
The data economy represents a huge business opportunity for companies of all sizes and sectors. According to European Commission estimates, the Data Economy will be worth €829 billion in 2025 for the 27 member states. But for the data economy to develop properly, structures are needed to facilitate the exchange of data and, with it, the development of business models based on its exploration and exploitation.
Data spaces fulfil this function by facilitating the development of an ecosystem where different actors share data in a voluntary and secure manner. To do so, they must follow common governance, organisational, regulatory and technical mechanisms.
One way to ensure that this is done properly is through reference models, such as the IDS-RAM (International Data Spaces Reference Architect Model), an initiative developed by the International Data Space Association and endorsed by the European Union.
What is the International Data Space Association?
IDSA (International Data Spaces Association) is a coalition currently comprised of 133 international, not-for-profit companies, which emerged in 2016 to work on the concept of data spaces and the principles that their design should follow in order to obtain value from data through sharing, based on secure, transparent and fair mechanisms for participants, which guarantee sovereignty and trust. These companies represent dozens of industry sectors and are based in 22 countries around the world.
IDSA is connected to different European initiatives, including BDVA, FIWARE and Plattform Industrie 4.0, participating in more than twenty European research projects, mainly in the Horizon 2020 programme.
IDSA's mission is to drive the global digital economy. To this end, among other things, it promotes an architectural reference model called IDS (International Data Spaces), a secure and sovereign data exchange system. The aim of this model is to standardise data exchange in such a way that participants can obtain all possible value from their information without losing control over it, setting the conditions for the use of their own data.
IDS-RAM architecture
The IDS-RAM (Reference Architecture model) is characterised by an open architecture (they publish their code as open source software), reliable and federated for cross-sector data exchange, facilitating sovereignty and interoperability.
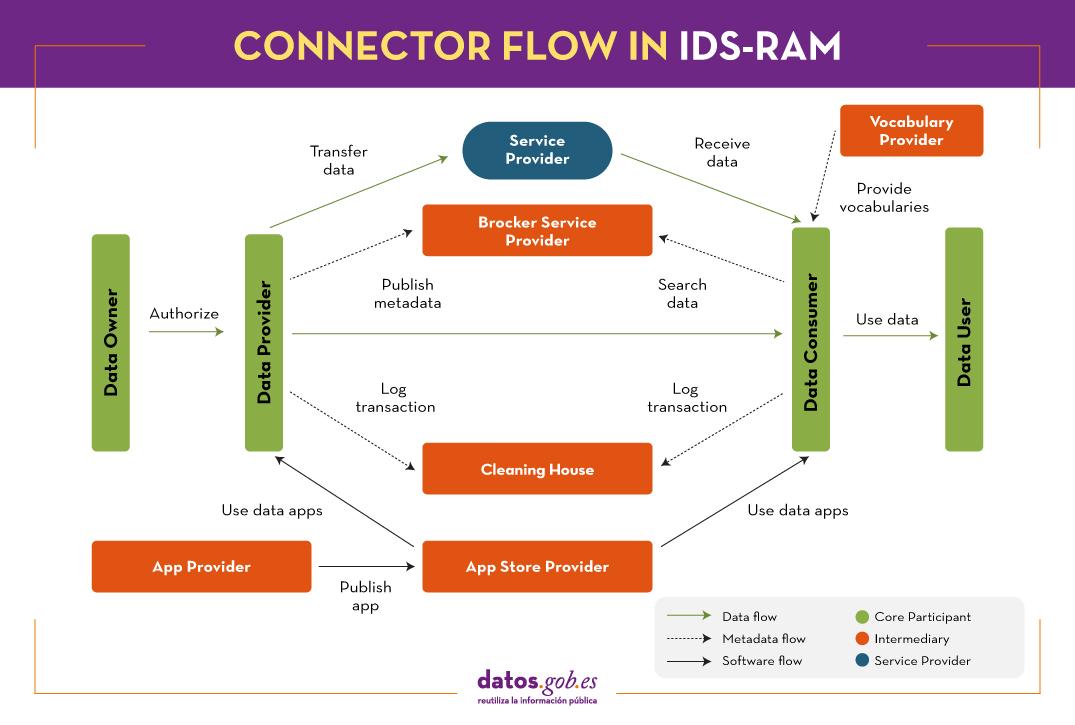
IDS-RAM establishes a series of standardised roles and interactions through a 5-layer structure (business, functional, process, information and system) that are addressed from the perspective of security, certification and governance, as shown in the following figure.

These layers are critical to ensure the success of a data sharing initiative. Let's look at each of them based on the IDSA's own "Reference architecture model" and Planetic's "Positioning on Data Spaces" report, where IDS-RAM is analysed as a success story.
The business layer defines the different existing roles and the interaction patterns between them, including contracts and data usage policies. Specifically, there are four roles:
- Essential participant: any organisation that owns, offers or consumes data.
- Intermediary: trusted entities and intermediaries, such as brokers, clearing houses, identity providers and others.
- Service/Software Provider: companies that provide services and/or software to participants.
- Governance body: such as certification bodies, which are essential to guarantee the capabilities of organisations and generate an environment of trust. The IDS Association itself would also be included in this section.
These roles are related in an ecosystem marked by six categories of requirements, defined in the functional layer:
- Trust, achieved through identity management and user certification.
- Security and data sovereignty, which includes authentication and authorisation, usage policies, trusted communication and technical certification.
- Data Ecosystem, which includes the description of data sources, data brokering and vocabularies used for metadata.
- Standardisation and interoperability, which ensures the operability necessary for successful data exchange.
- Value-added applications, which allow data to be transformed or processed.
- Data marketisation, which covers aspects such as billing, usage restrictions, governance, etc., necessary when data sharing is done under payment models.
The process layer captures the interactions that take place within the data space, including the on-boarding of users, for which they need to acquire an identity provided by a certification body and request a data connector (a technical component to be installed) from a software provider.
identity provided by a certification body and request a data connector (a technical component to be installed) from a software provider. This layer also defines the processes required for data exchange and the publication and use of data apps.
The information layer explains the information model and the common vocabulary to be used to facilitate compatibility and interoperability, so that data exchange can be automated. A proprietary ontology based on an RDF schema is used for its definition.
Finally, the system layer assigns a concrete architecture of data and services to each role in order to guarantee functional requirements.
All these abstractions of layers and perspectives enable the exchange of data between data providers and data consumers, using the appropriate software connectors, accessing the metadata broker where data catalogues and their conditions of use are specified, with the possibility of deploying applications for data processing and keeping track of the transactions carried out (clearing house), all of this guaranteeing the identity of the participants.
Ultimately, it is a functional framework that provides a governance framework for secure and reliable interoperability and an open software architecture to ensure maximum adoption. In this sense, the IDSA has set itself the following objectives:
- Establish the IDS model (RAM) as the international standard for data exchange in the economy of the future.
- Evolve this reference model according to use cases.
- Develop and evolve an adoption strategy for the model.
- Support its deployment based on certifiable software solutions and commercial models.
This standard is already being used by many companies as diverse as Deutsche Telekom, IBM or Volkswagen.
The role of IDS-RAM in Gaia-X and the European Data Strategy
The IDS reference architecture model is part of the initiatives deployed within the overall framework of the EU data strategy.
Through various initiatives, the European Commission seeks to promote and interconnect data spaces in order to foster the consultation, sharing and cross-exploitation of available data, while ensuring their privacy. It is in this framework that Gaia-X has been launched, an European private sector initiative for the creation of an open, federated and interoperable data infrastructure, built on the values of digital sovereignty and data availability, and the promotion of the data economy.
The IDSA association, promoter of the IDS reference architecture, is actively participating in Gaia-X, so that the initiatives currently underway to develop reference models and implementations for data sharing with sovereignty and trust can be brought together in a de facto open standard.
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.