EDP publishes new report analyzing Copernicus data use cases
Fecha de la noticia: 22-04-2021

The European Data Portal (EDP) has presented its report "Copernicus data for the open data community", prepared by con.terra as part of the EDP consortium. As we have reported before, Copernicus is the European Union's Earth Observation program that provides accurate, timely and easily accessible information to improve environmental management, understand and mitigate the effects of climate change and ensure civil security.
The report aims to help users harness the potential of Copernicus data to create Earth observation applications by answering three basic questions:
- What can I do with Copernicus data?
- How can I access the data?
- What tools do I need to use the data?
After an introduction reviewing the main activities and services available from the program, the report is divided into two parts: a first part where examples of Copernicus data applications are examined and a second, more practical part, where a particular use case is replicated in depth.
Copernicus use cases
The first part covers a series of possible use cases at a general level to answer the first of the questions posed above: what can be done with Copernicus data?
The use cases discussed are linked to the thematic areas addressed by the Copernicus program (emergency, security, marine, land, climate change and atmospheric monitoring), as well as to its services and tools. These examples cover the observation of plastic pollution of the oceans, land change due to mining activities, the impact of volcanic activities, ice loss, the creation of artificial islands, deforestation, forest fires, storms or pests.
The report highlights the importance of knowing what data are appropriate for each specific use case. For example, SENTINEL 2 MSI data is suitable for land monitoring, emergency management and security services, while SENTINEL 3 Altimetry data is linked to the areas of marine monitoring and climate change. To assist in this identification task, the guide includes references to various user guides with specifications on the missions, the instruments used to collect the data and the data products generated.
Case study on the use of Copernicus data
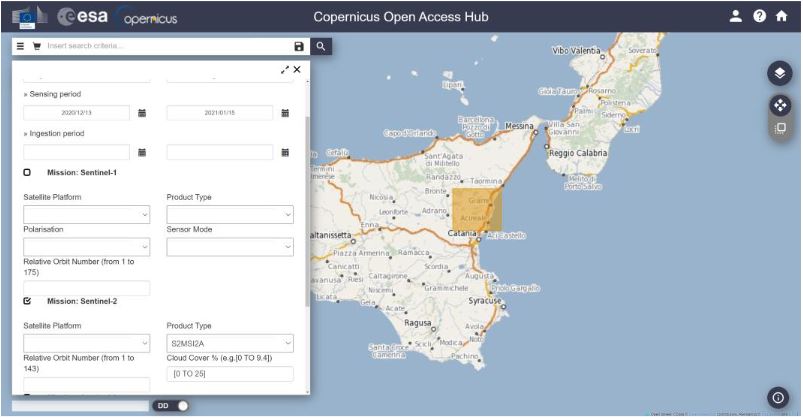
The second part of the report focuses on a particular use case that it addresses in depth, including how to download the appropriate data, process it and build applications with it. Specifically, it addresses the mapping of the lava flow of the Etna volcano using data from the Copernicus emergency management service. The aim is to track the impact of volcanic activities on nature and urban areas.
First, the report shows how to search and download data for this area of interest. In this case, Sentinel-2 products are used from the Copernicus Open Access Hub. The entry point for accessing the Copernicus data is their own website, which provides an overview of the data access points. Through different images, the report shows search and filter options to locate the appropriate data.
To visualize and process the data, it is proposed to use commercial software such as ArcGIS Pro, free GIS tools such as QGIS, open source processing tools such as SNAP or programming libraries such as GDAL. In the case of the example, SNAP (Sentinel Application Platform), the European Space Agency (ESA) platform, is used to view the lava flow.
Some explanations on workflow automation with the Open Access Hub API and the SNAPgraph tool are given at the end of the chapter.
Final conclusions
The report ends with several conclusions, among which the following stand out:
- Users can extract great value from Copernicus data but to do so they need to be familiar with the platforms involved and the necessary tools.
- For most use cases, it is necessary to combine Copernicus data with in situ data. The Copernicus program itself uses data from ground-based sensors, for example, for calibration and validation of its products.
Spain's role in Copernicus
The Ministry of Transport, Mobility and Urban Agenda, through the National Geographic Institute, and the Ministry for Ecological Transition (MITECO) represent Spain in the Copernicus User Forum, for the monitoring and evolution of the program. In this interview Nuria Valcárcel, Deputy Assistant Director (Observation of the Territory) of the General Directorate of Geodesy and Cartography, in the D.G. National Geographic Institute (IGN) delves into the services of Copernicus and its usefulness in the economic and social field.
In datos.gob.es you can also find this other interview with Stéphane Ourevitch, founder of SpaceTec, who participated as a speaker at the Encuentro Aporta 2019, where he tells us about the usefulness of data for space observation and how the Copernicus program promotes entrepreneurship through actions such as hackathons.
Copernicus data are very useful all over the world. In our country, we also find multiple services and applications developed based on Copernicus data, some of which are collected in this article.











