
A few weeks ago, we picked up on an article what were the most demanded datasets among all those offered by the Autonomous Communities, and that met certain standards that encouraged their reuse.On this occasion, we would like to focus on local entities. In order to draw up the list, we have taken the same questionnaire as a reference, where they were asked to identify in a simple way sets of data published by their organisation and which, from their point of view, meet the aforementioned characteristics. The Provincial Councils and Municipalities that have collaborated are:
All these organizations share data openly and in formats that facilitate their use by companies, researchers or the general public, through different spaces, accessible in the previous links. Most of the participants are local councils, but there are also two provincial councils. Provincial councils play a very important role in the open data ecosystem, as they promote the opening of data in small town councils, which without them would not be able to carry out these tasks. They are fundamental when it comes to highlighting interesting and useful regional data.
These 17 local entities are just a small sample of the open data ecosystem at the local level in Spain, but the presence in our country of this type of project is much greater. Specifically, in datos.gob.es we have identified 230 local initiatives open data.
Transport, environment and public sector, the most demanded data categories
From the responses of the organizations participating in the survey, it is extracted that the most demanded local data sets are the following:
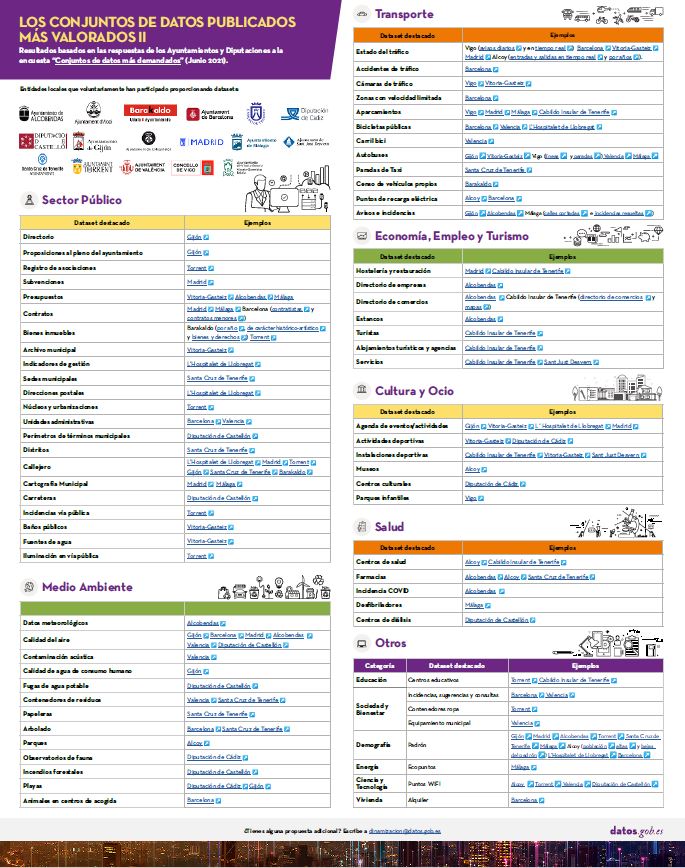
Click here to see the infographic in full size and in its accessible version.
Three categories stand out: transport, environment and public sector data. Three fundamental sectors to achieve efficient and sustainable cities.
In the case of transport data, those related to the state of traffic, parking lots and public services (such as public buses or bicycles) stand out, key to promoting an environmentally friendly transport system, in line with the marked on the "Sustainable and smart mobility strategy". These data are usually provided in real time, facilitating their re-use and helping public administrations, private companies and individuals to manage mobility more efficiently.
The air quality data are the most prominent in the environment section, highlighting the growing concern about pollution in our cities. Do not forget that according to the study Air quality in the Spanish State during 2020, prepared by Ecologists in Action, 42 million people breathed polluted air during the past year (that is, 88.4% of the population), which caused 30,000 premature deaths. Public agencies are increasingly aware of this situation, and carry out air quality assessments on a regular basis, which has led to the installation of more monitoring stations. Spain currently has 616 monitoring stations for official assessment, of which 535 measure NO2 and 475 record information on PM10 levels, generating valuable data for reutlisation and policy decisions.
In the environment category we also find datasets related to garbage management, noise pollution or trees in cities.
Regarding the public sector, we find a large number of datasets related to urban planning and infrastructures, such as the street map, municipal cartography or real estate. Datasets related to the activity of Public Administrations and their transparency, such as contracts, budgets or subsidies, also stand out.
Other prominent categories are the economy, employment and tourism, with datasets such as the Directory of businesses or hotels and restaurants; culture and leisure, where we find datasets on sports facilities or the events agenda; or health, with information on health centers, pharmacies or covid data. Finally, data on education, society and well-being, demography, science and technology, and housing have also been collected.
It should be noted that a large majority of the data sets highlighted by the Town Halls and Provincial Councils are included in the guide. Open data FEMP 2019: 40 datasets to be published by Local Entities, elaborated by the Federation of Municipalities and Provinces of Spain(FEMP). It contains a series of datasets considered priority and that should be published openly by local organizations, as well as instructions to do so in a harmonized way that facilitates interoperability.They also coincide with the vocabularies promoted by the Ciudades Abiertas project. It is, therefore, an opportunity to advance in the standardisation of the way in which data is published.
Why is local open data important?
The possibility of having local data, updated and differentiated by municipalities (or even districts or streets), allows to know the reality of each geographical area in a more concrete way. It allows us to appreciate differences and needs, and based on this, make more accurate decisions that help promote public policies aligned with the demands of citizens.
This data can also be reused, both by the administration itself and by third parties, to launch products that bring public services closer to citizens. This is the case of transport applications, which inform us about the most efficient and fastest way to reach our destination; or apps to recycle, which tell us where the closest waste containers are.
In short, the publication and reuse of open data not only benefits citizens, but also administrations when it comes to performing a more efficient management.



Genial infografía.