
The humanitarian crisis following the earthquake in Haiti in 2010 was the starting point for a voluntary initiative to create maps to identify the level of damage and vulnerability by areas, and thus to coordinate emergency teams. Since then, the collaborative mapping project known as Hot OSM (OpenStreetMap) has played a key role in crisis situations and natural disasters.
Now, the organisation has evolved into a global network of volunteers who contribute their online mapping skills to help in crisis situations around the world. The initiative is an example of data-driven collaboration to solve societal problems, a theme we explore in this data.gob.es report.
Hot OSM works to accelerate data-driven collaboration with humanitarian and governmental organisations, as well as local communities and volunteers around the world, to provide accurate and detailed maps of areas affected by natural disasters or humanitarian crises. These maps are used to help coordinate emergency response, identify needs and plan for recovery.
In its work, Hot OSM prioritises collaboration and empowerment of local communities. The organisation works to ensure that people living in affected areas have a voice and power in the mapping process. This means that Hot OSM works closely with local communities to ensure that areas important to them are mapped. In this way, the needs of communities are considered when planning emergency response and recovery.
Hot OSM's educational work
In addition to its work in crisis situations, Hot OSM is dedicated to promoting access to free and open geospatial data, and works in collaboration with other organisations to build tools and technologies that enable communities around the world to harness the power of collaborative mapping.
Through its online platform, Hot OSM provides free access to a wide range of tools and resources to help volunteers learn and participate in collaborative mapping. The organisation also offers training for those interested in contributing to its work.
One example of a HOT project is the work the organisation carried out in the context of Ebola in West Africa. In 2014, an Ebola outbreak affected several West African countries, including Sierra Leone, Liberia and Guinea. The lack of accurate and detailed maps in these areas made it difficult to coordinate the emergency response.
In response to this need, HOT initiated a collaborative mapping project involving more than 3,000 volunteers worldwide. Volunteers used online tools to map Ebola-affected areas, including roads, villages and treatment centres.
This mapping allowed humanitarian workers to better coordinate the emergency response, identify high-risk areas and prioritize resource allocation. In addition, the project also helped local communities to better understand the situation and participate in the emergency response.
This case in West Africa is just one example of HOT's work around the world to assist in humanitarian crisis situations. The organisation has worked in a variety of contexts, including earthquakes, floods and armed conflict, and has helped provide accurate and detailed maps for emergency response in each of these contexts.
On the other hand, the platform is also involved in areas where there is no map coverage, such as in many African countries. In these areas, humanitarian aid projects are often very challenging in the early stages, as it is very difficult to quantify what population is living in an area and where they are located. Having the location of these people and showing access routes "puts them on the map" and allows them to gain access to resources.
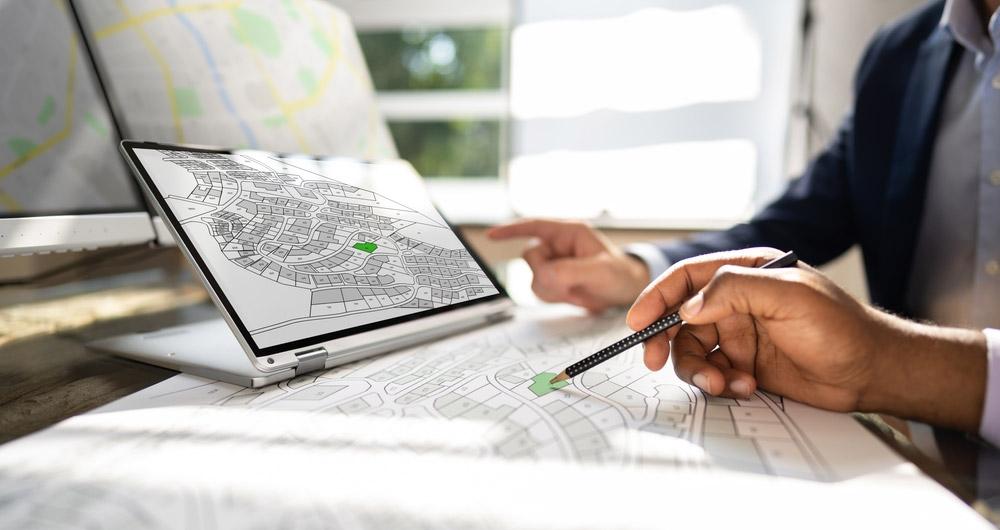
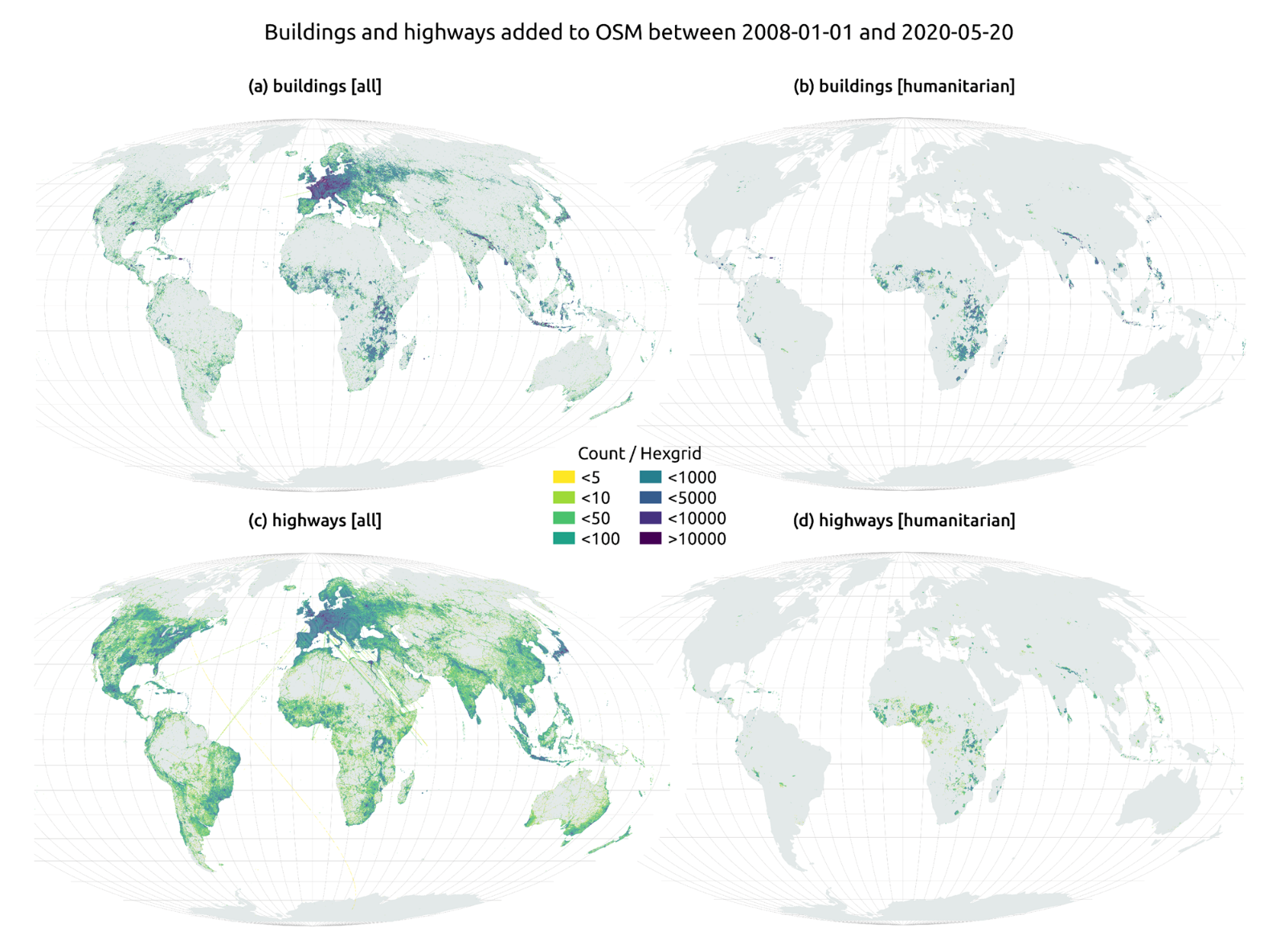
In this article The evolution of humanitarian mapping within the OpenStreetMap community by Nature, we can see graphically some of the achievements of the platform.
How to collaborate
It is easy to start collaborating with Hot OSM, just go to https://tasks.hotosm.org/explore and see the open projects that need collaboration.
This screen allows us a lot of options when searching for projects, selected by level of difficulty, organisation, location or interests among others.
To participate, simply click on the Register button.
Give a name and an e-mail adress on the next screen:

It will ask us if we have already created an account in Open Street Maps or if we want to create one.
If we want to see the process in more detail, this website makes it very easy.
Once the user has been created, on the learning page we find help on how to participate in the project.
It is important to note that the contributions of the volunteers are reviewed and validated and there is a second level of volunteers, the validators, who validate the work of the beginners. During the development of the tool, the HOT team has taken great care to make it a user-friendly application so as not to limit its use to people with computer skills.
In addition, organisations such as the Red Cross and the United Nations regularly organise mapathons to bring together groups of people for specific projects or to teach new volunteers how to use the tool. These meetings serve, above all, to remove the new users' fear of "breaking something" and to allow them to see how their voluntary work serves concrete purposes and helps other people.
Another of the project's great strengths is that it is based on free software and allows for its reuse. In the MissingMaps project's Github repository we can find the code and if we want to create a community based on the software, the Missing Maps organisation facilitates the process and gives visibility to our group.
In short, Hot OSM is a citizen science and data altruism project that contributes to bringing benefits to society through the development of collaborative maps that are very useful in emergency situations. This type of initiative is aligned with the European concept of data governance that seeks to encourage altruism to voluntarily facilitate the use of data for the common good.
Content by Santiago Mota, senior data scientist.
The contents and views reflected in this publication are the sole responsibility of the author.