
The Data Spaces Business Alliance (DSBA) was born in September 2021, a collaboration of four major organisations with much to contribute to the data economy: the Big Data Value Association (BDVA), FIWARE, Gaia-X and the International Data Spaces Association (IDSA). Its goal: to drive the adoption of data spaces across Europe by leveraging synergies.
How does the DSBA work?
The DSBA brings together diverse actors to realise a data-driven future, where public and private organisations can share data and thus unlock its full value, ensuring sovereignty, interoperability, security and reliability. To achieve this goal, DSBA offers support to organisations, as well as tools, resources and expertise. For example, it is working on the development of a common framework of technology agnostic blocks that are reusable across different domains to ensure the interoperability of different data spaces.
The four founding organisations, BDVA, FIWARE, Gaia-X and IDSA, have a number of international networks of national or regional hubs, with more than 90 initiatives in 34 countries. These initiatives, although very heterogeneous in focus, legal form, level of maturity, etc., have commonalities and great potential to collaborate, complement each other and create impact. Moreover, by operating at local, regional and/or national level, these initiatives provide regular feedback to European associations on the different regional policies, cultures and entrepreneurial ecosystems within the EU.
In addition, DSBA's application has been successful in the European Commission's call for the creation of a Support Centre, which will promote and coordinate actions related to sectoral data spaces. This centre will make available technologies, processes, standards and tools to support the deployment of common data spaces, thus enabling the re-use of data across sectors.
The DSBA hubs
The DSBA hubs refer to the global network combining the existing BDVA, FIWARE, Gaia-X and IDSA initiatives, as shown in the figure below.
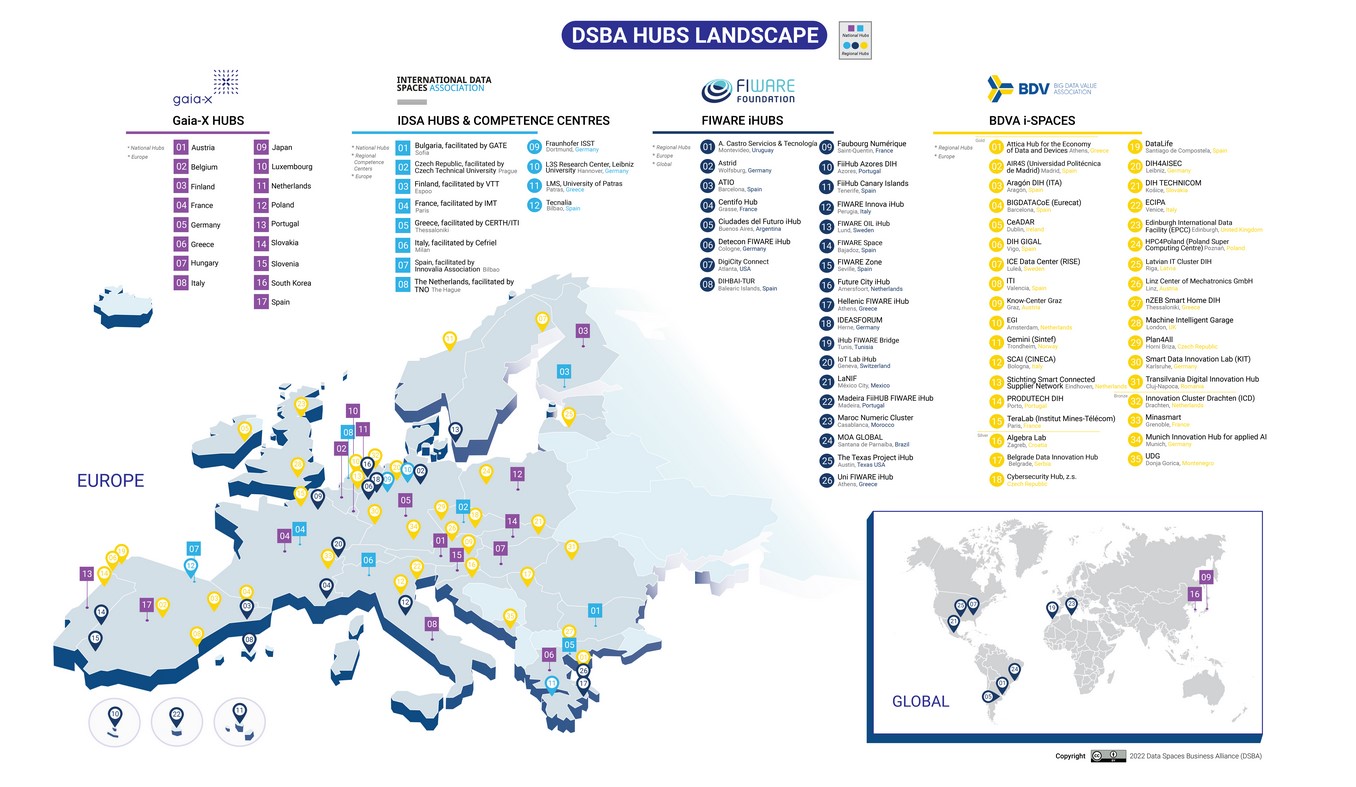
BDVA i-Spaces
BDVA i-Spaces are cross-sector and cross-organisational data incubators and innovation hubs, aimed at accelerating data-driven innovation and artificial intelligence in the public and private sectors. They provide secure experimentation environments, bringing together all the technical and non-technical aspects necessary for organisations, especially SMEs, to rapidly test, pilot and exploit their services, products and applications.
i-Spaces offer access to data sources, data management tools and artificial intelligence technologies, among others. They host closed and open data from corporate and public sources, such as language resources, geospatial data, health data, economic statistics, transport data, weather data, etc. The i-spaces have their own Big Data infrastructure with ad hoc processing power, online storage and state-of-the-art accelerators, all within European borders.
To become an i-Space, organisations must go through an assessment process, using a system of 5 categories, which are ranked according to gold, silver and bronze levels. These hubs must renew their labels every two years, and these certifications allow them to join a pan-European federation to foster cross-border data innovation, through the EUHubs4Data project.
FIWARE iHubs
FIWARE is an open software community promoted by the ICT industry, which - with the support of the European Commission - provides tools and an innovation ecosystem for entrepreneurs to create new Smart applications and services. FIWARE iHubs are innovation hubs focused on creating communities and collaborative environments that drive the advancement of digital businesses in this area. These centres provide private companies, public administrations, academic institutions and developers with access to knowledge and a worldwide network of suppliers and integrators of this technology, which has also been endorsed by international standardisation bodies.
There are 5 types of iHubs:
- iHub School: An environment focused on learning FIWARE, from a business and technical perspective, taking advantage of practical use cases.
- iHub Lab: Laboratory where you can run tests and pilots, as well as obtain FIWARE certifications.
- iHub Business Mentor: Space to learn how to build a viable business model.
- iHub Community Creator: Physical meeting point for the local community to bring together all stakeholders, acting as a gateway to the local and global FIWARE ecosystem.
Gaia-X Hubs
The Gaia-X Hubs are the national contact points for the Gaia-X initiative. It should be noted that they are not as such part of Gaia-X AISBL (the European non-profit association), but act as independent think tanks, which cooperate with the association in project deployment, communication tasks, and generation of business requirements for the definition of the architecture of the initiative (as the hubs are close to the industrial projects in each country).
Through them, specific data spaces are developed based on national needs, as well as the identification of funding opportunities to implement Gaia-X services and technology. They also seek to interact with other regions to build transnational data spaces, facilitating the exchange of information and the scaling up of national use cases internationally. To this end, the AISBL provides access to a collaborative platform, as well as support to the respective hubs in the distribution and communication of the use cases.
IDSA Hubs
The IDSA Hubs enable the exchange of knowledge around the reference architecture (known as the IDS-RAM) at country level. By bringing together research organisations, innovation promotion organisations, non-profit organisations, and companies that use IDS concepts and standards in the region, they seek to foster their adoption, and thus promote a sovereign data economy with greater capillarity.
These centres are driven in each country by a university, research organisation, or non-profit entity, working with IDSA to raise awareness of data sovereignty, transfer knowledge, recruit new members, and disseminate IDS-RAM-based use cases. To this end, they develop activities ranging from training sessions to meetings with decision-makers from different public administrations. They also promote and coordinate research and development projects with international organisations and companies, as well as with governments and other public entities.
Conclusion
As we said at the beginning, there is a great potential for synergies between these groups, which should be explored, discussed and articulated in concrete actions and projects. We are facing a promising opportunity to join forces and make further progress in the development and expansion of data spaces, in order to generate a significant impact on the Data Economy.
To stimulate the initial debate, the Data Spaces Business Alliance has prepared the document "Data Spaces Business Alliance Hubs: potential for synergies and impact", which explores the situation described above.