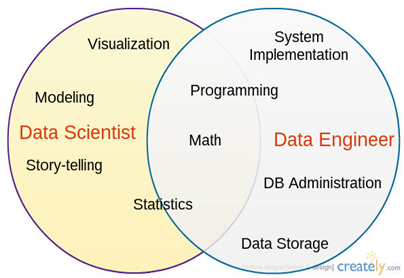
The most common roles in the configuration of a data science team are data scientist, data engineer and business analyst, all working at the intersection of several disciplines: mathematics, computer science and, of course, knowledge of the business problems.
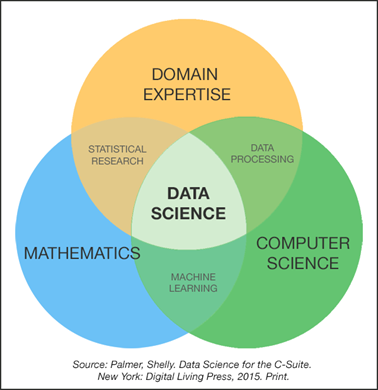
- The data scientist role is usually responsible for extracting knowledge and designing products based on data from exploration, creation and experimentation with models and visualizations. For all this, he usually use a combination of statistical, mathematical and programming techniques.
- The data engineer role, on the other hand, usually has the mission of designing and implementing infrastructures and software capable of managing the needs of data projects at the appropriate scale.
- The business analyst role brings knowledge related to the business problem to the team: the correct understanding of the results derived from the analysis and modeling of the data, as well as the application of the data-based products generated in the projects.
Normally we find professionals that work as engineer or data scientist with the most diverse training: either related to the sciences, such as mathematics, physics or statistics, or related to different engineering branches such as computer science, telecommunications, aeronautics or industrial engineer. Usually, they are people who have decided to lead their career to data science learning different masters or postgraduate offered by universities, MOOCs, or non-regulated training courses offered by companies aimed at their own staff or to attract talent.
Universities are also adapting to this market demand in order to provide more specific training and, in addition to the postgraduate programs, double degrees are becoming common, combining two of these disciplines such as computer science and statistics. We can even find course oriented to data science such as the bachelor´s degree in Science and Data Engineering, the bachelor´s degree in Mathematical Engineering in Data Science or the Degree in Data Science and Engineering.
The business analyst role, also called analytics translator or data translator is much more unique, because he/she must combine business knowledge with sufficient technical competence to understand data science problems and approaches and, thus, be an effective interface between data science team and business expectations.
The importance and uniqueness of this role means that companies are opting for large-scale internal training programs, so that professionals with a good knowledge of operations and a certain technical competence can lead their professional careers in this direction.
However, it is not an easy transition due to the traditional separation between science or engineering training, with very few competences related to business, and business disciplines, without practically technical competence. In this sense, there is a wide margin for improvement, so that university training goes into erasing these separation lines, in order to get people to acquire more complete training incorporating economics, marketing or programming in disciplines traditionally unconnected.
As Steve Jobs said and demonstrated, best ideas emerge from the intersection of technology and the humanities.
Content prepared by Jose Luis Marín, Head of Corporate Technology Startegy en MADISON MK and Euroalert CEO.
Contents and points of view expressed in this publication are the exclusive responsibility of its author.
New technologies are changing the world we live in. The society changes, the economy changes, and with that, the jobs change. The implementation of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Big Data or Internet of Things are driving the demand for new professional profiles that we did not even conceive a decade ago. In addition, the possibilities of automating tasks currently developed by humans, executing task more quickly and efficiently, leads some professionals to consider that their job could be in danger. Responding to this situation is one of the big challenges we have to overcome.
According to the report It's learning. Just not as we know. How to accelerate skills acquisition in the age of intelligent technologies, carried out by G20 Young Entrepreneurs' Alliance and Accenture, if skill-building doesn’t catch up with the rate of technological progress, the G20 economies could lose up to US$11.5 trillion in cumulative GDP growth in the next ten years.
But this change is not simple. It is not correct just to assume that intelligent technologies will eliminate some jobs and create new ones. In fact, the biggest effect will be the evolution of traditional roles. According to the study, 90% of each worker time will be affected by new technologies. Taking the average of all sectors, 38% of worker time is currently dedicated to tasks that will be automated, while 51% are activities that can be improved (or augmented), using new technologies that help to increase our skills. In short, the solution is not just to train more engineers or data analysts, since even these profiles will have to evolve to adapt to a future that is closer than it seems.
To know how this change will affect the different professional profiles, the report analyse the tasks and skills necessary to carry out the current work positions, determining how they will evolve in the future. To facilitate the analysis, the professions have been grouped around 10 different roles. The following table shows the result of the study:
| Role cluster | Typical activities | Illustrative occupations | Illustrative task evolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Management & Leadership | Supervises and takes decisions | Corporate managers and education administrators | Marketing managers handle data and take decisions based on social media and web metrics |
| Empathy & Support | Provides expert support and guidance | Psychiatrists and nurses | Nurses can focus on more patient care rather than administration and form filling |
| Science & Engineering | Conducts deep, technical analyzes | Chemical engineers and computer programmers | Researchers focus on sharing, explaining and applying their work, rather than being trapped in labs |
| Process & Analysis | Processes and analyzes information | Auditors and clerks | Accountants can ensure quality control rather than crunch data |
| Analytical subject-Matter Expertise | Examines and applies experience of complex systems | Air traffic controllers and forensic science technicians | Information security analysts can widen and deepen searches, supported by AI-powered simulations |
| Relational subject-matter Expertise | Applies expertise in environments that demand human interaction | Medical team workers and interpreters | Ambulance dispatchers can focus on accurate assessment and support, rather than logistical details |
| Technical Equipment maintenance | Installs and maintains equipment and machinery | Mechanics and maintenance workers | Machinery mechanics work with data to predict failure and perform preventative repairs |
| Machine Operation & Manoeuvring | Operates machinery and drives vehicles | Truck drivers and crane operators | Tractor operators can ensure data-guided, accurate and tailored treatment of crops, whilst “driving”. |
| Physical Manual Labor | Performs strenuous physical tasks in specific environments | Construction and landscaping workers | Construction workers reduce re-work as technology predicts the location and nature of physical obstacles |
| Physical Services | Performs services that demand physical activity | Hairdressers and cooks | Transport attendants can focus on customer needs and service rather than technical tasks |
The results show how some skills, such as administrative management, will decline in importance. However, for almost every single role described in the previous table, a combination of complex reasoning, creativity, socio-emotional intelligence and sensory perception skills will be necessary.
The problem is that these types of skills are acquired with experience. The current education and learning systems, both regulated and corporate, are not designed to address this revolution, so it will be also necessary their evolution. To facilitate this transition, the report provides a series of recommendations:
- Speed up experiential learning: Teaching has traditionally been based on a passive model, consisting of absorbing knowledge by listening or reading. However, experiential learning becomes more and more powerful, that is, through the practical application of knowledge. This would be the case of airplane pilots, who learn through flight simulation programs. New technologies, such as augmented reality or artificial intelligence, help to make these solutions based on experience more personalized and accessible, covering a greater number of sectors and job positions.
- Shift focus from institutions to individuals: Inside a work team it is common to found workers with different capacities and abilities, in such a way that they complement each other, but, as we have seen, it is also necessary to put more emphasis on expanding the variety of skills of each individual worker, including new skills such as creativity and socio-emotional intelligence. The current system does not drive the learning of these subjects, so it is necessary to design metrics and incentives that encourage the mix of skills in each person.
- Empower vulnerable learners: Learning must be accessible to all employees, in order to close the current skills gap. According to the study, in general, the most vulnerable workers to technological change are the least qualified, because their jobs tend to be easier to automate. However, they also tend to receive the least training from the company, something that must change. Other groups to pay attention to are the older workers and those from small companies, with fewer resources. An increasing number of companies are using modular and free MOOC courses to facilitate the equal acquisition of skills among the entire workforce. In addition, some governments, such as France or Singapore, are providing training aids.
In short, we are in a moment of change. It is necessary to stop and reflect on how our work environment will change in order to adapt ourselves to it, acquiring new skills that provide us with competitive advantages in our professional future.
By 2020, the amount of data stored in IT systems will be doubled compared to 2018. Given this scenario, it seems logical that the demand for professionals with analytical and data management capabilities is growing, something we have already spoken about on numerous occasions.
One way to boost the learning of these skills is through open data and its use in the classroom as another educational resource. The development of collaborative projects where students have to search and filter information, analyse data or generate visualizations have a place in almost all subjects. With this type of project, students can acquire a great diversity of capacities: from the use of technological tools and the capacity for analysis and argumentation, to the improvement of so-called soft skills such as teamwork - also fundamental for professional development -.
The first step: train teachers
One of the fundamental pillars for open data to be integrated into classrooms is the previous training of teachers. In this sense, programs such as Use (Open Research) Data in Teaching project (UDIT) try to help higher education professors to be able to use open research data in their classes. Among other activities, the website offers courses that show good practices and examples of learning activities based on the reuse of open data.
Along the same lines, the National Library of Spain and Red.es have created the BNEscolar educational platform with digital content prepared from the documentary collection of the Hispanic Digital Library. The website includes a search engine to facilitate the location of the desired resources, as well as workshops, videos, educational sequences and interactive challenges (such as an escape game). The contents of BNEscolar are aimed at pre-university students, with special focus on the latest levels of Primary and Secondary Education.
Contests and activities to boost the use of data in classrooms
In addition to these platforms, concrete activities, contests and challenges that seek to promote the use of open data among the youngest citizens are also increasingly common. Examples are the Reto BCN Dades Obertes or the Open Data Contest of Castilla y León, which included a special prize for students in each of the main categories, as well as a specific category for the creation of teaching resources that could be used in the classrooms. Another example is Escuelas Comciencia initiative, created by the Observatory of Scientific Communication and the Cyberimaginary research group, where students learn to carry out a research project using open data.
But we can also find such initiatives internationally. The programs developed by Technovation stand out here, aimed at identifying problems in student communities and solving them using disruptive technologies. An example is Technovation Girls, aimed at girls around the world. This program seeks to teach girls how to identify a problem and brainstorm ideas to solve it, and create an application to launch a business. Also noteworthy is the AI Family challenge contest, which brings learning to the family environment, another of the fundamental foundations of children's education. The AI Family Challenge invites families to learn about Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology and solve a problem using data tools and AI systems. The original approach of the contest, in which parents and children combine their abilities and learn together in a fun way, has driven the success: 7,500 people from 13 countries participated in the first edition. The deadline for submitting to the second edition will be open until February 2020.
The importance of government involvement
The results obtained in all the previously highlighted activities have been very positive, clearly showing the benefits of incorporating open data in classrooms: the improvement of technological and analytical capabilities, but also of critical thinking.
But if you want to go one step further, it would be advisable to incorporate open data directly into educational plans. This is what Switzerland has done through the Lehrplan21 plan, adopted to standardize education in the 21 German-speaking and multilingual cantons. The plan includes the learning of basic concepts related to data in the educational itinerary: structures, formats, management and analysis of databases, etc.
These types of measures are essential if we want to promote more active learning, where open data helps students to better understand their environment, in a reasoned way, to become the professionals that our future needs.
The presentation of the BNEscolar project took place on July 2. The event was attended by the Secretary of State for Education, Alejandro Tiana, the General Director of the National Library of Spain (BNE), Ana Santos, and the General Director of Red.es, David Cierco.
BNEscolar is a portal aimed at the educational community where you can find digital content created using the documentary collection of the Biblioteca Digital Hispánica. The project, developed by the BNE and Red.es, is framed in BNElab, a space that concentrate BNE's new digital strategy. This portal and all its resources aim to promote access and reuse of the library's digital resources, showing the Spanish-speaking educational community formulas and methodologies that allow creating new content for its teaching application.
Specifically, BNEscolar is aimed at teachers and pre-university students, with special focus on the last levels of Primary and Secondary Education. All of them will have at their disposal various contents and functionalities:
- Search engine. After a detailed analysis, the BNE has selected those contents of the Hispanic Digital Library that have a high potential to be used as learning resources, in accordance with the educational programs of the formal education. These contents have been enriched with metadata that facilitate their search. Through a search engine, users can filter the contents according to different parameters, such as the educational level or the subject they are most appropriate for. Other filters that are included are authors, languages or types of resources (texts, illustrations, audios, etc.).
- Didactic sequences. Teachers and students have at their disposal didactic sequences with different activities and challenges to resolve using BNE resources. All the contents are accompanied by methodological guides for its use in the classroom. The objective is to promote project-based learning, and the active and collaborative participation of students. For example, one of the didactic sequences is a role-playing game for a better knowledge of the Semana Trágica: Students will have to put themselves in the shoes of the people involved and recreate the events that took place in real time using Twitter or Instagram.
- Interactive challenges. One aspect that has been taken into account from the origin of the project is the incorporation of playful elements that invite to work with the BNE resources. Two applications have been created based on the reuse of its contents: a digital escape game, located at the San Petesburg Arts Academy, and a geolocalized question-answer game.
- Workshops and videos. Through different workshops, students will be able to deepen in a selection of contents in a practical way, using digital tools. In addition, a series of short videos have been included to review the contents in a fun and entertaining way.
- My BN Escolar. BNEscolar also includes a personal section for teachers where they can organize their resources and create collections. The BNE invites teachers to reuse the materials of the Library to develop their own contents or dynamic sequences
The portal has been valued, in a first pilot phase, by a set of educational centers. This collaboration has allowed to validate the contents so that they respond to the technical and curricular needs of the students and teachers. Now a second phase begins, in which a broad dissemination is planned through social networks in order to reach the entire educational community. The expansion of the BNEscolar contents is also underway. Developing BNEscolar has taken months of work. BNEscolar expands, develops and improves an initial proposal.
BNEscolar joins the list of projects developed by the BNE in favor of opening and reusing our cultural heritage, such as comunidad.bne.es or ChefBNE. On this occasion, the focus is on education and the informational competence of teachers and students, a key aspect to be critical, creative and autonomous citizens in the digital society.
Analytical skills, data management, or knowledge of business intelligence tools ... These are just some of the terms that we surely find repeated if we perform a quick search in the most popular job portals.
Data has become a fundamental element of our economy, and it is not surprising that companies increasingly demand more profiles with these capabilities. Specific profiles are searched (as data scientists), as well as multidisciplinary professionals that encompass different areas of knowledge. One of these areas is data. In addition, even if you are already a professional with knowledge in this area, data is a constantly evolving field, so updating your knowledge is necessary to be up-to-day of new trends and techniques.
A few months ago, datos.gob.es made a compilation of some degrees, masters and courses to acquire or improve data management and analysis capabilities. In the article, we talked about the shortage of talent in these areas. As we commented, the offer does not stop growing, reason why we have considered appropriate to make a new compilation:
- Carlos III University of Madrid has been one of the pioneers in training options for data analysis. The University offers two masters (Master in Big Data Analytics and Master in Statistics for Data Science) that are taught entirely in English, aimed at people with knowledge of Computer Science, statistics or mathematics who want to improve their knowledge. In addition, it also offers two degrees: Degree in Data Science and Engineering and Degree in Statistics and Business. While the fist one emphasizes new digital technology tools, including statistics, artificial intelligence or machine learning, the second one is more focused on the business sector and the training of professionals with quantitative skills, capable of transforming data into useful information for decision making in sectors such as finance, banking, insurance or business consulting.
- The Universitat Oberta de Catalunya also offers a Degree in Applied Data Science, with the aim of training experts in the capture, analysis and visualization of data. Students will acquire knowledge of programming, mathematics, statistics, and management, essential to creatively develop their activity as a data scientist. This center also offers a Master's Degree in Data Science, to train expert professionals in data analysis, whether in big data environments, word processing, analysis of social networks or data in geolocalized environments. Its offer of shorter courses also highlight: specialized in specific subjects such as Python Programming for Data Science or Fundamentals of Business Intelligence.
- The University of Deusto has a Big Data and Business Intelligence Program aimed at a heterogeneous audience: 50% of its students come from t business area and the remaining 50% are technical profiles. Its objective is to train professionals capable of completing complete data analysis cycles (extraction, management, processing (ETL) and visualization) to offer business intelligence services to organizations, companies and individuals.
- The University of Valencia has developed a Data Science Degree and a University Master in Data Science. Both courses cover from the exploratory analysis of data to techniques of advanced visualization or machine learning.
- In addition, business schools specializing in Big Data, Data Science and Artificial Intelligence technologies such as MBIT School are emerging. Its training offer is divided into Master Executive Programs, for people seeking a change through new knowledge, Expert Programs, to acquire knowledge in a specific area through their business application, and specific Programs designed to provide concrete knowledge in a reduced time and in a practical way. Some examples are the executive master in data science for professionals or the expert program in artificial intelligence for the company. The methodology that follows is the “learning by doing”: the students have theoretical-practical classes whit sets of real data to apply the different algorithms / concepts that are taught during the classes.
- Highlight also the training offer of organizations such as the Barcelona Open Data Initiative, the ODI node in Catalonia, which offers degrees in open data with internationally recognized certification. Through Open Data School Barcelona, 2 certificates are offered: Higher Certificate in Governance, oriented to the application of open data in public administration, and the Professional Degree in Data Journalism, aimed at journalists who want to learn how to transform data into information of public interest.
This is just a selection, but there are many more options. We encourage you to share in the comments other courses, masters or degrees related to data that you consider of interest.
The Instituto de Ingeniería del Conocimiento (Institute of Knowledge Engineering or IIC) is a pioneering R+D+i center on Artificial Intelligence, expert for more than 30 years in data analysis and Big Data technologies. The IIC core, experience and trajectory in these years revolves around data analysis and its constant research work. Its value is the development of custom analysis algorithms and techniques, making use of the existing storage and processing technologies, so that they develop Big Data solutions highly adapted to the problems of each client.
SIRIS Academic is a consulting and research company that designs and implements strategies and policy solutions in the field of higher education, research and innovation. They work with agents in charge of political decision-making, providing tools, processes and reflections that help to establish and address key issues for their mission.
SIRIS Academic is focused on organizations with public or social vocation. This perspective places success in the generation of added value for society, aligned with its values, culture and focus.
GIS4tech is a Spanish Spin-Off company founded in 2016, as a result of the research activity of the Cluster Territorial group and the Department of Urban Planning of the University of Granada. GIS4tech is dedicated to technical assistance, advice, training, research and development supported by Geographic Information Systems and related technologies. The team has more than 20 years of experience in territory studies, elaboration of cartographies and Geographic Information Systems.