More and more media outlets have articles on their pages linked to so-called data journalism. This form of journalism uses the technologies and tools related to to data to provide readers with more documented, easier to understand and more engaging information.
In this article we explain what data journalism consists of and we show you some examples of media that already incorporate this modality within their informational processes.
What is data journalism?
Data journalism or data journalism is a journalistic discipline that incorporates different fields such as computer science, programming, engineering, statistics, design and journalism. to combine in the same space the analysis of data together with the narrative of the press. According to him Data Journalism Handbookdata can be the tool used to tell a story, the source a story is based on, or both.
Data journalism has its origin in Precision Journalism -evolution of investigative journalism-, where disciplines such as sociology and statistics are incorporated into traditional journalism, and Computer Assisted Journalism (Computer Assisted Reporting or CAR), which emerged in 1969 when journalists began to use computer systems to support them when dealing with the information they collected.
Data Journalism goes one step further and is the result of the digital transformation present today in the daily work of many newsrooms throughout the world. Using resources and tools related to data analytics, information is extracted from large databases. In this way, information of greater value and more complete is offered, adapted to the dynamism that digital reading requires.
What products does data journalism offer?
According to the digital magazine Journalists notebooks, there are at least four productions that can derive from this discipline, and that are generally complementary to each other:
- Data-driven articles: These are short articles that are made from large databases. These types of articles are typical of investigative journalism, since their common denominator is based on surveys or statistics.
- Applications news: The services that group information and send notifications to users about news of their interest from different media are becoming more and more common. For example, the main providers. For instance, Google Discover or Samsung Daily.
- Open datasets (datasets): Some media offer open data, the result of their research, in order to democratize information through the accessibility of data and its availability on the Internet in reusable and free formats. As an example, the New York Times offers data on the coronavirus openly.
- Interactive visualizations: such as infographics, graphics or applications that allow the information obtained from the databases to be viewed more clearly, facilitating the understanding of complex topics by readers. Visualizations can complement articles or be a product of their own when accompanied by short explanatory texts.
Data journalism in the media
More and more media have a news production based on data. Here are some examples:
At the national level
Among others, The country,The world or The newspaper They have a specific section within their digital newspapers dedicated to data journalism. Within both, newspapers address current affairs from the perspective offered by the data and through which they generate visualizations.like the following. In it, you can see a map that shows the inequalities in mortality according to the area in which you reside.
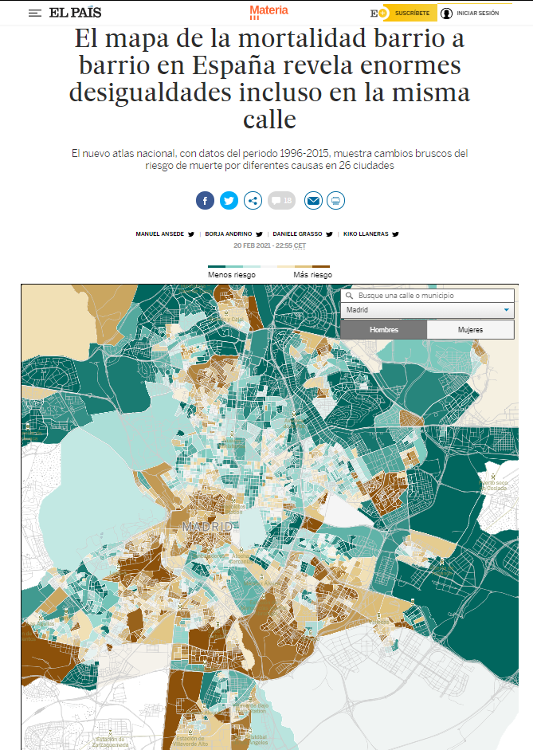
For its part, EpData is the platform created by Europa Press to facilitate the use of public data by journalists, with the aim ofboth to enrich the news with graphs and context analysis and to contrast the figures offered by the various sources. EpData also offers tools for creating and editing charts. An example of the activity they carry out is this article, where you can check the status of the dependency waiting lists in Spain.
Another example of data journalism is Newtral. It is an audiovisual content startup founded in 2018 in which data is the basis of all his work, especially in the fight against fake news. For instance, in this article different visualizations of data related to the oscillation of the price of light can be seen during different months.
On an international level
Data journalism is part of some of the most important international newspapers. It is the case of The Guardian, which also has a specific section dedicated to the production of journalistic material through articles, graphics and data-based visualizations. For instance, on this interactive map You can check which areas of Australia suffered the greatest natural disasters in 2020.
Another international media that also has a specific section for data-based journalism is the Argentine newspaper The nation, that through its section The Data Nation offers numerous informative productions in which it combines facts and news. For instance, in this article you can see an indicator of mobility of Argentine citizens.
Masters and studies related to data journalism
The digital transformation has meant that data journalism is here to stay. For this reason, more and more universities and education centers offer studies related to data journalism. For example, him Own Master's Degree in Data and Visualization Journalism from the University of Alcalá; the Master in Digital and Data Journalism taught by Atresmedia and the University of Nebrija or the Data Journalism Course from the UAM-El País School of Journalism.
In short, we are facing a modality with a future, which needs media that continue to bet on this discipline and professional capecesto handle data analysis and treatment tools, but also to tell stories, capable of transmitting what is happening in our environment with the support of data in a truthful and close way.
Therefore, it is not surprising that this form of journalism continues to grow in the coming years and that, in addition to the examples included in this article, the mass media and studies related to data journalism will increase. If you know any more and want to share it, do not hesitate to write to us contacto@datos.gob.es or leave us a message in the comments.
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
Group of professionals specialized in data management and use at different levels.
A reference team in the development, extraction and processing of information, turning it into strategy and value for their clients.
Based on the idea that “the future reusers are, nowadays, in schools”, the Barcelona City Council organizes, once again, the Barcelona Dades Obertes Challenge, a contest with a high social impact whose main objective is to bring open data benefits closer to students and thus increase the number of people with open data knowledge and skills, taking advantage of all the benefits that entails. And it is aimed at the youngest citizens, from very soon.
What does it consist of?
The Barcelona Dades Obertes Challenge Third edition 2020 is a contest where students will have to develop real analysis and / or interpretation projects, using data sets from the Open Data BCN portal. It is intended that students apply their critical vision to suggest improvements that affect the city and the lives of its inhabitants, while discovering the potential of open data.
In addition to the Barcelona City Council, other organism that participate in the organization of the Barcelona Dades Obertes Challenge are: the Consorci d'Educació de Barcelona, the Center for Specific Pedagogical Resources for Support to the Innovation and Educational Research (CESIRE) and Barcelona Activa S.A.
Who can participate?
The contest is aimed, mainly, at students from the 3rd and 4th grades of the E.S.O., and students from formative courses, prioritizing public funding centres. Participation takes place through their teachers, without restrictions by the subject they teach.
Teachers who wish can take part in a volunteer training program. There are currently 12 centers enrolled in this course, which includes training on general open data concepts, the Open Data BCN portal and tools for the treatment of data.
What is the deadline for submitting projects?
The deadline for submitting applications will open on February 17 and close on April 17, 2020.
Each centre will participate with only one project which will be evaluated by the jury of experts in the field. This jury will select a maximum of 10 projects from all the proposals received.
The students of the selected centers will have to defend their project before the jury in a final act that will be held on May 7, 2020, where the 3 finalists will be chosen.
Are you looking for inspiration? Discover the finalist projects of the 2 previous editions
The previous editions of the Barcelona Dades obertes Challenge were a success. 14 educational centers participated, more than 40 teachers and about 500 students who demonstrated their ability to acquire new knowledge and the educational opportunities offered by open data, presenting all projects of high quality and interest.
The first year, the winner was the Institut Ferran Tallada, with a work titled "Social cohesion goes by neighborhoods" that analyze social cohesion indexes (ICS) to measure and compare the city inequalities by districts. You can watch the video summary here.
The second year, the Institut Vila de Gràcia won the main award, thanks to the project “Gentrification in the neighborhoods in Barcelona”. This project showed the process of urban transformation caused by the phenomenon of gentrification, using datasets such as the number of inhabitants who leave their neighborhoods or the rent variation in € / m2. The projects of the EAT Institut Lluïsa Cura and the Institut Joan Brossa won a deserved second and third prize. You can watch the video summary here.
How can I participate?
The registration period is not yet open although the rules will be published shortly and then the call. From Barcelona City Council and datos.gob.es we will inform you of all the news that may arise.
You can follow all the information about the Barcelona Dades Obertes Challenge on twitter under the #OpenDataBCN hashtag.
The Junta de Castilla y León has launched their third edition of the open data contest. Its objective is "to recognize the development of projects that use datasets from the Open Data portal of the Junta de Castilla y León". In short, it look for boosting open data and re-users community in Castilla y León.
On this occasion, 3 categories have been established:
- Ideas Category: Ideas to create a study, service, website or application for mobile devices, using datasets from the Open Data portal of the Junta de Castilla y León. It give an opportunity to those people or entities that, without having the technical capacity, the resources or the time to implement a project with open data, do have the idea.
- Products and Services Category: Projects that are accessible to all citizens via the internet through a url. These projects must consist of studies, services, websites or applications for mobile devices, using datasets from the Open Data portal of the Junta de Castilla y León.
- Educational Resource Category: Creation of new and innovative open educational resources (published with Creative Commons licenses) using data sets from the Open Data portal of the Junta de Castilla y León to help teaching in the classroom.
A jury, made up of representatives of the Autonomous Administration and the sponsoring company, GMV, will choose the eight winners based on a series of criteria, such as its usefulness, originality or public value. Three prizes will be awarded to the Ideas Category, three to the Products and Services Category, and two to the Educational Resources Category made by educational centers. In the first two categories (Ideas and Products and Services) an award will be reserved for students enrolled in the courses 2017-2018 or 2018-2019.
The prizes will consist of an economic endowment (12,000 euros to be distributed) and individualized advice on business development, provided by the Business Development Area of the Institute for Business Competitiveness of Castilla y León (ICE):
- Ideas Category: First prize: € 2,000 / Second prize: € 1,000 / Prize for students: € 1,000.
- Products and Services Category: First prize: € 3,000 / Second prize: € 1,500 / Prize for students: € 2,000.
- Educational Resource Category: First prize: 1,000 euros in technological material / Second prize: 500 euros in technological material.
The candidatures can be presented at the electronic headquarters of the Regional Government of Castilla y León: Open Data Contest of the Community of Castilla y León (2018). The contest is open to both natural and legal persons, with the exception of public administrations and those individuals or legal entities that have participated directly or indirectly in the call. The deadline to submit the projects is from December 21, 2018, to February 10, 2019.
The international open data community has an appointment in Buenos Aires on September 27-28, 2018, in the new edition of the International Open Data Conference (IODC). Under the title "The future is open", a participatory event has been launched to address open data challenges and opportunities. The ultimate goal is to promote collaboration among professionals to define a strategy to promote the use of open data both globally and locally.
People interested in attending only have to fill out this online form. Registration is free and the process will be open until the day of the event. Also, journalists wishing to cover the conference can contact contact@opendatacon.org.
An inclusive and innovative agenda
The collaborative atmosphere of the event was reflected on the agenda. Through a global call for proposals, citizens and researchers could include their vision of open data, emphasizing their interests and concerns. The result is an agenda aligned with the needs of the attendees, which includes presentations, discussion panels, discussion groups and dynamic workshops.
The event will begin on the 27th at 9:00 a.m. local time with an official welcome, followed by an opening plenary session, where speakers will share an overview of the current status of open data in the world. Then, there will be a series of parallel sessions where different topics will be addressed:
- General sessions, focused for example on how to implement an open data policy, and other more specific sessions focused on the influence of open data in specific fields such as agriculture, journalism, Smart cities or the environment.
- Some sessions will address how open data can help solve some of humanity's current challenges (such as migration and refugee crises, gender issues or climate change).
- Regional sessions will also be held to provide information on the status of open data initiatives in specific territories such as LATAM, Asia, Western Europe or sub-Saharan Africa, among others.
All sessions that will take place in the main plenary room will be livestreamed. Also, there will be simultaneous translation services available, both for English and Spanish, in all rooms.
A week full of activities
In addition to these sessions, a series of pre-events will be held the prior days. These events are complementary to the program and allow more opportunities to engage and learn about different topics. Some example of these events are:
- September 24th. Attendees can visit the Open cities Summit, whit the support of Open Data for Development (OD4D). The objective of this event is to create a road map that includes concrete actions to develop an open city to improve the lives of citizens. Through presentations, panels and working groups, solutions will be sought to overcome previously identified challenges.
- September 25th. The Open Data Research Symposium is held, with the participation of The Governance Lab (The GovLab), ), Open Data for Development (OD4D), Open Data Research Network (ODRN) e International Development Research Center (IDRC). In this event, researchers present 8 -12 papers that provide a critical perspective and allow the development of empirically tested theories on the publication and use of open data. These papers will address issues such as the role of open data for decision-making or its value for developing economies. In addition, during the event, there will be a workshop to share relevant tools or processes for the research community.
- September 26. A day before the IODC start, attendees could enjoy ABRELATAM, an event whose organizers describe as a "no-conference", since it moves away from the traditional format of speaker who introduce a topic to a reactive audience. In this case, there will be multiple simultaneous sessions moderated by a facilitator that will encourage dialogue among small groups of attendees, based on topics gathered from the common agenda (entrepreneurship, security and privacy, algorithms and technology, etc.).
All these events will serve as a prelude to the intense IODC days, full of activities. As in the previous edition, celebrated with great success in the city of Madrid, it is expected that the event will consolidate international relations and encourage concrete actions that will go a step further in the development of open data strategies around the world.
The Basque Government organizes two open data competitions with the help of the Provincial Councils of Álava, Bizkaia and Gipuzkoa and the city councils of Bilbao, Donostia-San Sebastián and Vitoria-Gasteiz. The objective is to promote the culture of reuse information generated by the local public administrations. For this reason, the projects must use at least one of the datasets belonging to the following catalogs: Open Data Euskadi, Gipuzkoa Irekia, Bilbao Open Data, Open Data Vitoria-Gasteiz, Open data of the City of Donostia-San Sebastián and Open Data Bizkaia.
The registration period begins on May 22th. You can register on the website of each of the contests, free of charge, until June 30.
Next, we tell you the main characteristic of each contests.
Ideas contest
The ideas contest seeks innovative ideas to create a service, study, web application or mobile application, using some of the aforementioned open datasets. The two best ideas will be awarded 4,000 and 2,000 euros respectively.
This contest is aimed at students, professionals, companies or organizations from all sectors. To participate, it is not necessary to have technical knowledge, but an idea of what could be achieved using open data.
Application contest
On the contrary, the application contest focuses on real projects that provide any type of service, study, web application or mobile application, using the open datasets previously indicated. In this case, the economic endowment is 8,000 euros, to be divided between the first and the second classified (5,000 and 3,000 respectively). Due to they are real projects, in this case programming knowledge will be necessary.
Both in the ideas contest and the applications contest, the projects will be selected based on a series of criteria, such as its usefulness - taking into account the magnitude of the problem it solves and the number of potential users -, its potential to generate business and obtain profitability, its social value or its innovative character, among other factors.
The commitment of the regional and local administrations in favor of the reuse of open data is driving an increasing number of meetings of this type, where technology and open data are combined to create solutions that add value to society.
Join in and participate!
The interest in open data is growing and proof of this is the large number of events around this subject that will be held in our country during the coming months. Here we summarize the most important ones.
A must-attend event is the Open Gov Week, which will take place from May 7th to 11th. This international event is promoted by the Open Government Partnership, a multilateral initiative of 76 countries, including Spain, to "promote transparency, empower citizens, fight corruption, and harness new technologies to strengthen governance". The activities include courses, seminars, public debates, presentations, open days, contests and hackathons, among other activities (you can see all the activities here).
Public information opening, to promote its reuse and generate valuable services for citizens, is one of the topics that will be addressed. The opening session, entitled The Open State: Main Challenges and Opportunities for Public Authorities and Civil Society, include a panel discussion where representatives of public authorities, experts and civil society will share their vision on the value of open data and the need to protect information. This session will take place on Monday, May 7th from 9:00 a.m.
In addition, during the Open Gov Week, different activities have been organized to promote some of the Spanish open data portals. This is the case of Madrid City Council Open Data Portal. During 2 sessions - on Thursday, May 10th at 3:30 p.m. and Friday 11th at 12:00 p.m. – the people in charge of the service will explain how they manage public information access. This activity is aimed at teachers of secondary school and university.
The Transparency and Data Protection Council of Andalusia will also promote its Open Data Portal, in a session that include, among other things, simple examples of public information reuse. The event can be followed by streaming or in-person on Friday 11th at 10:30 a.m.
But not only public administrations promote events around open data, but also we increasingly see private events that address this topic, among other issues. On June 6th and 7th, the OpenExpo Europe 2018 will be held in Madrid, where experts will share the latest trends in Open Source, Free Software and Open World Economy (where open data has a prominent role). It is a professional event where companies linked to technological innovation from different fields, such as Business Intelligence, Cloud Computing, cybersecurity or IoT, will showcase their innovations and technological solutions.
Finally, it is also important to highlight the activities aimed at promoting the use of open data among the youngest citizens. On the 3rd of May, the final presentation of a pilot project of the City Council of Barcelona is held. Through a contest, 3rd and 4th ESO students have learned to use analysis tools and to elaborate proposals based on data from Open Data BCN. Another example is the Open Summer of Code, an international program to be held in July in Spain and Belgium with the aim of "providing students with the training, support and network necessary to transform open innovation projects into powerful real-world services".
These are just some of the appointments that will take place in the coming months, but every day there are more and more activities designed to give citizens an understanding of open data world, spreading its value and promoting its reuse.
For one more year, the VI Data Journalism and Open Data Workshop takes place at Medialab Prado (Alameda 15, Madrid), on this occasion organized by "Datalab". This is a meeting aimed at journalists, programmers or anyone interested in generating content using data. The meeting takes place between April 19 and 22 with the participation of different representatives from public administrations, companies, research groups, social organizations and experts.
This event is part of the Data Journalism Workshop, composed of 5 sessions (we spoke about it in a previous article). The topics included in the current agenda revolve around the Sustainable Development Goals (also known by the acronym SDG or Agenda 2030, because we project these objectives towards 2030), a project approved by the UN for "end poverty, protect the planet and ensure prosperity".
Under the slogan, Data of the SDGs, the different sessions of this Conference focus on the fight against climate change, including different aspects related to the environment in Madrid region. The objective is to create an inclusive event, where participants can acquire knowledge, share their opinion and establish relationships that encourage the creation of data-based stories.
The meeting begins on Thursday 19 at 10 in the morning with a session dedicated to "mobility data", whit the participation of Madrid City data portal, EMT (Municipal Transport Company of Madrid) and its MobilityLabs, among other. On the afternoon, there is a critical session on the SDGs, with the participation of Carmen Borja Segade, of ISI Argonauta, José Manuel Naredo, economist and statistician, and Ignacio Santos Molina, consultant on environment, development and international cooperation.
On Friday 20 in the morning, there is a symposium of touristification data, one of the contents that has created most interest, organized together with Montera 34. This symposium include, in the afternoon, the beginning of the touristic data workshop. During 3 sessions - Friday afternoon and Saturday and Sunday morning - we manage some tools for obtaining, cleaning and analyzing data. The objective is to collectively produce a report that helps to understand the impact of rental platforms for tourist accommodation in Madrid, using the question and answer method.
In addition to these contents, the VI Data Journalism and Open Data Workshop is also useful to present different initiatives related to data and SDGs, such as the Tipi Ciudadano project (Friday 20, 18 hours), an online tool that facilitate to follow the activity of @Congreso_es related to poverty and inequality, with its scanner and personalized warning system – in July 2018 it will also focus on compliance with the SDGs-; the Innovation and Human Rights project (Saturday 21, 18 hours) that promotes innovation to protect human rights; the presentation of the projects approved in the first round of data journalism workshop (Saturday 21, 16 hours); the session of JournoCodersMAD (Saturday 21, 17 hours); or the latest news in data training according to the "Specialization Diploma in Data Journalism and Visualization of Blanquerna".
You can see the full and updated agenda on its website and you can follow the ewent through the hashtags #datosods or #jpd18, or the accounts @datalabx and @jpdatos on Twitter. Medialab-Prado organizes the sixth edition of Data Journalism Workshop. This year, it will focus on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). The purpose of this event is to create stories based on data related to SDGs and the fight against climate change in Madrid.
For those interested in participating with their project, the deadline for submission is now open until March 12. Registration is free, but the projects must meet the following requirements: reuse data to create a story or journalistic tool; use reliable and localized data sources, and be focused on the topic selected in this edition. The list of selected projects will be published on March 20.
This event is aimed at those professionals - from developers and analysts to journalists - who want to work with data. It is composed of five sessions that will be held in the following months.
The first session, dedicated to free software, already took place on February 13-14. The second appointment will be held on the occasion of Open Data Day. Since 2017, the Data Journalism Workshop is linked to International Open Data Day celebration. For this reason, on March 2-3, Medialab organizes different activities to learn how to make open data requests into open data catalogs, how to use linked data, how to understand scraping techniques or how to delve into different aspects such as ontologies.
The second session agenda will include a talk on open data, within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals, as well as six work stations, during the course of the day, where it will be showed how to leverage the potential of Madrid data catalog, how to search data on the Net or how to work with sources such as Wikidata.
Later, in the following session of Data Journalism workshop (April 17-22), the selected projects will be presented and the work teams will be established; every team will work from June 8 to 10, supporting by mentors and associated journalists. For all those interested in working on any of the projects presented, Medialab-Prado will open the call for contributors on March 6.
Finally, the workshop will end with the fifth session (June 22-24): the working groups can finalize the projects and show them to the rest of the participants.
The fifth edition of the International Open Data Conference (IODC) is already underway. This year, it will be held in Buenos Aires, Argentina, on September 27-28. This biannual event brings together the international open data community with the objective of sharing, planning and collaborating on different current and future initiatives.
IODC seeks to identify and explore new trends that are emerging around open data, promoting innovative solutions capable of generating economic and social impact in different sectors. The event is also an opportunity to consolidate international relations and promote common resources development.
The Future is Open, central topic of this edition
2018 IODC sessions will focus on challenges and opportunities facing the open data community, under the title The Future is Open.
IODC organizers are committed to creating an inclusive and innovative event, including issues of concern to the international community. Therefore, the agenda will be created through a global call for proposals, that search for inclusion of all voices achieve the greatest possible level of gender balance and regional diversity.
The call for porposals will be open between February 14 and April 1, 2018. A committee comprised of open data experts, including representatives of public and private organizations and academic institutions, will evaluate all submissions received.
Submissions should target one of three conference tracks:
- The Big Picture (45 minutes-1 hour): Panels and debates focused on the exploration of emerging trends and challenges. They can include topics related to privacy, gender, algorithms, Big Data, artificial intelligence or other emerging technologies.
- Action Track (45 minutes-1 hour): Sessions and workshops that allow for the exchange of information. This category includes interactive discussions, brainstorming sessions, cases studies or roundtables. Sessions should contribute to enrich international collaboration areas identified in previous conferences.
- Impact Track (10-15 minutes): Short and dynamic sessions that show concrete examples of open data use within the different sectors, such as agriculture, education, health or transport, among others.
It is important to mention that those proposals that identify specific challenges and promote the search for solutions through dialogue will have preference. Proposals focused on gender issues that promote parity in participation, practices and processes will also highlight.
This year's conference will also highlight The State of Open Data initiative. This project focuses on the review of open data movement development during the last 10 years, with the aim of learning from errors and generating recommendations and good practices.
Madrid, headquarter of the previous edition
IODC previous edition took place in Madrid, on October 6 - 7, 2018. More than 1,600 attendees from a hundred countries visited the Spanish capital to participate in some of the 87 sessions given by more than 300 experts.
You can read event conclusions in the following link: IOCD Madrid 2016 conclusions.