The FEMP's Network of Local Entities for Transparency and Citizen Participation has just presented a guide focused on data visualisation. The document, which takes as a reference the Guide to data visualisation developed by the City Council of L'Hospitalet, has been prepared based on the search for good practices promoted by public and private organisations.
The guide includes recommendations and basic criteria to represent data graphically, facilitating its comprehension. In principle, it is aimed at all the entities that are members of the FEMP's Network of Local Entities for Transparency and Citizen Participation. However, it is also useful for anyone wishing to acquire a general knowledge of data visualisation.
Specifically, the guide has been developed with three objectives in mind:
- To provide principles and good practices in the field of data visualisation.
- To provide a model for the visualisation and communication of local authority data by standardising the use of different visual resources.
- Promote the principles of quality, simplicity, inclusiveness and ethics in data communication.
What does the guide include?
After a brief introduction, the guide begins with a series of basic concepts and general principles to be followed in data visualisation, such as the principle of simplification, the use of space or accessibility and exclusive design. Through graphic examples, the reader learns what to do and what not to do if we want our visualisation to be easily understood.
The guide then focuses on the different stages of designing a data visualisation through a sequential methodological process, as shown in the following diagram:
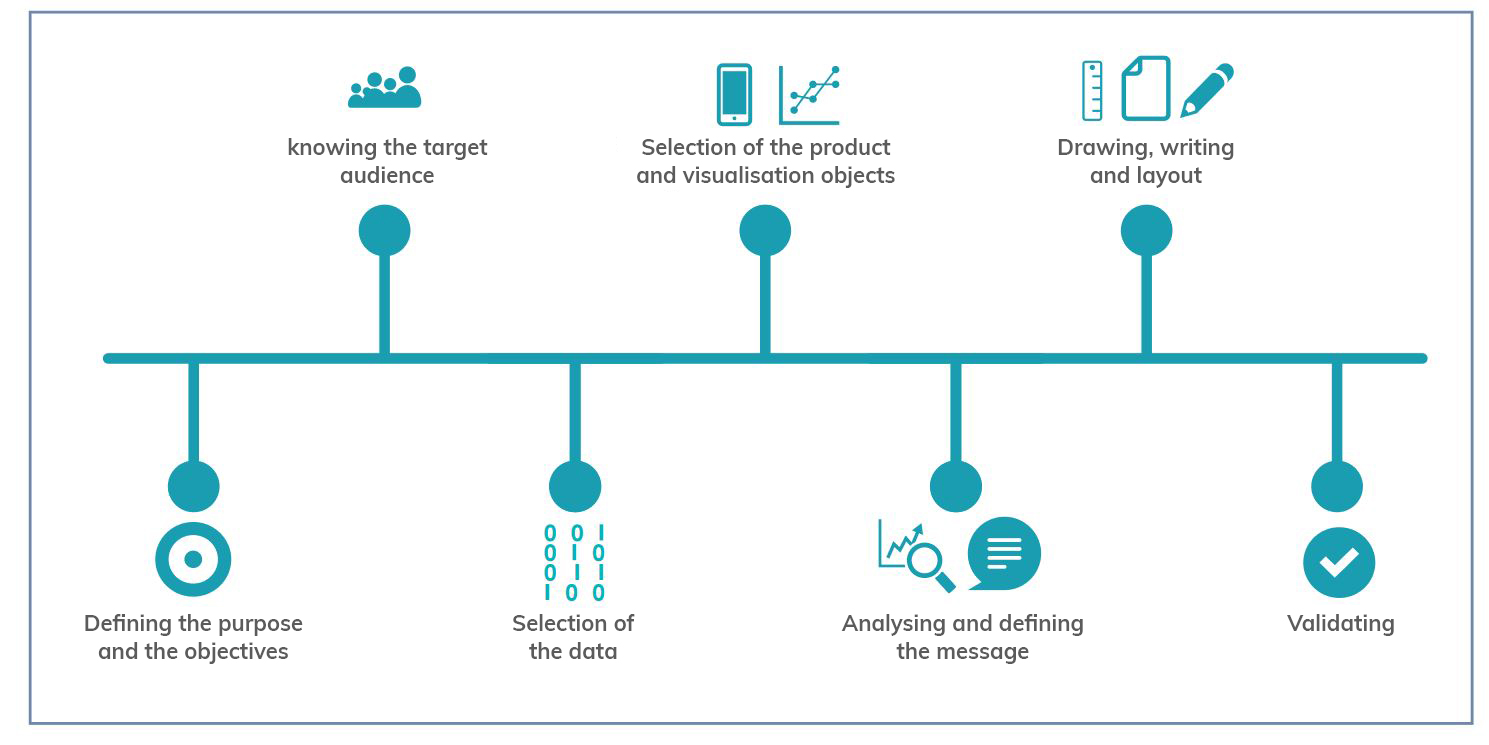
As the image shows, before developing the visualisation, it is essential to take the time to establish the objectives we want to achieve and the audience we are targeting, in order to tailor the message and select the most appropriate visualisation based on what we want to represent.
When representing data, users have at their disposal a wide variety of visualisation objects with different functions and performance. Not all objects are suitable for all cases and it will be necessary to determine the most appropriate one for each specific situation. In this sense, the guide offers several recommendations and guidelines so that the reader is able to choose the right element based on his or her objectives and audience, as well as the data he or she wants to display.
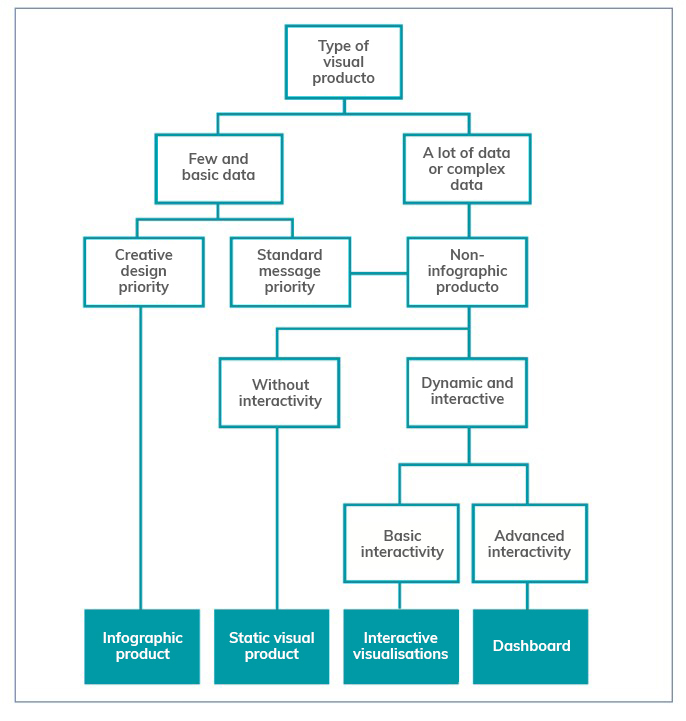
The following chapters focus on the various elements available (infographics, dashboards, indicators, tables, maps, etc.) showing the different subcategories that exist and the good practices to follow in their elaboration, showing numerous examples that facilitate their understanding. Recommendations on the use of the text are also provided.
The guide ends with a selection of resources for further knowledge and data visualisation tools to be considered by anyone who wants to start developing their own visualisations.
You can download the complete guide below, in the "Documentation" section.
Programming libraries are sets of code files that are used to develop software. Their purpose is to facilitate programming by providing common functionalities that have already been solved by other programmers.
Libraries are an essential component for developers to be able to program in a simple way, avoiding duplication of code and minimising errors. They also allow for greater agility by reducing development time and costs.
These advantages are reflected when using libraries to make visualisations using popular languages such as Python, R and JavaScript.
Python libraries
Python is one of the most widely used programming languages. It is an interpreted language (easy to read and write thanks to its similarity to the human language), multiplatform, free and open source. In this previous article you can find courses to learn more about it.
Given its popularity, it is not surprising that we can find many libraries on the web that make creating visualisations with this language easier, such as, for example:
Matplotlib
- Description:
Matplotlib is a complete library for generating static, animated and interactive visualisations from data contained in lists or arrays in the Python programming language and its mathematical extension NumPy.
- Supporting materials:
The website contains examples of visualisations with source code to inspire new users, and various guides for both beginners and more advanced users. An external resources section is also available on the website, with links to books, articles, videos and tutorials produced by third parties.
Seaborn
- Description:
Seaborn is a Python data visualisation library based on matplotlib. It provides a high-level interface to draw attractive and informative statistical graphs.
- Supporting materials:
Tutorials are available on their website, with information on the API and the different types of functions, as well as a gallery of examples. It is also advisable to take a look at this paper by The Journal of Open Source Software.
Bokeh
- Description:
Bokeh is a library for interactive data visualisation in a web browser. Its functions range from the creation of simple graphs to the creation of interactive dashboards.
- Supporting materials:
Users can find detailed descriptions and examples describing the most common tasks in the guide. The guide includes the definition of basic concepts, working with geographic data or how to generate interactions, among others.
The website also has a gallery with examples, tutorials and a community section, where doubts can be raised and resolved.
Geoplotlib
- Description:
Geoplotlib is an open source Python library for visualising geographic data. It is a simple API that produces visualisations on top of OpenStreetMap tiles. It allows the creation of point maps, data density estimators, spatial graphics and shapefiles, among many other spatial visualisations.
- Supporting materials:
In Github you have available this user guide, which explains how to load data, create colour maps or add interactivity to layers, among others. Code examples are also available.
Libraries for R
R is also an interpreted language for statistical computing and the creation of graphical representations (you can learn more about it by following one of these courses). It has its own programming environment, R-Studio, and a very flexible and versatile set of tools that can be easily extended by installing libraries or packages - using its own terminology - such as those detailed below:
ggplot 2
- Description:
Ggplot is one of the most popular and widely used libraries in R for the creation of interactive data visualisations. Its operation is based on the paradigm described in The Grammar of Graphics for the creation of visualisations with 3 layers of elements: data (data frame), the list of relationships between variables (aesthetics) and the geometric elements to be represented (geoms).
- Supporting materials:
On its website you can find various materials, such as this cheatsheet that summarises the main functionalities of ggplot2. This guide begins by explaining the general characteristics of the system, using scatter diagrams as an example, and then goes on to detail how to represent some of the most popular graphs. It also includes a number of FAQs that may be of help.
Lattice
- Description:
Lattice is a data visualisation system inspired by Trellis or raster graphs, with a focus on multivariate data. Lattice's user interface consists of several generic "high-level" functions, each designed to create a particular type of graph by default.
- Supporting materials:
In this manual you can find information about the different functionalities, although if you want to learn more about them, in this section of the web you can find several manuals such as R Graphics by Paul Murrell or Lattice by Deepayan Sarkar.
Esquisse
- Description:
Esquise allows you to interactively explore data and create detailed visualisations with the ggplot2 package through a drag-and-drop interface. It includes a multitude of elements: scatter plots, line plots, box plots, multi-axis plots, sparklines, dendograms, 3D plots, etc.
- Supporting materials:
Documentation is available via this link, including information on installation and the various functions. Information is also available on the R website.
Leaflet
- Description:
Leaflet allows the creation of highly detailed, interactive and customised maps. It is based on the JavaScript library of the same name.
- Supporting materials:
On this website you have documentation on the various functionalities: how the widget works, markers, how to work with GeoJSON & TopoJSON, how to integrate with Shiny, etc.
Librerías para JavaScript
JavaScript is also an interpreted programming language, responsible for making web pages more interactive and dynamic. It is an object-oriented, prototype-based and dynamic language.
Some of the main libraries for JavaScript are:
D3.js
- Description:
D3.js is aimed at creating data visualisations and animations using web standards, such as SVG, Canvas and HTML. It is a very powerful and complex library.
- Supporting materials:
On Github you can find a gallery with examples of the various graphics and visualisations that can be obtained with this library, as well as various tutorials and information on specific techniques.
Chart.js
- Description:
Chart.js is a JavaScript library that uses HTML5 canvas to create interactive charts. Specifically, it supports 9 chart types: bar, line, area, pie, bubble, radar, polar, scatter and mixed.
- Supporting materials:
On its own website you can find information on installation and configuration, and examples of the different types of graphics. There is also a section for developers with various documentation.
Other libraries
Plotly
- Description:
Plotly is a high-level graphics library, which allows the creation of more than 40 types of graphics, including 3D graphics, statistical graphics and SVG maps. It is an Open Source library, but has paid versions.
Plotly is not tied to a single programming language, but allows integration with R, Python and JavaScript.
- Supporting materials:
It has a complete website where users can find guides, use cases by application areas, practical examples, webinars and a community section where knowledge can be shared.
Any user can contribute to any of these libraries by writing code, generating new documentation or reporting bugs, among others. In this way they are enriched and perfected, improving their results continuously.
Do you know of any other library you would like to recommend? Leave us a message in the comments or send us an email to dinamizacion@datos.gob.es.
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
The data-related skills are becoming more cross-cutting. The data analytics has become essential for take decisions in organisations of all sizes and sectors. But to communicate the results of the analytics to the different interlocutors, it’s necessary to work with graphics, visualisations and narratives that allow a simple and easy appreciation of the conclusions. As a result of this, the search for profiles capable of working with the most important data visualization tools has grown.
To develop in this area, it’s necessary to have a miminum knowledge of statistics and analytics, but also to know the trends in design and in visual communication. On the market, we can find a lot of courses or MOOC that could help us to learn more about this skills in a online and flexible way.
General courses about data visualization
There are many schools that offer courses for those people who don’t want to specialise in a particular tool, but they prefer to get an overview of the data visualization.
Big Data: data visualization
- Imparted by: the Autonomous University of Barcelona, in Coursera.
- Duration: 9 hours, in 4 weeks.
- Language: spanish
- Price: free
This MOOC is an introductory course that explain the key concepts of the massive data visualization, through examples in different contexts. The aim of this course is that the students could learn to formulate the problem and choose the best tool. It has 4 modules, one per week: the context for the present data visualization, analitycs tools and data visualization, the creation process of the data visualization and others issues about data visualization.
Fundamentals of data visualization
- Imparted by: Marco Russo (In Udemy)
- Duration: 2 hours
- Language: English
- Price: Free
This course is designed to teach the students how to create modern and complete data visualizations. This MOOC starts with a basic notions about the application of data visualization and what it is used for. After a simple introduction, the students will learn how to interact with the different graphics, how to differentiate between Bussiness Analitycs and Data Analytics, or how to understand data visualization through practical examples.
Data journalism and visualization with free tools
- Imparted by: Knight Center for Journalism in the Americas
- Duration: 30 hours (6 weeks)
- Language: Spanish
- Price: Free
This course is available for free to anyone who is interested in data journalism, visualisation and the tools that the market offers for free. Thanks to this course, the students can learn how to search and collect data, how to find stories inside them, how to prepare data and how to make visualisations.
Specific course about different visualization tools
On the other hand, those who want prefer more specific training in one of the most popular data visualization tools, can find a lot of options on the internet.
Fundamentals of Data Visualisation with Tableau
- Imparted by: University Austral (In Coursera)
- Duration: 8 hours
- Language: Spanish
- Price: Free
Tableau mixes a graphical interface with common elements of Business Intelligence tools. This course is for users who have never worked with this tool or want to learn more about it, without previous technical or analytical knowledge. It explains fundamental concepts of data visualisation and how to use the various tools offered by Tableau.
Create and share reports with Tableau Public!
- Imparted by: Adrian Javier Tagüico (through Udemy)
- Duration: 1,5 hours
- Language: English
- Price: requires payment of a fee.
This course shows you how to create dynamic and intuitive reports, dashboards and stories step by step thanks to Tableau Public. The students will learn how to import data sources (using example public data), how to prepare the data, how to model the data and how to create visualisations, using filters (data segmentation, interaction of visualisations or different options in each visualisation). In this case, you will need a basic knowledge of data types.
Google Data Studio – Data Visualization and Dashboards
- Imparted by: Start-Tech Academy (In Udemy)
- Duration: 4 video hours. You could do it in 6 hours.
- Language: Spanish
- Price: requires payment of a fee.
Data Studio is a free tool from Google to make very visual reports with analytical data, and it allows their automation. The aim of this course is that the students learn how to create all kinds of graphics in Google Data Studio, as well as to learn more about the specific advanced characteristics of the tool. This is a start course for preople who don’t have previous knowledge.
Data Visualization with Kibana
- Imparted by: Start-Tech Academy (in Udemy)
- Duration: 5.5 hours
- Language: English
- Price: requires payment of a fee.
Course to learn the basic skills of Kibana, an open software code that is part of the Elastic Stack product pack. The students can learn from basic security issues (users, roles and spaces), to how to create advanced visualisations or dashboards, using the Kibana Query Language (KQL).
Grafana
- Imparted by: Sean Bradley (In Udemy)
- Duration: 6 hours
- Language: English
- Price: requires payment of a fee.
Grafana began as a part of Kibana, but now is a completely independent tool. In this course you will learn how to explore graphic panels, statistics, indicators, bars, tables, text, heat maps and logs. It includes everything from installing different data fonts (MySQL, Zabbix, InfluxDB, etc.) and the creation of dynamic dashboards with automatic display placement, the installation the server SMTP, or the configuration notification channel by email or Telegram
Data visualization library courses
In addition to the previous generic tools, there are also more specific visualization libraries on the market. These libraries are more versatile, but require that the students know the programming language where the library is implemented. Some examples of courses in this area are:
Data visualization course with Python
- Imparted by: Abraham Requena (In Open webinars).
- Duration: 3 hours
- Language: Spanish
- Price: for free
This course focuses on two Python’s libraries: Matplotlib and Seaborn. The course starts with an introduction where is discussed the importance of visualisation and graphic types. Then, the work with each of the libraries, including exercises, is discussed.
Data Visualization with Python
- Imparted by: Complutense University of Madrid
- Duration: 40 hours (8 weeks)
- Language: Spanish
- Price: requires payment of a fee.
This course focuses on the development of visualizations using Python. After an introduction about the key aspects for create and effective data visualisations, the course focuses on the development of data visualizations in Python using Matplotlib and Plotly. The course uses the Jupyter Notebook environment. You will need a minimum knowledge of Python and data analysis with Pandas.
Bid Data: data visualization. Introduction to R and ggplot2
- Imparted by: Autonomous University of Barcelona (in Coursera).
- Duration: 9 hours
- Language: Spanish
- Price: Free
This is the fourth course of the specialised programme "Big Data - Introduction to the practical use of massive data". This programme has been designed to motivate and teach the students key concepts about data visualisation, as well as to provide them with criterium for formulating problems and choosing the correct tool for each visualization. This course is divided into four main modules with different subjects, for example, contexts, tools or creation processes for data visualizations.
All this courses are just an example of all the offer in the market. If you know any other that you would like to recommend us, please send us an email to dinamizacion@datos.gob.es or leave a comment.
What cannot be denied is that with these types of courses you will improve your professional profile and you will expand your competitive skills in the labour market.
Nowadays, no one can deny the value hidden in data: trends, areas for improvement or business opportunities are just some of the knowledge that can be found behind a series of figures. A correct analysis of an organization's internal and external data can provide a great competitive advantage and drive better decision making.
However, extracting that value is not always easy. The data can be difficult to understand and the analyses made from it need to be communicated effectively. In this sense, the usual mechanism for displaying data is visualizations. But in a world so saturated with data and knowledge, visualizations alone may not achieve the desired result. It is often necessary to add a good explanation in the form of a story to make an impact on the receiver.
The importance of narrative
We all like to be told stories that catch our attention. We remember things better if they are integrated into a narrative. Proof of this is this study in the book Made to Stick): after a series of one-minute interventions in which an average of 2.5 statistics were provided, only 5% of the listeners were able to remember an individual figure. However, 63% remembered the story told.
Stories manage to engage us, giving the data a context related to our interests and concerns. In this way, the data acquire greater meaning, and it is easier to drive the implementation of related actions.
This is the context in which data storytelling appears.
What is data storytelling?
Data storytelling consists of communicating the information resulting from data analysis through a story. It involves three ingredients: data, visualization and narrative. These three elements combine to result in effective communication:
- By combining narrative and data we move into the realm of explanation: thanks to context the audience understands what is happening (or going to happen) and why it is important.
- By combining visual elements with data, what we can call "enlightenment" happens: insights are displayed in a way that is eye-catching and easy to understand, allowing relationships and patterns to be observed.
- By combining narrative and visual elements, you connect with the audience, generating engagement: thanks to formulas linked to the entertainment sector, you get the audience's attention.
When combined, you get a data-driven story that can influence and drive change.
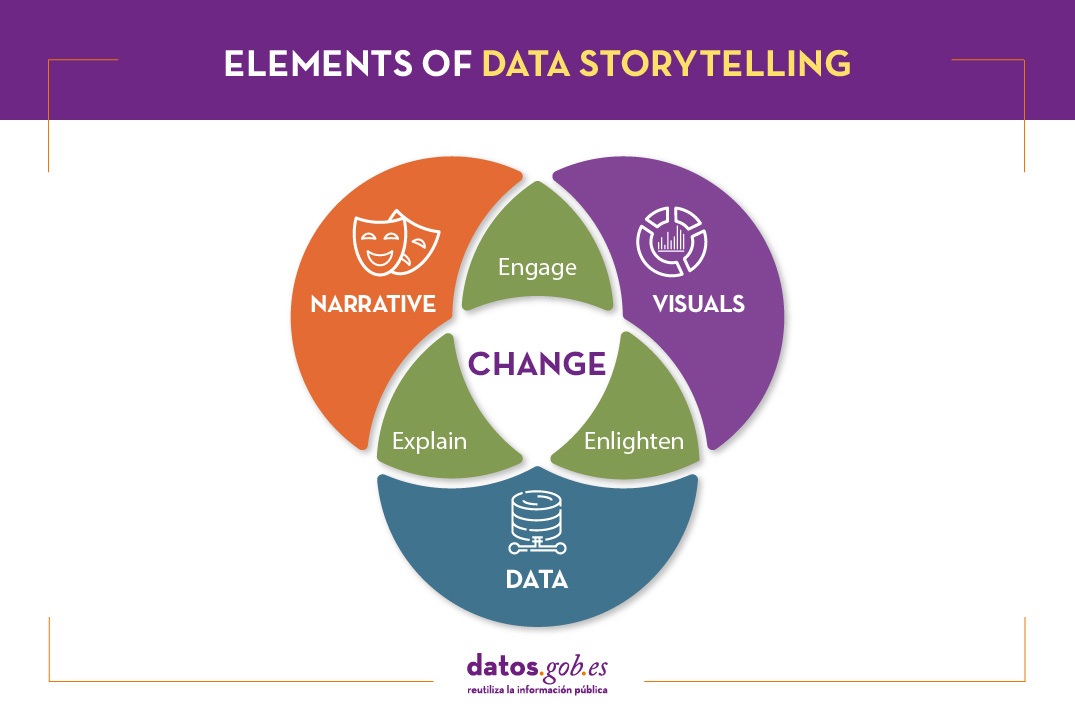
Data storytelling is the foundation of data journalism, but it is also increasingly used within public and private organizations to convey the ideas behind the data both internally and externally.
What do you need to consider in order to tell a story with data?
Transforming data into valuable information and telling a story requires knowledge in all three of the above areas.
The first step is to think about what our objective is. Based on this we will determine the message we want to launch, which must be clear and simple. In order to communicate it effectively, it is necessary to know the audience and their level of knowledge on the subject. The approach, tone, medium and data we use will depend on this.
It is also necessary to know the basics of data analysis and visualization. There are a multitude of tools at our disposal that we can use. It is important to choose the type of graphic to use, depending on what we want to show (comparative, trends, distributions, etc.), as well as to pay great attention to the use of color and hierarchies in the information.
To meet these needs, it is sometimes necessary to have multidisciplinary teams where different types of skills are mixed. However, simple tools designed for use by anyone are also emerging, as we shall see below.
Integrating data storytelling in open data portals: the example of Aragon Open Data
Data storytelling is also reaching open data portals as a way to bring data closer to citizens and boost its reuse, amplifying its impact.
Aragon's open data portal has developed Open Data Focus, a free service that allows portal users to develop and share their own stories based on the region's open data. It is a very intuitive tool, for which no technical knowledge is required. In the portal you can see some of the digital narratives developed around different topics of interest. In this document you can learn more about the context, objectives, methodology and results of the project.
Aragón Open Data Focus is an innovative and pioneering experience in our country, which brings public sector information closer to citizens. Given the importance of narrative and visualization in the understanding of data, it is not surprising that soon we will know more success stories in this regard.
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
R is one of the programming languages most popular in the world of data science.
It has a programming environment, R-Studio and a set of very flexible and versatile tools for statistical computing and creation of graphical representations.
One of its advantages is that functions can be easily expanded, by installing libraries or defining custom functions. In addition, it is permanently updated, since its wide community of users constantly develops new functions, libraries and updates available for free.
For this reason, R is one of the most demanded languages and there are a large number of resources to learn more about it. Here is a selection based on the recommendations of the experts who collaborate with datos.gob.es and the user communities R-Hispanic and R-Ladies, which bring together a large number of users of this language in our country.
Online courses
On the web we can find numerous online courses that introduce R to new users.
Basic R course
- Taught by: University of Cádiz
- Duration: Not available.
- Language: Spanidh
- Free
Focused on students who are doing a final degree or master's project, the course seeks to provide the basic elements to start working with the R programming language in the field of statistics. It includes knowledge about data structure (vectors, matrices, data frames ...), graphics, functions and programming elements, among others.
Introduction to R
- Taught by: Datacamp
- Duration: 4 hours.
- Language: English
- Free
The course begins with the basics, starting with how to use the console as a calculator and how to assign variables. Next, we cover the creation of vectors in R, how to work with matrices, how to compare factors, and the use of data frames or lists.
Introduction to R
- Taught by: Anáhuac University Network
- Duration: 4 weeks (5-8 hours per week).
- Language: Spanish
- Free and paid mode
Through a practical approach, with this course you will learn to create a work environment for R with R Studio, classify and manipulate data, as well as make graphs. It also provides basic notions of R programming, covering conditionals, loops, and functions.
R Programming Fundamentals
- Taught by: Stanford School of Engineering
- Duration: 6 weeks (2-3 hours per week).
- Language: English
- Free, although the certificate costs.
This course covers an introduction to R, from installation to basic statistical functions. Students learn to work with variable and external data sets, as well as to write functions. In the course you will hear one of the co-creators of the R language, Robert Gentleman.
R programming
- Taught by: Johns Hopkins University
- Duration: 57 hours
- Language: English, with Spanish subtitles.
- Of payment
This course is part of the programs of Data science and Data Science: Basics Using R. It can be taken separately or as part of these programs. With it, you will learn to understand the fundamental concepts of the programming language, to use R's loop functions and debugging tools, or to collect detailed information with R profiler, among other things.
Data Visualization & Dashboarding with R
- Taught by: Johns Hopkins University
- Duration: 4 months (5 hours per week)
- Language: English
- Of payment
Johns Hopkins University also offers this course where students will generate different types of visualizations to explore the data, from simple figures like bar and scatter charts to interactive dashboards. Students will integrate these figures into reproducible research products and share them online.
Introduction to R statistical software
- Taught by: Spanish Association for Quality (AEC)
- Duration: From October 5 to December 3, 2021 (50 hours)
- Language: Spanish
- Of payment
This is an initial practical training in the use of R software for data processing and statistical analysis through the simplest and most common techniques: exploratory analysis and relationship between variables. Among other things, students will acquire the ability to extract valuable information from data through exploratory analysis, regression, and analysis of variance.
Introduction to R programming
- Taught by: Abraham Requena
- Duration: 6 hours
- Language: Spanish
- Paid (by subscription)
Designed to get started in the world of R and learn to program with this language. You will be able to learn the different types of data and objects that are in R, to work with files and to use conditionals, as well as to create functions and handle errors and exceptions.
Programming and data analysis with R
- Taught by: University of Salamanca
- Duration: From October 25, 2021 - April 22, 2022 (80 teaching hours)
- Language: Spanish
- Payment
It starts from a basic level, with information about the first commands and the installation of packages, to continue with the data structures (variables, vectors, factors, etc.), functions, control structures, graphical functions and interactive representations, among others topics. Includes an end-of-course project.
Statistics and R
- Taught by: Harvard University
- Duration: 4 weeks (2-4 hours per week).
- Language: English
- Payment
An introduction to basic statistical concepts and R programming skills required for data analysis in bioscience. Through programming examples in R, the connection between the concepts and the application is established.
For those who want to learn more about matrix algebra, Harvard University also offers online the Introduction to Linear Models and Matrix Algebra course, where the R programming language is used to carry out the analyzes.
Free R course
- Taught by: Afi Escuela
- Duration: 7.5 hours
- Language: Spanish
- Free
This course was taught by Rocío Parrilla, Head of Data Science at Atresmedia, in virtual face-to-face format. The session was recorded and is available through Yotube. It is structured in three classes where the basic elements of R programming are explained, an introduction to data analysis is made and visualization with this language is approached (static visualization, dynamic visualization, maps with R and materials).
R programming for beginners
- Taught by: Keepcoding
- Duration: 12 hours of video content
- Language: Spanish
- Free
It consists of 4 chapters, each of them made up of several short videos. The first "Introduction" deals with the installation. The second, called "first steps in R" explains basic executions, as well as vectors, matrices or data frames, among others. The third deals with the “Flow Program R” and the last one deals with the graphs.
Autonomous online course Introduction to R
- Taught by: University of Murcia
- Duration: 4 weeks (4-7 hours per week)
- Language: Spanish
- Free
It is a practical course aimed at young researchers who need to analyze their work data and seek a methodology that optimizes their effort.
The course is part of a set of R-related courses offered by the University of Murcia, onMultivariate data analysis methods, Preparation of technical-scientific documents and reports or Methods of hypothesis testing and design of experiments, among others.
Online books related to R
If instead of a course, you prefer a manual or documentation that can help you improve your knowledge in a broader way, there are also options, such as those detailed below.
R for Data Professionals. An introduction
- Author: Carlos Gil Bellosta
- Free
The book covers 3 basics in high demand by data professionals: creating high-quality data visualizations, creating dashboards to visualize and analyze data, and creating automated reports. Its aim is that the reader can begin to apply statistical methods (and so-called data science) on their own.
Learning R without dying trying
- Author: Javier Álvarez Liébana
- Free
The objective of this tutorial is to introduce people to programming and statistical analysis in R without the need for prior programming knowledge. Its objective is to understand the basic concepts of R and provide the user with simple tricks and basic autonomy to be able to work with data.
Statistical Learning
- Author: Rubén F. Casal
- Free
It is a document with the notes of the subject of Statistical Learning of the Master in Statistical Techniques. Has been written inR-Markdown using the package bookdown and is available in Github. The book does not deal directly with R, but deals with everything from an introduction to statistical learning, to neural networks, through decision trees or linear models, among others.
Statistical simulation
- Author: Rubén F. Casal and Ricardo Cao
- Free
As in the previous case, this book is the manual of a subject, in this case ofStatistical simulation of the Master in Statistical Techniques. It has also been written inR-Markdown using the package bookdown and is available in the repository Github. After an introduction to simulation, the book addresses the generation of pseudo-random numbers in R, the analysis of simulation results or the simulation of continuous and discrete variables, among others.
Statistics with R
- Author: Joaquín Amat Rodrigo
- Free
It is not a book directly, but a website where you can find various resources and works that can serve as an example when practicing with R. Its author is Joaquín Amat Rodrigo also responsible forMachine Learning with R.
Masters
In addition to courses, it is increasingly common to find master's degrees related to this subject in universities, such as:
Master in Applied Statistics with R / Master in Machine Learning with R
- Taught by: Esucela Máxima Formación
- Duration: 10 months
- Language: Spanish
The Esucela Máxima Formación offers two masters that begin in October 2021 related to R. The Master in Applied Statistics for Data Science with R Software (13th edition) is aimed at professionals who want to develop advanced practical skills to solve real problems related to the analysis, manipulation and graphical representation of data. The Master in Machine Learning with R Software (2nd edition) is focused on working with real-time data to create analytical models and algorithms with supervised, unsupervised and deep learning.
In addition, more and more study centers offer master's degrees or programs related to data science that collect knowledge on R, both general and focused on specific sectors, in their syllabus. Some examples are:
- Master in Data Science, from the Rey Juan Carlos University, which integrates aspects of data engineering (Spark, Hadoop, cloud architectures, data collection and storage) and data analytics (statistical models, data mining, simulation, graph analysis or visualization and communication) .
- Master in Big Data, from the National University of Distance Education (UNED), includes an Introduction to Machine Learning module with R and another of advanced packages with R.
- Master in Big Data and Data Science Applied to Economics, from the National University of Distance Education (UNED), introduces R concepts as one of the most widely used software programs.
- Master Big Data - Business - Analytics, from the Complutense University of Madrid, includes a topic on Data Mining and Predictive Modeling with R.
- Master in Big Data and Data Science applied to Economics and Commerce, also from the Complutense University of Madrid, where R programming is studied, for example, for the design of maps, among others.
- Master in Digital Humanities for a Sustainable World, from the Autonomous University of Madrid, where students will be able to program in Python and R to obtain statistical data from texts (PLN).
- Master in Data Science & Business Analytics, from the University of Castilla-La Mancha, whose objective is to learn and/or deepen in Data Science, Artificial Intelligence and Business Analytics, using R statistical software.
- Expert in Modeling & Data Mining, from the University of Castilla-La Mancha, where as in the previous case also works with R to transform unstructured data into knowledge.
- Master of Big Data Finance, where they talk about Programming for data science / big data or information visualization with R.
- Big Data and Business Intelligence Program, from the University of Deusto, which enables you to perform complete cycles of data analysis (extraction, management, processing (ETL) and visualization).
We hope that some of these courses respond to your needs and you can become an expert in R. If you know of any other course that you want to recommend, leave us a comment or write to us at dinamizacion@datos.gob.es.
Maps help us to understand the world in which we live and have therefore been fundamental in the development of humanity. They allow us to know the characteristics of a place and to understand social phenomena, such as the spatial behaviour of a disease or the traceability of trade flows.
If we show data through a map, we facilitate its understanding and interpretability. But in order to build such geospatial visualisations, we need georeferenced data.
What is georeferencing?
Georeferencing is a method of determining the position of an element based on a spatial coordinate system.
Much of the open data offered by public administrations is geo-referenced or can be geo-referenced, thus increasing its value. Through geo-referenced online services for viewing or downloading data such as Spatial Data Infrastructures (SDI) or geoportals, users can access a large amount of such data. But handling this type of information is not easy.
The user of georeferenced data needs to understand key concepts linked to the visualisation of geographic information such as coordinate reference systems, cartographic projections or the different data representation models with which they work: raster - pixel map images - or vector - points, lines, etc. representing different objects. These elements can be combined with each other on Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
This article includes a set of useful tools to tackle the tasks necessary to develop geospatial data visualisations, as well as libraries based on different programming languages for geographic information processing.
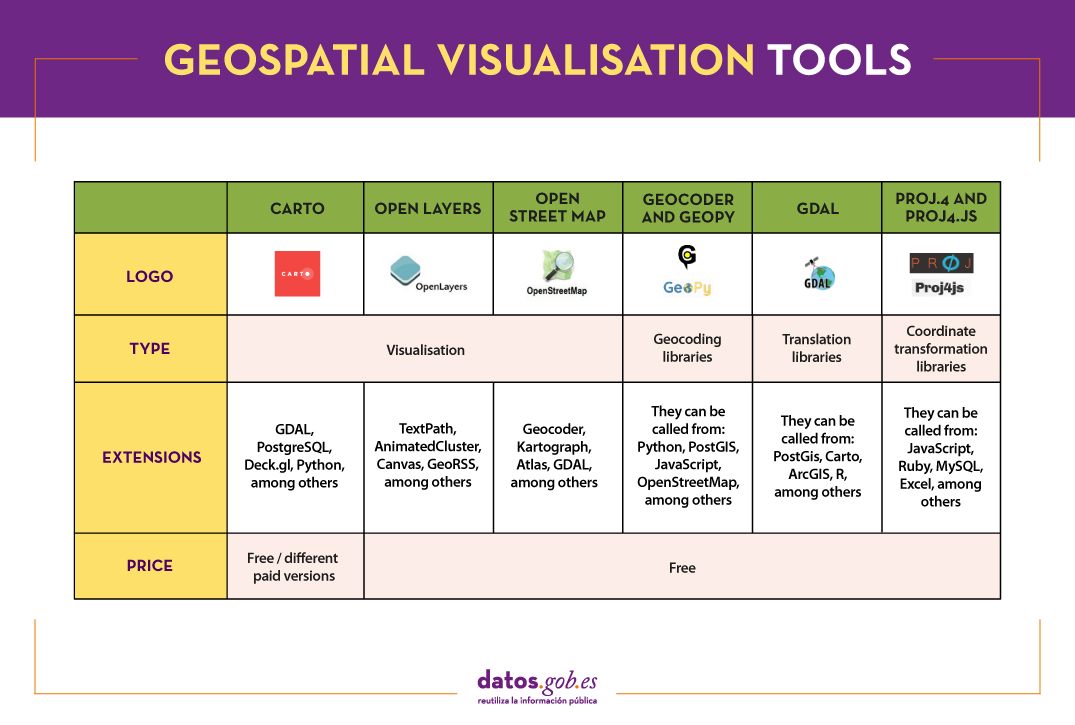
Geospatial visualisation tools
Carto
Functionality:
Carto is a geospatial data analysis platform, aimed at developers with no previous experience in geospatial information systems, which facilitates the creation of geolocated interactive applications.
Main advantages:
Its main advantage is that it allows the design and development of real-time maps that work on web platforms and mobile devices. It also allows linking with cartographic services such as Google Maps or MapBox, so that some of their functionalities, such as zoom or scrolling, can be used.
By using the PostGIS library, Carto allows querying and combining geospatial datasets, and CartoCSS can be used in the data layers to easily edit the format and appearance of the maps.
Do you want to know more?
- Support Materials: On its website, Carto offers user manuals, both for users who want to use the platform for spatial analysis and for those who want to develop apps using its suite of tools. It also offers tutorials for managing the account or configuring security, regular webinars with practical examples, a blog and various videos on its YouTube channel.
- Repository: On Github we find a multitude of repositories with resources for Carto.
- User community: Users can get in touch via Stackoverflow.
- Social media: You can keep up to date with Carto's news by following its profile on Twitter (@CARTO) or LinkedIn.
OpenLayers
Functionality:
OpenLayers is the open source JavaScript library that allows the inclusion of map-like components in any web page.
Main advantages:
OpenLayers allows you to overlay different layers and add different features such as points, lines, polygons and icons on which to link a legend. It incorporates a set of basic controls and a toolbar of advanced controls, which allows the necessary functionality to be embedded using the API. It also excels at rendering DOM elements anywhere on the map.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On the OpenLayers website there is a user manual that quickly explains how to put a simple map on a web page, or more advanced guides on the different components. There are also tutorials available that cover basic concepts, the background of OpenLayers or how to create an application. Outside of their website you can also find other helpful resources, some of which are listed in this article. If you are a beginner, we also recommend this video that explains basic functionalities in just 12 minutes.
- User community: If you want to know the experience of other users, and ask any questions, you can go to Stackoverflow.
- Social media: On their Twitter channel (@openlayers) you can participate in polls or find out related news. They also have a LinkedIn group.
OpenStreetMap
Functionality:
OpenStreetMap is a collaborative project focused on the creation of free, editable maps. These maps are created using geographic information captured with GPS devices, orthophotos and other public domain sources.
Main advantages:
Registered OpenStreetMap users can upload their GPS tracks, create and correct vector data using community-created editing tools. It also stands out because it uses a topological data structure that is stored in the WGS84 lat/lon (EPSG:4326) datum as a coordinate reference system.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In this wiki you can find information on how to use OpenStreetMap or a beginner's guide on how to start contributing. Video tutorials are also available.
- Repository: On Github there are several repositories and resources for further progress in the creation of maps.
- User community: OpenStreetMap has an official support forum, although users also have a meeting point on Stackoverflow.
- Social media: For news and trends, you can follow the Twitter account @openstreetmap or its LinkedIn profile.
Geographic information processing tools
Although these are not geospatial visualisation tools per se, it is worth highlighting the existence of libraries of different programming languages designed for the processing of geographic information.
Geocoder and Geopy:
Functionality:
Geocoder and Geopy are Python libraries designed to solve the geocoding problem. They convert postal addresses into spatial coordinates or vice versa.
Main advantages:
Both libraries incorporate the ability to calculate the distance between geolocated points.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: Users who want to work with Geopy, have at their disposal this manual that includes the installation, the use of different geocoders or how to calculate distances, among other things. If you prefer Godecoder, in this guide you will find how to install it and examples of its use.
- Repository: On Github there are repositories with resources for both Geopy and Geocoder.
- User community: En Stackoverflow puedes encontrar grupos de usuarios de Geopy y Geocoder.
GDAL
Functionality:
GDAL is an open source library available for different programming languages such as Python, Java, Ruby, VB6, Perl and R.
Main advantages:
This library allows the translation between vector and raster geospatial data. A good number of tools that incorporate Geographic Information System (GIS) functions, such as PostGIS, Carto or ArcGIS, integrate GDAL to carry out this process.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In this user manual you can find frequently asked questions and information about software and drivers. You can complement your reading with this tutorial.
- Repository: You can download everything you need to use it from Github.
- User community: Once again, it is on Stackoverflow where we find different open discussions about this tool.
- Social media: The @GdalOrg profile shares news of interest to all its users.
PROJ.4 and PROJ4.JS
Functionality:
PROJ.4 is a library available for several platforms, such as Ruby, Rust, Go or Julia, among others. PROJ4.JS is the implementation of PROJ.4 for JavaScript.
Main advantages:
PROJ.4 allows the transformation of geospatial coordinates from one coordinate reference system to another, as well as command line invocation for easy conversion of coordinates into text files.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: This manual includes information on cartographic projection, geodetic transformation or the known differences between versions, among other aspects
- Repository: On GitHub there is a space for PROJ.4 and another for PROJ4.JS.
- User community: On Stackoverflow there are also PROJ.4 and PROJ4.JS discussion groups.
The following table gives an overview of the tools mentioned above:
The criteria chosen to select these tools was their popularity, but we would like to know your opinion. Do not hesitate to leave us a comment.
These tools are included in the recently updated report "Data processing and visualisation tools". You can see more tools related to this field in the following monographs:
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
A couple of weeks ago, we commented in this article the importance of data analysis tools to generate representations that allow a better understanding of the information and make better decisions. In this article we divide these tools into 2 categories: generic data visualization tools - such as Kibana, Tableau Public, SpagoBI (now Knowage) and Grafana - and visualization libraries and APIs. We are going to dedicate this new post to the latter.
Libraries and visualization APIs are more versatile than generic visualization tools, but in order to work with them it is necessary for the user to know the programming language where the library is implemented.
There is a wide range of libraries and APIs for different programming languages or platforms, which implement functionalities related to data visualization. Next, we will show you a selection taking as a fundamental criterion the popularity that the User Community grants them.
Google Chart Tools
Functionality:
Google Chart Tools is Google's API for creating interactive visualizations. It allows the creation of dashboards using different types of widgets, such as category selectors, time ranges or autocompleters, among others.
Main advantages:
It is a very easy-to-use and intuitive tool that allows interaction with data in real time. Furthermore, the generated visualizations can be integrated into web portals using HTML5 / SVG technology.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On Youtube we find various tutorials made by API users.
- Repository: On Github we can access a common library for graphics packages, as well as know the supported chart types and examples of how to customize the components of each graphic, among others.
- User community: Users of Google Chart Tools can raise their questions in the Google community, in the space enabled for it.
JavaScript InfoVis Toolkit
Functionality:
JavaScript InfoVis Toolkit is the JavaScript library that provides functions for creating multiple interactive visualizations such as maps, hierarchical trees or line graphs.
Main advantages:
It is efficient in handling complex data structures and has a wide variety of display options, so it adapts to any developer need.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: East user manual explains the main display options and how to work with the library. Also available demos for creating different types of graphics.
- Repository: Users must download the project from http://thejit.org, although they also have available a repository on Github where, among other things, they can download extras.
- User community: Both in the Google user community like in Stackoverflow We found spaces dedicated to JavaScript InfoVis Tookit for users to share doubts and experiences.
Data-Driven Documents (D3.js)
Functionality:
Data-Driven Documents (D3.js) is the Javascript library that allows the creation of interactive graphics and complex visualizations. Thanks to it, data-based documents can be manipulated using open web standards (HTML, SVG and CSS), so that browsers can interpret them to create visualizations independently of proprietary software.
Main advantages:
This library allows the manipulation of a DOM (Object Model for Document Representation) by applying the necessary transformations to the structure based on the data linked to an HTML or XML document. This provides virtually unlimited versatility.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On Github You can find numerous tutorials, although mainly dedicated to the old versions (they are currently in the process of updating this section of the wiki and writing new tutorials on version 4.0 of D3).
- Repository: Also on Github we find up to 53 repositories, which cover different materials to manage thousands of simultaneous animations, group two-dimensional points in hexagonal trays or work with the d3-color module, among others. In this Gallery you can see some of the work done.
- User community:There are spaces for discussion about D3 in the Community of Google,Stackoverflow, Gitter Y Slack.
- Social media: On the Twitter account @ d3js_org experiences, news and use cases are shared. There is also a group in LinkedIn.
Matplotlib
Functionality:
Matplotlib is one of the most popular libraries in Python for creating high-quality graphics and visualizations. It is characterized by presenting a hierarchical organization that goes from the most general level, such as the outline of a 2D matrix, to a very specific level, such as coloring a certain pixel.
Main advantages:
Matplotlib supports text and labels in LaTeX format. In addition, users can customize its functionality through packages designed by third parties (Cartopy, Ridge Map, holoviews, among others).
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On its own website we find a user's GuideIt includes information on the installation and use of the various functionalities. Also available tutorials for both beginners, intermediate or advanced users.
- Repository: In this repository Github are the materials you need for installation. On the web you can see a Gallery with examples of works for your inspiration.
- User community: The official website has a community section, although you can also find user groups to help you with your questions in Stackoverflow and Gitter.
- Social media: On Twitter profile @matplotlib Examples of user work and visualizations are also shared, as well as information on the latest news in the tool.
Bokeh
Functionality:
Bokeh is the Python library oriented to the creation of interactive graphs based on HTML / JS. It has the ability to generate interactive visualizations with features such as floating text, zoom, filters or selections, among others.
Main advantages:
Its main advantage is simplicity in implementation: complex interactive visualizations can be created with just a few lines of code. In addition, it allows embedding JavaScript code to implement specific functionalities.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: This User's guide provides detailed descriptions and examples that describe many common tasks that can be performed with Bokeh. On the Bokeh website we also find this tutorial and application examples built with this tool.
- Repository: In this repository Github There are the materials and instructions for its installation, as well as examples of use. Examples are also available in this Gallery.
- User community: The official community can be found on the website of Bokeh, although the users of this tool also meet in Stackoverflow.
- Social media:To keep up to date with news, you can follow the Twitter account @bokeh or your profile in LinkedIn.
The following table shows a summary of the tools mentioned above:
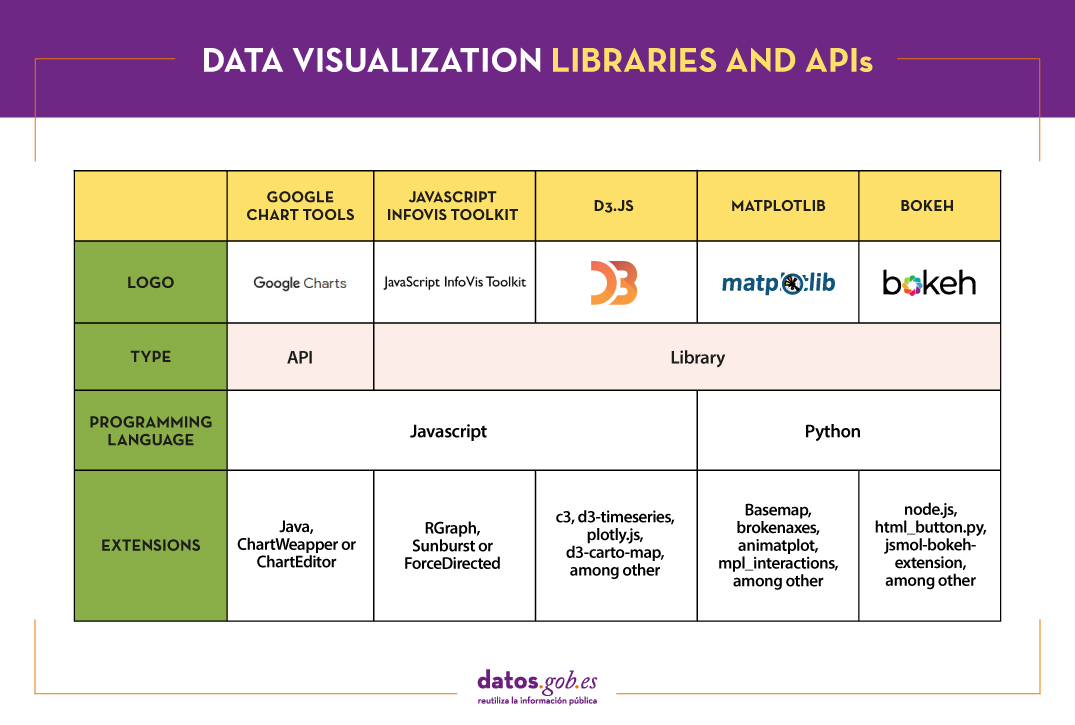
Are you agree with our selection? We invite you to share your experience with these or other tools in the comments section.
If you are looking for tools to help you in data processing, from datos.gob.es we put at your disposal the report "Data processing and visualization tools”, Recently updated, as well as the following monographic articles:
- The most popular data conversion and data cleaning tools
- The most popular data analysis tools
- The most popular data visualisation tools
- The most popular geospatial visualisation tools
- The most popular network analysis tools
Content elaborated by datos.gob.es team.
Data is a fundamental pillar in business decision making. Before making any decision, it is necessary to analyze the situation to understand the context and envision possible alternatives. And for this it is necessary to present the data in a clear and understandable way.
Data analysis is useless if we cannot get the result to be understood. And the best way to understand the data is to visualize it.
What is data visualization?
Data visualization is a task linked to data analysis whose objective is the graphical representation of the underlying information of the data. For this, basic graphic elements are used, such as line graphs, scatter graphs or heat maps, to complex visualizations configured on a dashboard or control panel.Data visualization allows you to detect patterns, trends or anomalous data, project predictions or communicate inferences derived froml data analysis, among other issues.
Thanks to these representations, people without advanced analytics knowledge can interpret and understand data more easily and make decisions based on them in fields as diverse as marketing, health, science, economics, journalism or even art.
We can divide the data visualization tools into two categories. On the one hand, the generic visualization tools and, on the other, the libraries and visualization APIs, which are more versatile, but require the use of programming languages.In this article we are going to focus on the former.
Top examples of generic data visualization tools
Kibana
Functionality:
Kibana is an open source software that is part of the product package Elastic Stack. Provides indexed data exploration and visualization capabilities on top of the analytics engine Elasticsearch.
Main advantages:
Its main advantage is that it presents the information visually through customizable dashboards, through the integration of faceted filters by ranges, information categories, geospatial coverage or time intervals, among others. In addition, it has a catalog of development tools (Dev Tools) to interact with the data stored in Elasticsearch.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On Elastic's own website we find this user manualIt includes basic concepts to configure Kibana, how to create and customize dashboards, how to interact with Kibana APIs, among others. Elastic also offers short videos on its channel Youtube and organizes, periodically, webinars where various aspects and use cases are explained on Kibana.
- Repository: In this Github you have different resources for its configuration, including plugins, tests and examples.
- User community: There is an official user community in their Web page, although you can also find discussion groups at Stackoverflow.
- Social media: You can follow the Twitter account @elastic to stay up-to-date with Kibana news and discover user experiences, or join their group of LinkedIn.
Tableau Public
Functionality:
Tableau Public is a tool designed to carry out visualizations combining a graphical interface with common elements of the Business Integillence tools, such as the variable organization model through the use of dimensions and the connection with databases or datasets.
Main advantages:
It stands out for its graphic, efficient and fast interface, and for its simple integration of databases or spreadsheets of any size. In addition, it allows the combination of various data sources in a single view.
As a negative point, in order to use the free version, both the data and the views must be published on your website in a public way, eliminating the confidentiality of the information.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: Tableau offers a manual with 8 stepsto get started with Tableau Desktop, including everything from connecting to your data to sharing your findings. You can also find on the Tableau website tutorials, a visualization gallery, resources for users (such as podcasts or contests) and a Blog with related articles.
- User community: In the official forum From Tableau you can find more than 450 user groups and answers to more than 195,000 questions.
- Social media: On the Twitter account @tableaupublic Examples of visualizations, experiences, and news information are included. Also available is a group of LinkedIn.
SpagoBI (Knowage)
Functionality:
Grafana allows you to create interactive and dynamic visualizations. Originally started as a component of Kibana, today they are completely independent tools.
Main advantages:
SpagoBI allows you to create customizable and exportable reports in different formats (HTML, PDF, XLS, XML, TXT, CSV and RTF) that can contain tables, cross tables, interactive graphics and text.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On this document you can find an installation manual, an administration manual, a user guide and information about the different functionalities. On his channelYoutubeYou can find different playlists with success stories, examples of visualizations, tutorials on different functionalities or webinars, among others. In the case of webinars, you can also access them fromtheir website, where the agenda with the next appointments is included.
- Repository: On Github there are different repositories with material of interest to SpagoBI users.
- User community: You can find different questions posed by users -and their answers- in Stackoverflow.
- Social media: The user community also has at its disposal a group of LinkedIn. On Twitter, channels coexist @SpagoBI and @knowage_suite, that inform about the news and show examples of work carried out with this tool.
Grafana
Functionality:
Grafana allows you to create interactive and dynamic visualizations. Originally started as a component of Kibana, today they are completely independent tools.
Main advantages:
This tool allows users to interact, exchanging data or dashboards. In addition, it integrates different databases such as: PostgreSQL, MySQL and Elasticsearch, from which you can obtain metrics, filter data or make annotations in real time.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In the Grafana websitethere is multiple information on how to install this tool, create a dashboard or manage alerts. They also have a Blog as well as with webinars and videos, also available in your Youtube channel.
- Repository: From this GitHub you can download packages and resources, like plugins.
- User community: As in some of the previous cases, we found an official community in the own Grafana website, and informal communities in Gitter and Stackoverflow.
- Social media: Twitter account @grafana shows examples of use and helps spread the news highlighted on the blog. Users can also join their group of LinkedIn.
The following table shows a summary of the tools mentioned above:
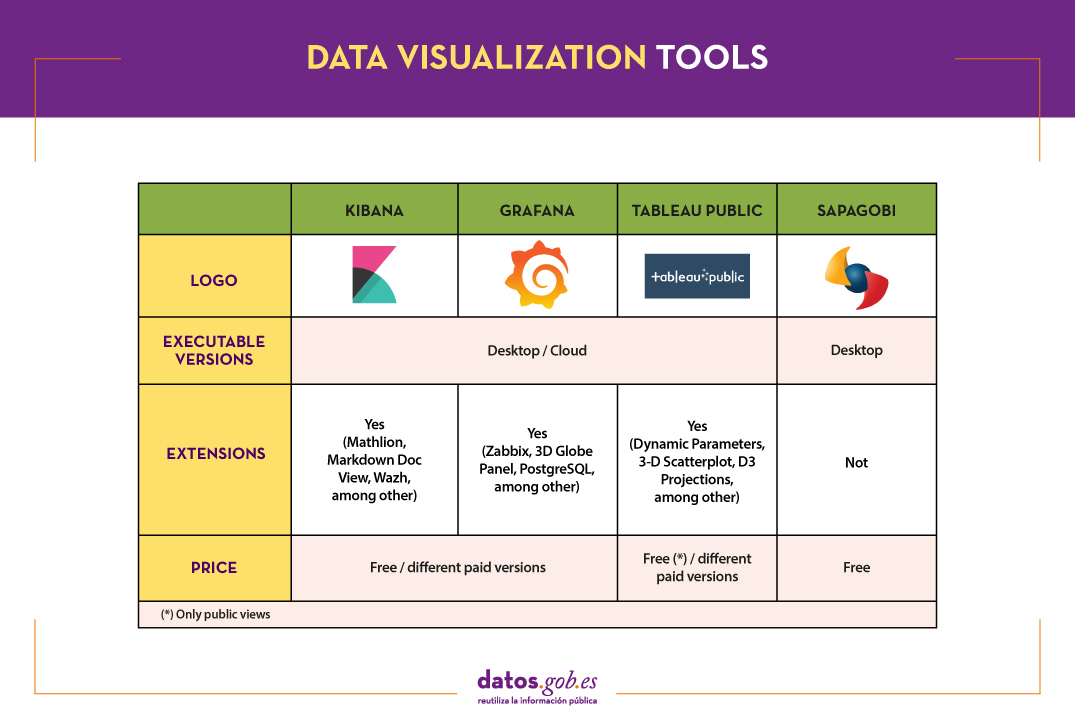
These are just 4 examples of popular tools fromdata visualization. Soon we will put at your disposal an article with examples of libraries and visualization APIs. We invite you to share your experience with these or other tools in the comments.
If you want to know more about the different phases of data processing, you can see the full report "Data processing and visualization tools", recently updated. In addition, you have at your disposal the following monographic articles:
- The most popular data conversion and data cleaning tools
- The most popular data analysis tools
- The most popular data visualisation libraries and APIs
- The most popular geospatial visualisation tools
- The most popular network analysis tools
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
Data analysis is a process that allows us to obtain knowledge of the underlying information of the data, with the purpose of drawing conclusions that allow us to make informed decisions. Without data analytics, companies and organizations are limited in examining their results and determining the direction to take to have the best chance of success.
Types of analytics
Within the field of analytics we find different processes that try to respond to the past, present and future of our activities:
- Exploratory analysis, which subjects the data to statistical treatment, to determine why a certain event has occurred.
- Descriptive analysis, which explores the data from different perspectives to find out what happened.
- Predictive analytics, which allows predicting future values of the variables of interest to know what will happen.
- Prescriptive analysis, that offers recommendations when testing the environment variables and suggesting those with the highest probability of generating a positive result.
This article contains a selection of popular data analysis tools that will allow you to perform these tasks, divided based on two target audiences:
- Tools that perform simple analysis and do not involve programming tasks, aimed at users without advanced technical knowledge.
- Tools that present greater versatility, but require the use of programming languages, so they are aimed at users with mathematical and computer knowledge.
It is convenient to remember that before carrying out any analysis of this type it is necessary to transform the data that we use so that they have the same structure and format, free of errors, something that we already saw in the article Data conversion and debugging tools.
Data analysis tools for non-programmers
WEKA
Functionality:
WEKA is a cross-platform machine learning and data mining software. Its functionalities can be accessed through a graphical interface, a command line or a Java API.
Main advantages:
One of its main advantages is that it contains a large number of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks and allows access to other tools such as scikit-learn, R and Deeplearning4j.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: As an appendix to the book Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning: tools and techniques, we found this WEKA manual that brings us closer to its panels and functionalities. It includes methods for the main data mining problems: regression, classification, clustering, association rules, and attribute selection. We also have at our disposal on the net this manual and these tutorials prepared by the University of Waikato, a body that has also launched a Blog on matter.
- Repository: The official WEKA source code is available at this url. You can also access it from this repository Github, as well as different packages or tools.
- User community: You can find user groups in Stackoverflow.
KNIME
Functionality:
KNIME is a data mining software that allows data analysis and visualizations through a graphical interface.
Main advantages:
The graphical interface on which the data analysis flows are modeled uses nodes, which represent the different algorithms and arrows that show the flow of data in the processing pipeline. In addition, it allows incorporating code developed in R and Python, as well as interaction with WEKA.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On KNIME's own website you can find different help documents, that guide you in its installation, the creation of workflows or the use of nodes. In addition, on his channe lYoutube you can find multiple videos, including playlists with basic aspects for users who are facing this tool for the first time.
- Repository: On GitHub Tools are provided to configure the KNIME SDK (Software Development Kit), so that you can work with the source code of the extensions or develop your own.
- User community: KNIME users have groups at their disposal to answer questions in Gitter Y Stackoverflow, as well as a discussion forum on the website of Knime.
- Social media: You can follow the Twitter account @knime and his profile of LinkedIn to keep up to date with KNIME news and related events or talks.
ORANGE
Functionality:
Orange is open machine learning and data mining software, similar to Knime.
Main advantages:
Orange creates the analysis and data visualizations using the drag and drop paradigm from awidget catalog representing different tasks. Also, it can be installed as a Python library.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In this case we highlight two books. First, Introduction to data mining with Orange, which collects the workflows and visualizations of the course on Introduction to Data Mining from Orange himself. Second, Orange Data Mining LibraryDocumentation, a brief introduction to scripting in Orange. You can also find video tutorials on the YouTube channel Orange Data Mining.
- Repository: From this GitHub you can download the necessary resources for its installation.
- User Community: In Gitter, StackExchange and Stackoverflow users have created spaces where they can ask questions and share experiences.
- Social media: On twitter profile@OrangeDataMiner and his LinkedIn account reports, events, use cases and news related to this tool are collected.
Data analysis tools for non-programmers
R (The R Project for statistical computing)
Functionality:
R is an interpreted object-oriented programming language, initially created for statistical computing and the creation of graphical representations.
Main advantages:
R is one of the most used languages in scientific research and this is due to its many advantages:
- It has a programming environment, R-Studio.
- It consists of a set of functions that can be easily expanded by installing libraries or defining custom functions.
- It is permanently updated due to its extensive community of users and programmers, who since its inception contribute to the development of new functions, libraries and updates available to all users freely and for free.
Do you want to know more?
- support materials: Due to its popularity, there are a large number of helpful materials. As an example we highlight the books R for Data Science and R manual. You can also find guides in the web space The R Manuals and the webinars that from the own R Studio they organize.
- User community: There is a discussion space in Stackoverflow. In addition, in Spain, we find two groups that carry out different activities (hackathons, conferences, courses ...) to promote the use of R: R-Hispanic community and R-Ladies. You can know more about them in this article.
- Social media: R has a LinkedIn group with almost 150,000 members.
Python
Funcionalidad:
Python is a dynamic, multi-platform, multi-paradigm interpreted programming language, partially supporting object-oriented programming, structured programming, imperative programming, and functional programming.
Main advantages:
It is a simple programming language. Its philosophy emphasizes providing human-readable, easy-to-use, and easy-to-learn code syntax. In addition, it allows the integration of libraries such as Matplotlib, Bokeh, Numpy, Pandas or spaCy, to implement functions that enable complex interactive graphing and statistical analysis.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: As with R, being a very popular language, we find a lot of materials and help on the net, such as tutorials The Python Tutorial Y LearnPython.org, or the portal with videos Pyvideo, where you can find various webinars.
- Repository: In Github you can find different repositories related to the Python programming language.
- Community of users: Those uruaries with questions can seek the help of people in the same situation in Stackoverflow or Gitter. On Python's own website you can also find a large number of communities Worldwide.
- Social media: The official twitter profile of the Python Software Foundation is @ThePSF. There is also group in Linkedin.
GNU Octave
Functionality:
GNU Octave is a programming language designed primarily to solve computational algebra tasks. It is the best known alternative to the commercial MATLAB solution, but free and open. Also, it does not have a graphical interface.
Main advantages:
GNU Octave has powerful built-in mathematical functions (differential equations, linear algebra, matrix calculus) and can be extended with the addition of libraries, such as Scientific Library, Dionysus or Bc. It also has a index package with numerous extensions that enrich the functionality of the tool.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In this link You have the notes of the GNU Octave course from the Complutense University of Madrid. On the GNU Octave website you can also find manuals and on your youtube profile, video tutorials.
- Repository: The GNU Octave developer community has a variety of repositories on Github with materials of interest.
- User Community: In Stackoverflow and in the GNU Octave website there is a space for users to share opinions and experience.
- Social media: You can follow the news related to this tool on the Twitter account @GnuOctave and this group of LinkedIn.
The following table shows a summary of the tools mentioned above:

This is just a selection of data analysis tools, but there are many more. We invite you to share your experience with these or other solutions in the comments.
For those who want to know more about these tools and others that can help us during the different phases of data processing, at datos.gob.es we offer you the recently updated report "Data processing and visualization tools". You can see the full report here.
You can see more tools related to this field in the following monographs:
- The most popular data conversion and data cleaning tools
- The most popular data visualisation tools
- The most popular data visualisation libraries and APIs
- The most popular geospatial visualisation tools
- The most popular network analysis tools
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.
When carrying out a data analysis project, it is usual to work with different sources, which in many cases include datasets with Heterogeneous formats and structures that do not always share the same quality. Therefore, one of the first phases in any data analysis process is known as data cleaning.
What is data cleaning?
When we talk about data cleaning, we refer to the set of processes necessary for the preparation and transformation of data from different sources for analysis. As a result of these processes, a homogeneous structure is generated, free of errors and in the appropriate format, which will be actionable in the subsequent stages of analysis. This resulting data set is known as a data mining view.
Cleannig is essential in data processing, as it standardizes and formats it before entering it into the target system, so that we can work with it appropriately.
Among the different processes that make up the data purification phase, the conversion of the data is included, which involves the transformation of the data to a specific format. In this way they can be used by tools that only accept certain formats.
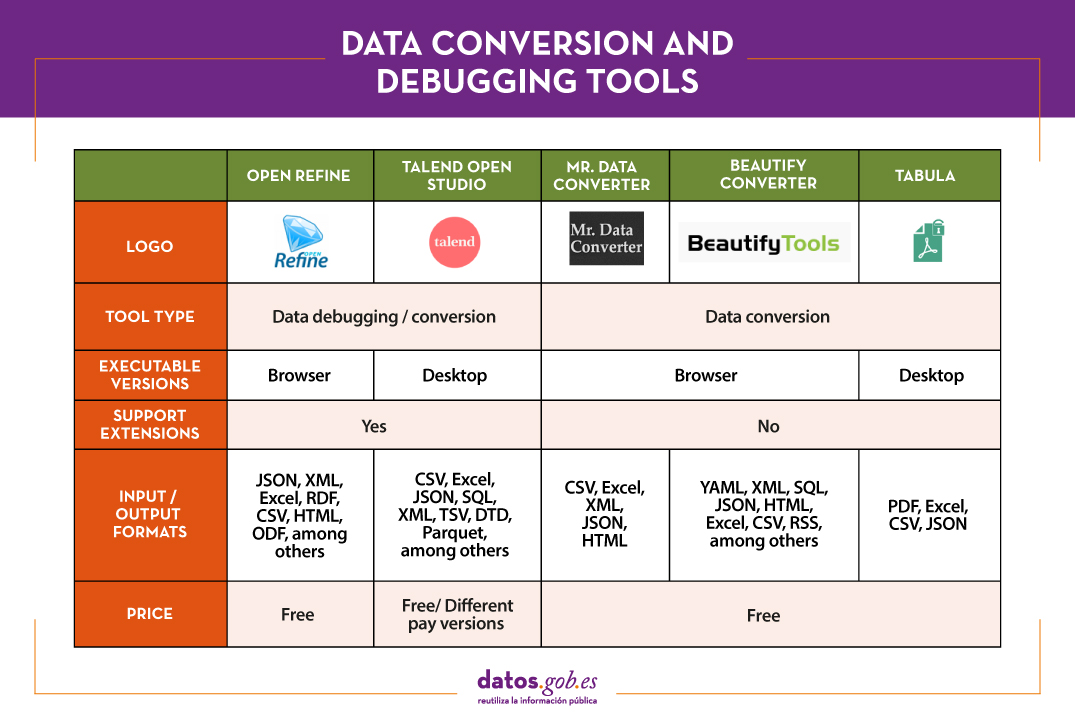
In the market we find many data cleaning tools that also convert them to other formats, although there are also tools that perform each of these tasks exclusively. Here are some examples selected in phase of their popularity, although we invite you to leave in comments any mention of other tools that may be of interest to you.
Top examples of data cleaning tools
Two of the most used tools in the field of data cleaning are Open Refine and Talend Open Studio.
OpenRefine
Functionality:
OpenRefine is a free tool that seeks to improve the quality and structure of the data by correcting common errors such as data duplication, incomplete data or inconsistencies. Thanks to it, users can organize, clean, apply transformations, convert to different formats, and enrich data by using web services and other external data sources.
Main advantages:
One of its main advantages is that it uses the language GREL (Google Refine Expression Language), which allows you to perform advanced debugging tasks by applying a large number of functions using regular expressions. In addition, it allows incorporating additional extensions by accessing functions to georeference information, link data from the DBpedia or other sources, generating data linked in RDF.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: In this user manual all aspects of configuring and using Open Refine 3.4.1 are covered, including all functions and features of the interface and this youtube account different video-tutorials.
- Repository: In this GitHub there are the necessary resources so that you can operate OpenRefine from Mac OS, Linux and Windows.
- User community:OpenRefine users can find discussion groups atGoogle, and Stackoverflow.
- Social media:On the Twitter account of @OpenRefine You can find videos, guides, information about the latest news or upcoming events related to OpenRefine.
Talend Open Studio
Functionality:
Talend Open Studio is an open source solution that integrates a set of ETL (Extract, Transform and Load) tools designed to extract, debug and transform data sets for further analysis. As a result, it generates standardized code in Perl and Java that can be reused in different projects.
Main advantages:
This tool stands out for its intuitive interface based on component programming, a technique that consists of concatenating processes with various functionalities through input and output flows.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: On Talend's own website you can find different user manuals Y tutorials to discover Talend Studio and its interface, and create a project, along with simple sample jobs.
- Repository: This GitHub contains the Talend Open Studio source files, which files should be used in conjunction with the common code contained in tcommon-studio-se
- User community: OnStackoverflow There are channels where users share their experience and ask different questions.
- Social media: Talend Open Studio has a page of LinkedIn and the perfil@Talend on Twitter, where they share news, experiences and use cases, among others.
Top Examples of Data Conversion Tools
In the case of data conversion, Mr Data Converter, Beautify Converters and Tabula stand out for their popularity.
Mr Data Converter
Functionality:
Mr Data Converter is a web application that allows you to easily convert data found in CSV or Excel to other formats such as CSV, JSON, HTML and XML.
Main advantages:
One of its strengths is that the data is incorporated by copying and pasting on the application interface, without the need to upload any files. The same happens when exporting, where it is enough to copy and paste the generated code. On the negative side of the scale, we find a limitation in the maximum size of the data, which should not exceed 300 MB.
Do you want to know more?
- Repository: You can find information about the license and different materials in this GitHub.
Beautify Converters
Functionality:
Beautify Converters a web application that allows you to convert data to JSON, SQL, CSV or Excel formats, among others. It belongs to the Beautify Tools collection of free online tools.
Main advantages:
As with Mr Data Converter, the user can incorporate the data by copying and pasting on the application interface. You can also do this by uploading the file from a local computer. Unlike the previous tool, it supports a significantly higher number of formats, SQL, YAML or RSS.
Do you want to know more?
- Repository: In this repository GitHub You have information about the license and the rest of the tools in the Beautify Tools collection.
Tabula
Functionality:
Tabula allows you to extract tables from PDF reports -except for those that are only image-, in formats reusable by data analysis and visualization tools.
Main advantages:
Its main advantage is a very simple interface. It will only be necessary to upload the PDF, select the tables that we want to extract and finally select the desired format, Excel, CSV or JSON.
Do you want to know more?
- Support materials: The Junta de Andalucía has developed thistutorialwhere it tells how to upload a PDF file to Tabula and extract the tabular data in CSV format, ready for use in spreadsheets. The process is exemplified with the data setSanitary quality of bathing water.
- Repository: You can download the materials from this link or GitHub.
- Social media: Twitter. Account @TabulaPDF Although it is not very up-to-date, it offers, among others, information on bug fixes and maintenance, guides and comments from users who use this tool.
The following table shows a summary of the tools mentioned above:
The adaptation and conversion of the data can consume a great amount of resources, economic and temporary, of any project. These types of tools help to carry out these activities with agility and efficiency, freeing up data scientists to focus on other activities.
For those who want to know more about these tools and others that can help us during the different phases of data processing, at datos.gob.es we offer you the recently updated report "Data processing and visualization tools". You can see the full report here.
You can see more tools related to this field in the following monographs:
- The most popular data analysis tools
- The most popular data visualisation tools
- The most popular data visualisation libraries and APIs
- The most popular geospatial visualisation tools
- The most popular network analysis tools
Content prepared by the datos.gob.es team.