The amount of data we generate does not stop growing. 90% of the data created in the history of humanity were produced during the last year and a 40% annual growth is estimated for the next decade. These figures highlight the importance of data in today's economy and society. The data provide us with knowledge, which facilitate to make the right decisions at the right time.
To optimize the advantages that the use of data can bring to our day to day, an increasing number of organizations and companies are implementing new technologies that help to improve their management and obtain greater value. The report New trends and challenges in the data world analyzes some of these technological and social trends that are revolutionizing the world of data. These technologies are big data and artificial intelligence, decision algorithms, internet of things and blockchain.
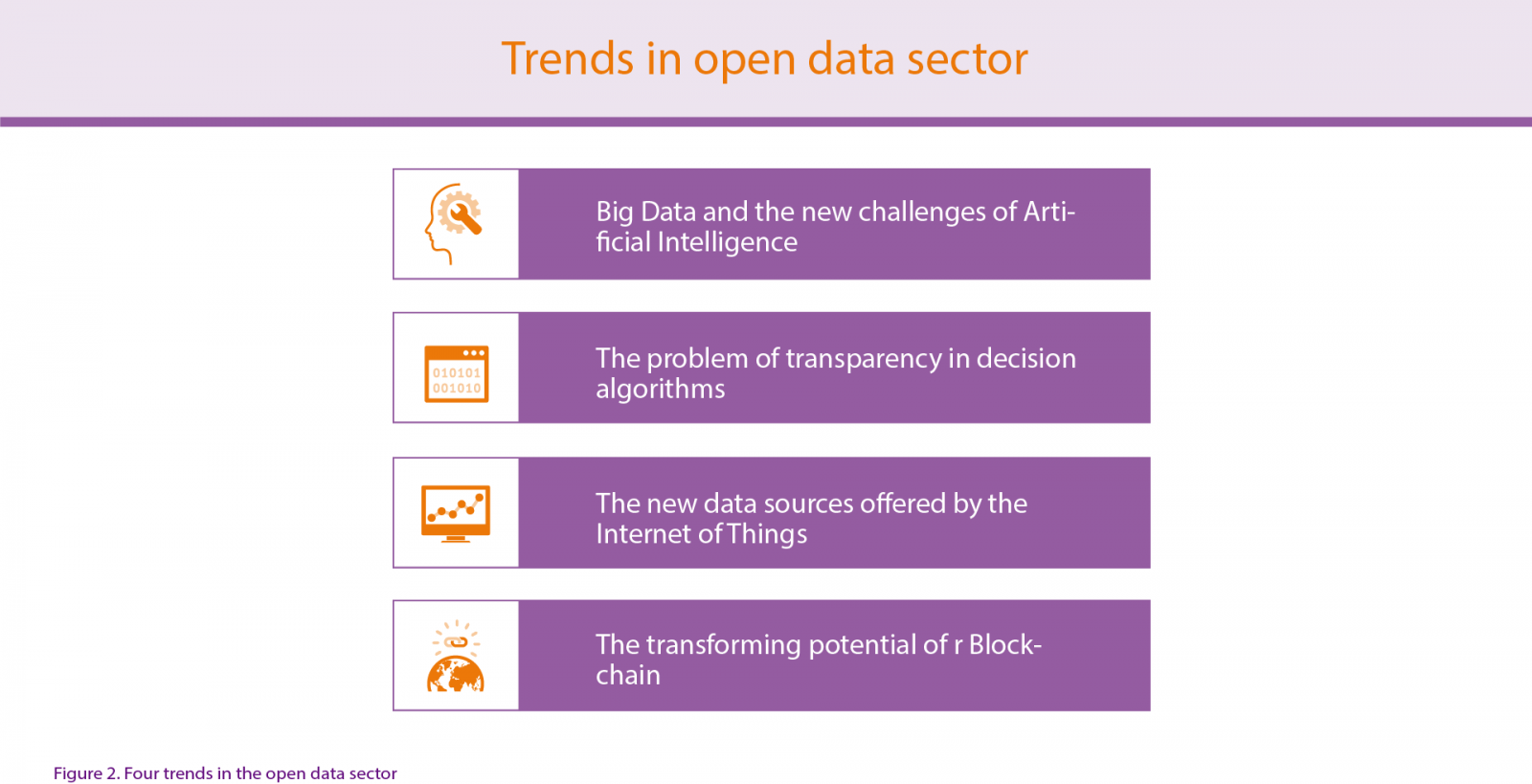
The following are some of the main conclusions of the report:
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence
- What is it? The analysis of large volumes of data, from different sources and with different formats, in real time, acquires a new dimension combined with artificial intelligence technologies, which apply reason guidelines to data.
- What are its advantages? Thanks to these technologies, companies and organizations can better understand the current and future functioning of their environment, and face the challenges at the right time. The combination of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data can boost economic growth, respond to citizens needs and optimize public services. In addition, it can contribute to the strengthening of democracy.
- What are its challenges? The lack of talent with the necessary skills, the limitation in current infrastructures and the privacy protection are the main challenges that organizations have to face when implementing a Big Data initiative.
The decision algorithms
- What is it? These are automated agents capable of extracting value from a large volume of data in an agile and efficient way, facilitating automatic decision making.
- What are its advantages? Decision algorithms allow more efficient, transparent and equitable decision making.
- What are its challenges? Among the challenges faced by people in charge of algorithms management is ensuring the quality and availability of data through controls and audits, as well as ensuring their integrity, ethics and independence.
Internet of Things
- What is it? When we talk about Internet of Things (IoT) we refer to a network of connected objects, by wireless or cable, capable of generating data without human intervention.
- What are its advantages? IoT facilitates processes automation and provides new and multiple forms of interaction that contribute to improving universality and accessibility to services.
- What are its challenges? The main inhibitors of IoT are security and privacy, interoperability and the need for new infrastructures. It is also important to bear in mind that IoT can contribute to increasing the existing gap between different social classes according to their possibilities of data and services access.
Blockchain
- What is it? Blockchain is a distributed database that controls the transfer of digital information. That is, a kind of account book where the records are encrypted and interleaved, so change in one of the blocks affects the others.
- What are its advantages? Its main advantage is the security and privacy of information, the integrity, the sustainability, the transparency and the (quasi) anonymity. This will allow us to transform our political system and enable profound social changes.
- What are its challenges?
- The lack of qualified talent, the regulatory changes, the electronic security of citizens and the limits on institutions ability to adapt the new enviroment are the main challenges highlighted in the report.
Thanks to Big Data and artificial intelligence, decision algorithms, Internet of Things or Blockchain, organizations and companies can extract the necessary value from the data, which will help them to improve services and products for citizens. Although these four technologies are still in a phase of incipient adoption, they are expected to grow rapidly over the next few years, once the above-mentioned challenges are overcome - if you want to delve into these challenges you can read the report New trends and challenges in the world of data.
.dge-detail__img{display:none;}
As a result of transparency and citizen participation demand, an increasing number of towns are focus on initiatives that facilitate citizen access to institutions and administrations´ information. However, defining, implementing and documenting an open data policy could be a challenging issue. Some of the most frequently asked questions by agents involved in these initiatives are:
-
Which data are more strategic and which fundamental aspect should be consider at publishing?
-
How could I facilitate datasets integration from different sources?
-
What is the regulatory framework?
In this context, AENOR elaborated the Technical Standard UNE 178301: 2015. It provides a series of recommendations to standardize open data publication and improve data management. This Technical Standard includes a list of 11 datasets considered a priority by AENOR: shops catalog, cultural agenda, population (municipal census), air quality, contracts, initial budget and budget in execution, public parking, regular bus, traffic situation, tourist interest points and street guide.
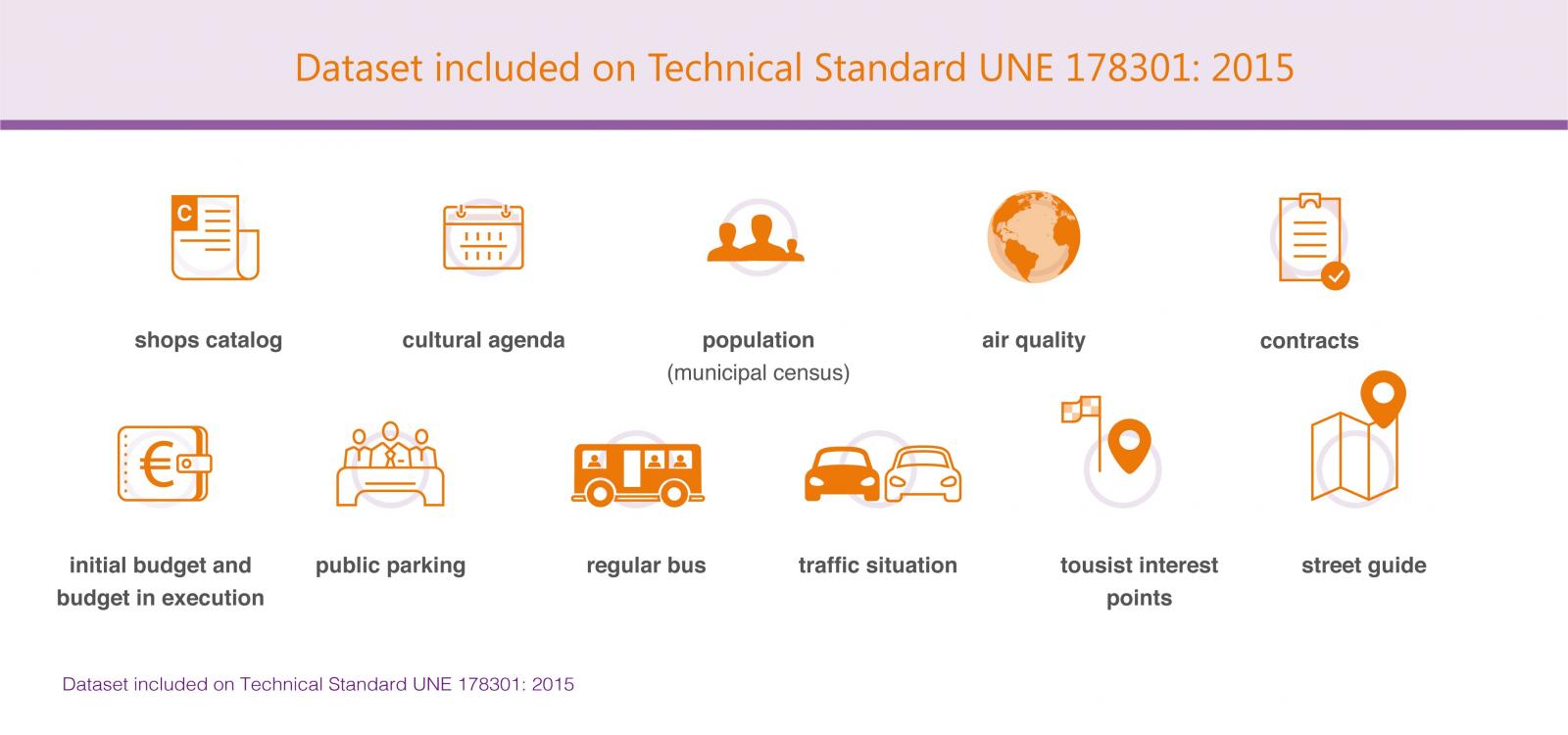
In addition, Technical Standard UNE 178301: 2015 includes recommended vocabulary to optimize data publication, framed within Linked Data paradigm (a set of best practices, articulated through W3C standard technologies). The objective is to facilitate the development of a data website where different elements can be linked, simplifying navigation and data location, within a common international framework.
The report "Open data representation vocabulary in Digital Cities" provides an analysis of this Technical Standard. It include the description of each dataset, potential use cases and legislative framework- when applicable–, and common publication formats. In addition, the report includes an assessment of AENOR´s semantic proposal adequacy and development degree.
Although, nowadays more and more data sources are available, this does not imply that they are easy to use. In fact, multiple barriers hinder their access and reuse, reducing their quality.
Iniciativa Aporta publishes the Practical Manual to improve Open Data Quality; a handbook that proposes how to measure such quality, while reviewing the most frequent faults and practical recommendations to avoid them: rigid search tools; very limited, fragmented and outdated data; non-standardized formats, differentiated access according to the user or omission in data licenses, among others.
However, since open data quality is not only defined through the attributes of the data, the document also addresses how some reference datasets should be published, according to the recommendations developed by the Web Foundation and Open Knowledge International, belonging to three areas of knowledge:
- Accountability
- Social politics
- Innovation
In this final section, details are included about the strengths, weaknesses, reference standards, national data as well as a list of high quality datasets published by other countries in each area.
The Practical Manual to improve Open Data Quality is conceived as an support material for those new or existing open data initiatives that seek to improve the services offered to the community through quality and reusable information.
The Iniciativa Aporta publishes the Guide to publish open data quickly and easily (with CKAN); a handbook that shows how to articulate an open data project without the need of extensive knowledge or prior experience in the opening of public sector information. In addition, this material includes a set of graphs, explanatory and visual tables designed to facilitate the understanding of the guidelines of the document.
The guide is structured so in the first part of the document, guidelines and recommendations are provided to locate and prepare the data for its opening, to subsequently show in detail how they are published on the web using the open source tool CKAN.
The public sector is not only a large supplier of open data but also one of the largest users and beneficiaries of the opening of government data. The report ‘The value of open data for the Government’ that we published on Datos.gob.es outlines a large number of examples of how the government could see benefits in various areas and rely on the data for feedback and to reflect, cooperate, understand, optimise, and learn.
The creation of an open database in Japan to improve support for victims of the devastating earthquake in 2011, the early warning system to detect trends in diseases or epidemics launched by the Korean government, the portal for the quality of teaching in public schools in Brazil that drew on data from the Ministry of Education, the buildings in France in order to optimise supply, and the large global database of companies presented by Open Corporates are excellent examples of how to make public administration more agile and efficient by making good use of data.
El sector público no es únicamente un gran proveedor de datos abiertos, sino que es también uno de los mayores usuarios y beneficiarios de la apertura de los datos gubernamentales. El informe “El valor de los datos abiertos para la Administración” que publicamos en Datos.gob.es hace un recorrido por un buen número de ejemplos de cómo la administración puede beneficiarse en distintas áreas y apoyarse en los datos para retroalimentarse, reflexionar, colaborar, comprender, optimizar y aprender.
La creación de una base de datos abiertos en Japón para mejorar la asistencia a las víctimas del gran terremoto de 2011; el servicio de alarma temprana para detectar tendencias sobre enfermedades o epidemias puesto en marcha por el gobierno de Corea; el portal sobre la calidad de la enseñanza en las escuelas públicas de Brasil con datos procedentes del ministerio de educación; el estudio sobre los datos de consumo eléctrico en los edificios públicos de Francia para optimizar el suministro o la gran base de datos global de empresas que nos ofrece Open Corporates son grandes ejemplos de cómo lograr una administración pública más ágil y eficiente a través de un buen uso de los datos.
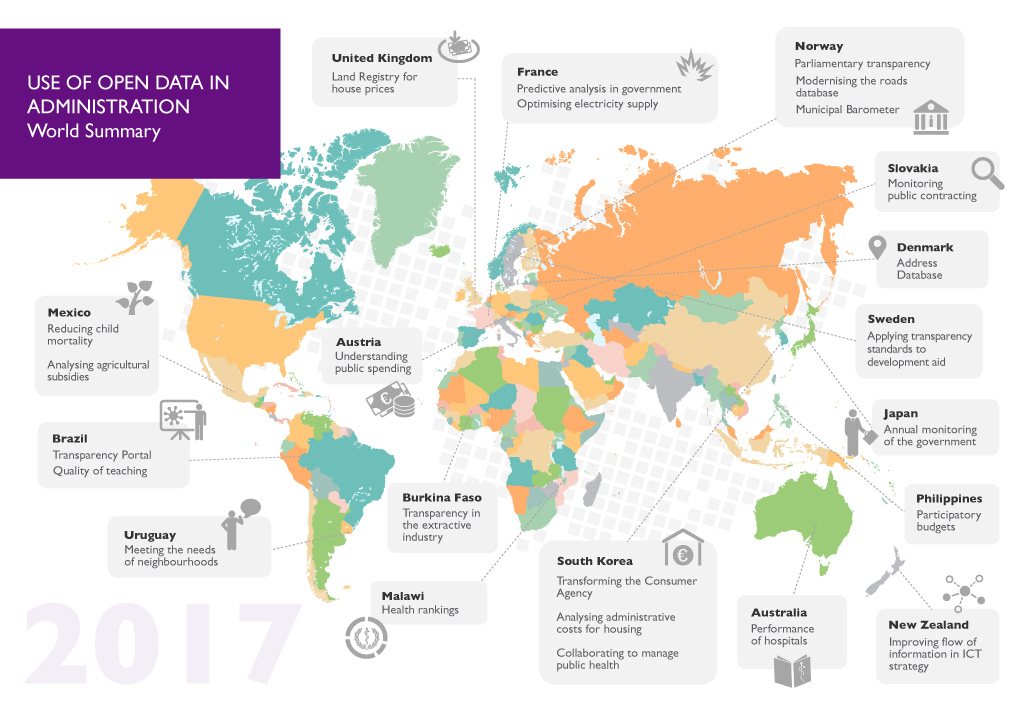
The report highlights how the use of open data improves the efficiency and effectiveness of the government itself through better planning of available resources, collaboration between different departmental areas, scrutiny of the correct use of resources, improvements in the interoperability of data and processes, as well as the adoption of standards that facilitate the sharing and storage of data.
It also emphasises that the use of such open data drives public innovation by contributing to the identification of patterns that help decision-making, to more active development and implementation of public policies, and the improvement of data quality thanks to public feedback.

The attached Report can be downloaded in PDF, Word, and ODT format.
Together with the Report on the Infomediary Sector Characterization 2016, the National Observatory of Telecommunications and the Public Information Society has published a report on success stories and best practices in the re-use of public information, based on the selection and subsequent study of eleven national companies.
In the elaboration of this document, all the companies belonging to the Spanish infomediary sector were taken into account, selecting and interviewing those ones that fulfilled in the most optimal way with the criteria of innovation, effectiveness, sustainability and replicability.
Through the qualitative analysis of their activities, the report draws conclusions that characterize the infomediary sector in Spain and also includes where the most relevant information related to the added value services and products based on the re-use of public information is shown.
The National Observatory of Telecommunications and the Information Society (ONTSI) publishes annually the report on the infomediary sector characterization which analyzes in detail the activities and influence of industry in the national socioeconomic sphere.
The fourth edition of this report collects data from 535 infomediary companies during 2015, all of them specialized in the development of products and services based on the re-use of public and/or private information. The necessary data for the elaboration of this study was collected through surveys to the different companies of the sector.
In this edition, as a novelty compared to previous years, the characterization study is accompanied by a document which lists eleven successful cases of infomediary companies in Spain. Thanks to both studies, it is possible to have a detailed image of the Spanish infomediary sector which encompasses both the volume of business, the jobs generated at national level, the origin of the re-used information, as well as the barriers and opportunities detected by the companies interviewed.
Esta unidad recoge las definiciones de los principales conceptos básicos que permiten comprender los datos abiertos, aclarar y reforzar las bases para poder ampliar conocimiento. Se enumeran los beneficios que aporta la apertura de los datos y se hace un recorrido por las principales barreras y retos a los que hacer frente al iniciar un proceso de apertura de datos.
Objetivos:
- Diferenciar conceptos básicos relacionados con los datos abiertos tomando como referencia el marco legislativo vigente en España.
- Reconocer los principios generales a tener en cuenta para asegurar que los datos abiertos son fácilmente reutilizables.
- Descubrir los principales beneficios económicos y sociales que supone la apertura de datos públicos.
- Conocer los aspectos clave ligados al ecosistema de los datos de cara a asegurar la generación de los beneficios apuntados.
- Identificar las principales barreras actualmente existentes y, en consecuencia, los retos a los que se ha de hacer frente.
Unidad didáctica:
Material complementario:
- Vídeos de ayuda para reutilizadores de datos en datos.gob.es
- Las administraciones públicas ante la reutilización de la información pública
- La importancia de la gestión de los datos maestros
- Crónica de la 12ª Conferencia Internacional de Reutilización de Información del Sector Público
- La ONU proporciona una serie de directrices para impulsar los datos estadísticos en abierto
- Use Case Observatory, una iniciativa del Portal Europeo de Datos Abiertos para medir el impacto del open data
- Pelando la cebolla de la gobernanza de los datos abiertos
- ¿Cuáles son los principales elementos de un espacio de datos?
- Los datos abiertos como bienes digitales públicos
- Inteligencia artificial y datos abiertos
- Explorando el papel de los datos abiertos en la web3
- Radiografía del dataspace nacional de Turismo: retos y oportunidades para el sector turístico
- Conceptos básicos, beneficios del Open Data y barreras para su aplicación
- Data.europa.eu y los espacios comunes de datos europeos: un informe sobre retos y oportunidades
- Datos en tiempo real: Enfoques para integrar fuentes de datos en tiempo real en data.europa.eu
Puedes acceder al resto de material complementario mediante el siguiente enlace.
Cities are increasingly gaining population. While large cities only occupy around 2% of the planet's land mass, nowadays half of humanity lives in cities, 70% of the population in Europe, and it is expected that by the year 2030, almost 60% of the world population will live in urban areas consuming approximately 80% of the planet's resources.
Demographic growth will be a major challenge in the sustainable and efficient management of cities.Transport, education, health care, waste management ... are just some of the areas that will be affected and may become an obstacle on the way to the Smart Cities. In this global context, data is an essential resource and its openness and reuse are key aspects to understand what is happening in cities and make the right decisions to ensure the optimal management of Smart Cities.
Aware of the potential of Open Data, Iniciativa Aporta has published a new version of its report "Open Data, as a tool for Smart Cities". A document that addresses both the strategic aspects of Open Data for a local administration and the necessary components for the success of an initiative of this nature, all exemplified by real cases of different cities in the world. In this way, the reader can locate in the globe the most significant international initiatives that re-use information of the public sector to improve the quality of life of citizens.
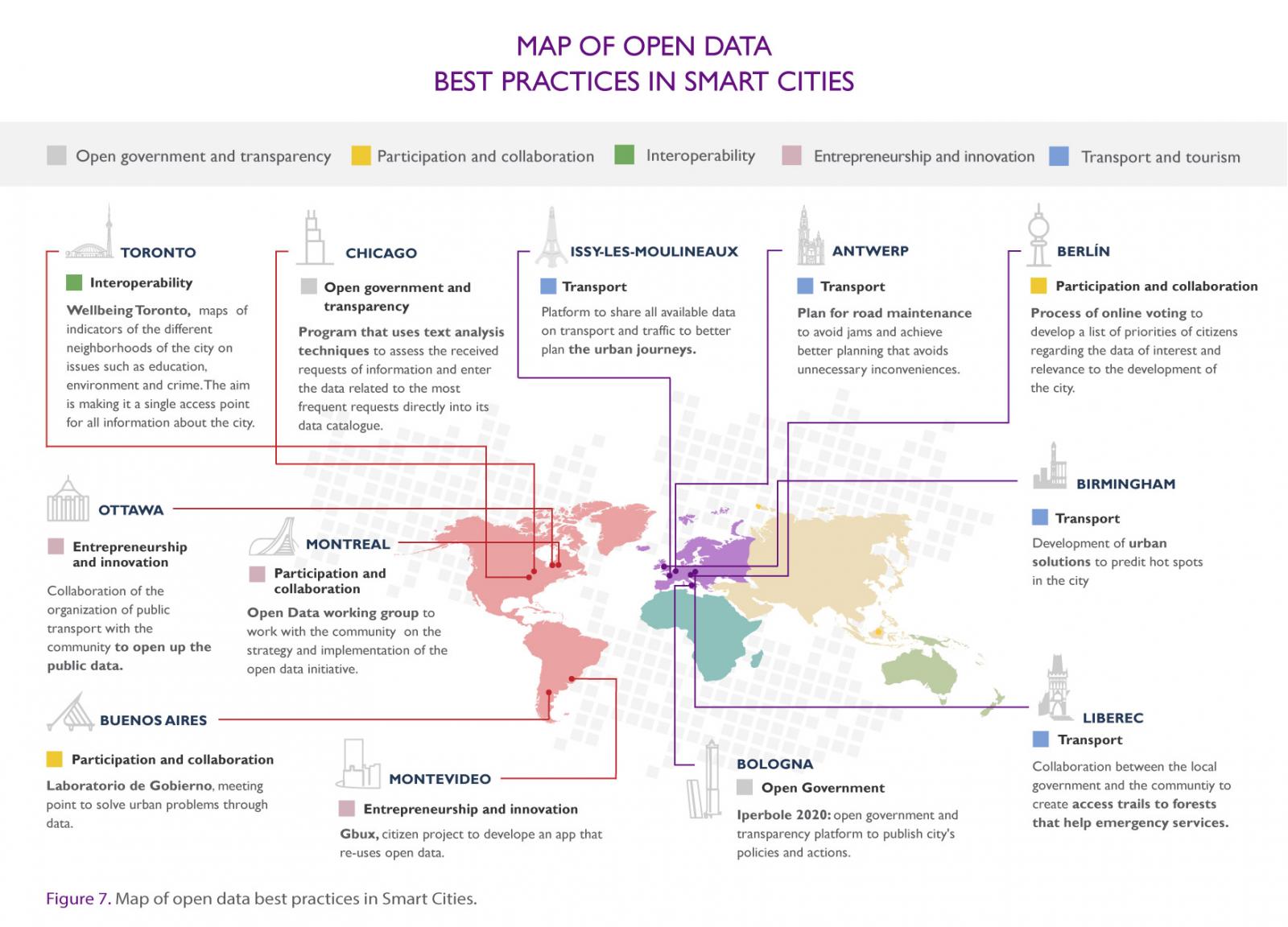
In order to improve and update this material, the content has been enriched with graphic elements that help its comprehension and dissemination. In addition, a map has been included where the world's most relevant Open Data and Smart Cities projects are located according to five priority themes: transport, tourism, open government, interoperability and entrepreneurship.
All the materials created to date are available in the Documentation section of the new portal datos.gob.es, where not only the documents are published but the user has also the opportunity to find resources from other organisms, all related to the re-use of public sector information.